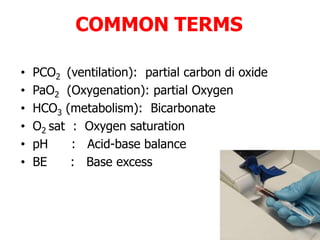
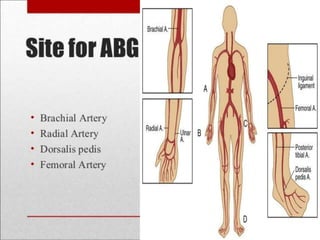
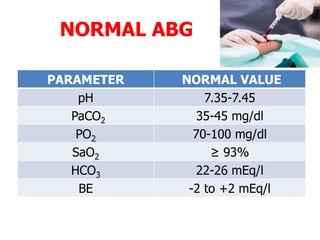
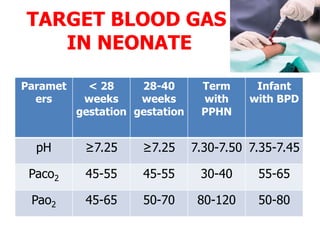
An arterial blood gas test measures levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH, and bicarbonate in arterial blood to evaluate respiratory and metabolic function. Abnormal results can indicate issues like respiratory failure, cardiac failure, or liver failure. The test is useful for monitoring treatment in critically ill patients and ventilated patients.