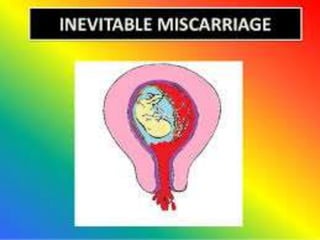
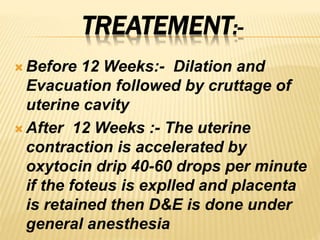
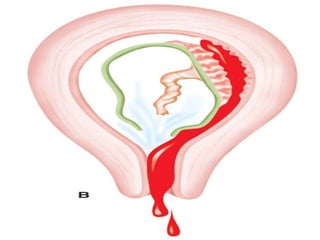
This document discusses abortion, also known as miscarriage. Abortion is defined as the termination of a pregnancy by removing the fetus or embryo before it can survive outside the uterus. The document covers the incidence, classification, etiology, signs and symptoms, investigations, and management of different types of miscarriages such as threatened, inevitable, incomplete, missed, septic, and recurrent miscarriages. Nursing management involves close monitoring of symptoms and vital signs and notifying the healthcare provider immediately if bleeding is noticed.