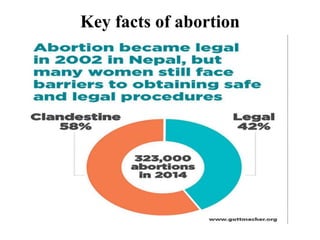
This document discusses abortion, including definitions, types, causes, and health effects. It defines abortion as the expulsion of the product of conception before 20 weeks of gestation or a fetus weighing less than 500g. There are two main types - spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) and induced abortion. Induced abortions can be medical/safe abortions or unsafe abortions. Unsafe abortions can lead to immediate complications like hemorrhage and infection as well as long term issues including infertility and psychological trauma. Prevention strategies include comprehensive reproductive health education and increasing access to family planning services.