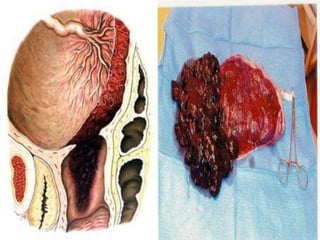
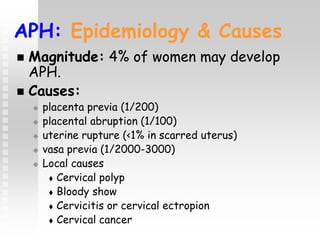
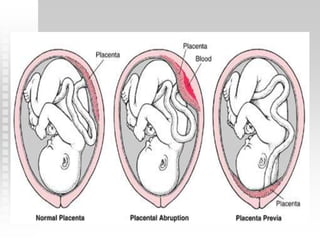
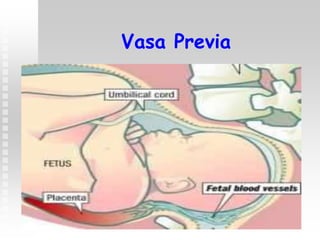
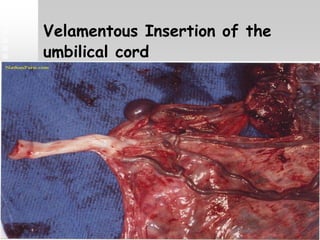
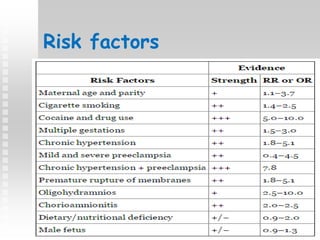
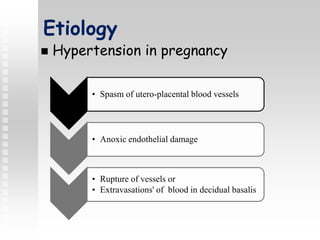
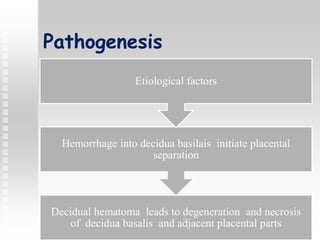
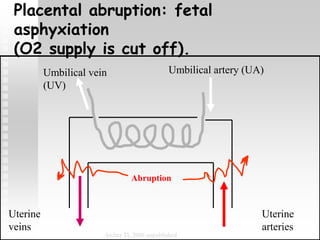
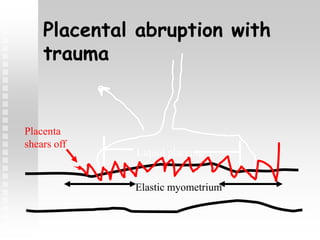
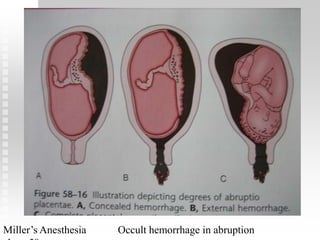
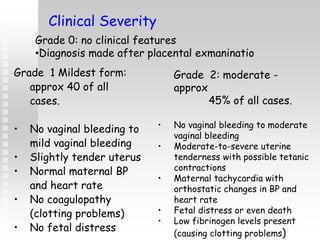
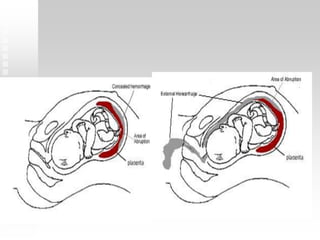
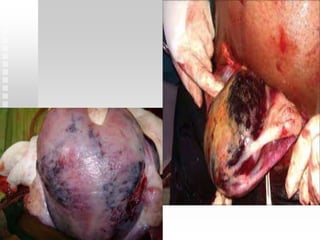
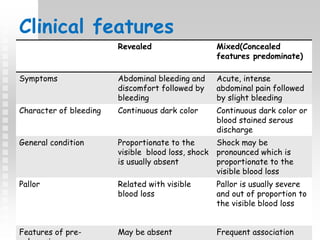
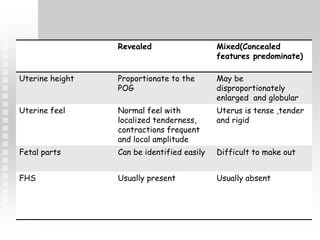
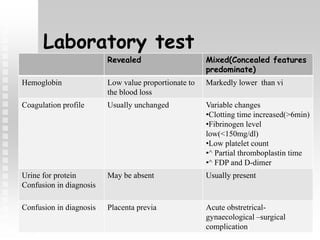
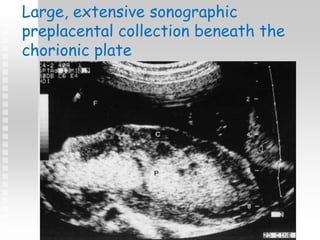
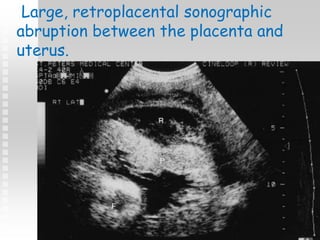
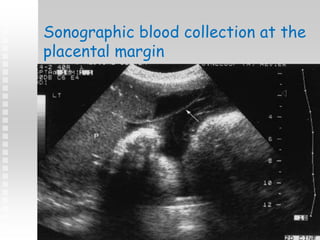
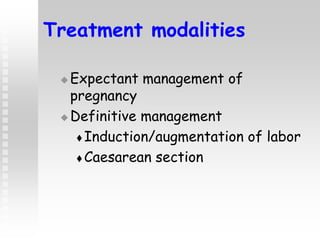
Vaginal bleeding in late pregnancy can be caused by placenta previa, placental abruption, or other local causes. Placental abruption occurs in about 1-2% of pregnancies and is a significant cause of perinatal mortality. Risk factors include hypertension, smoking, trauma, and sudden uterine decompression. Clinical features range from mild pain and bleeding to severe abdominal pain, heavy bleeding, and maternal shock. Management depends on fetal maturity, severity of bleeding, and presence of complications, and may include expectant monitoring, induction of labor, or caesarean section.