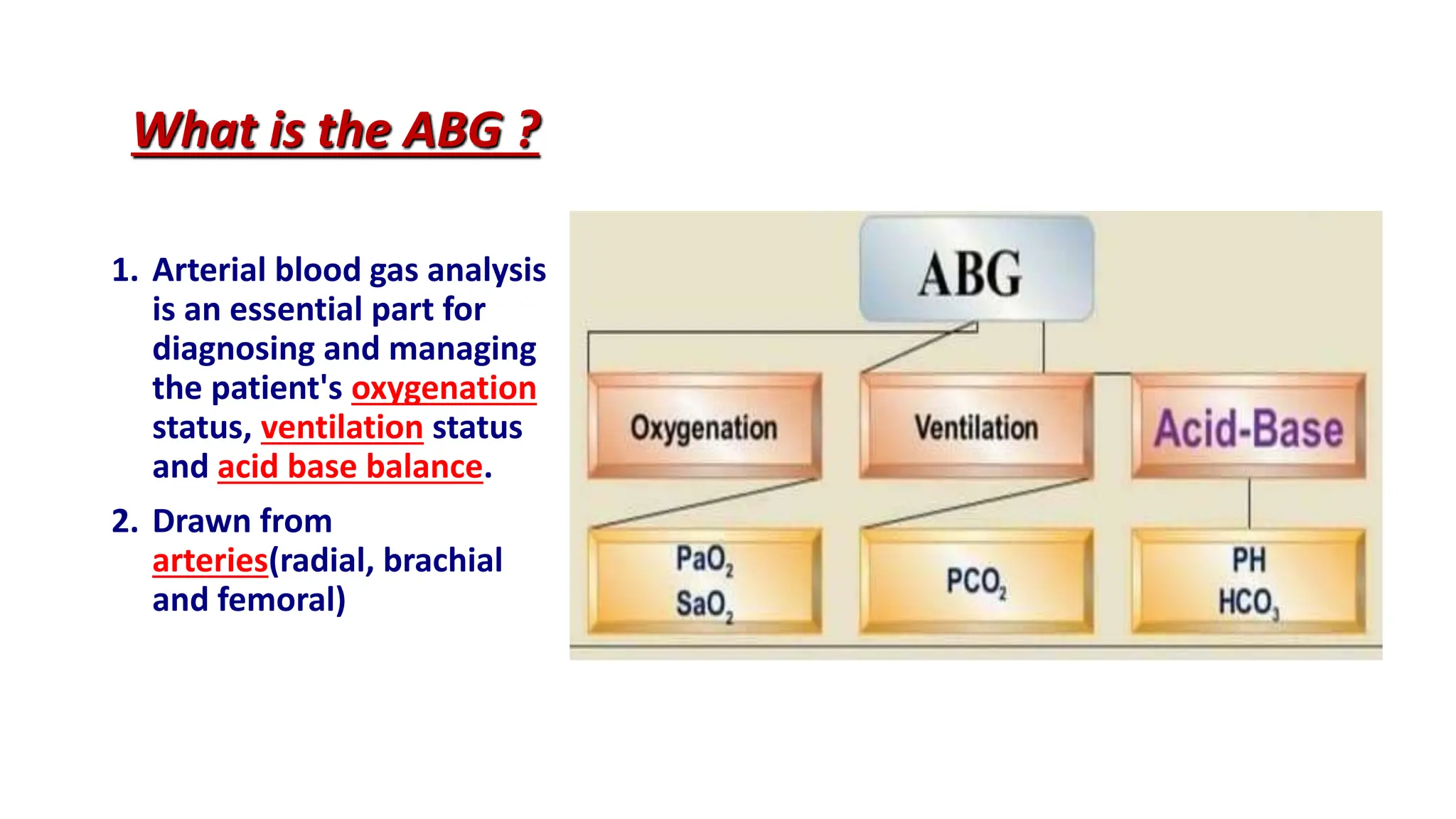
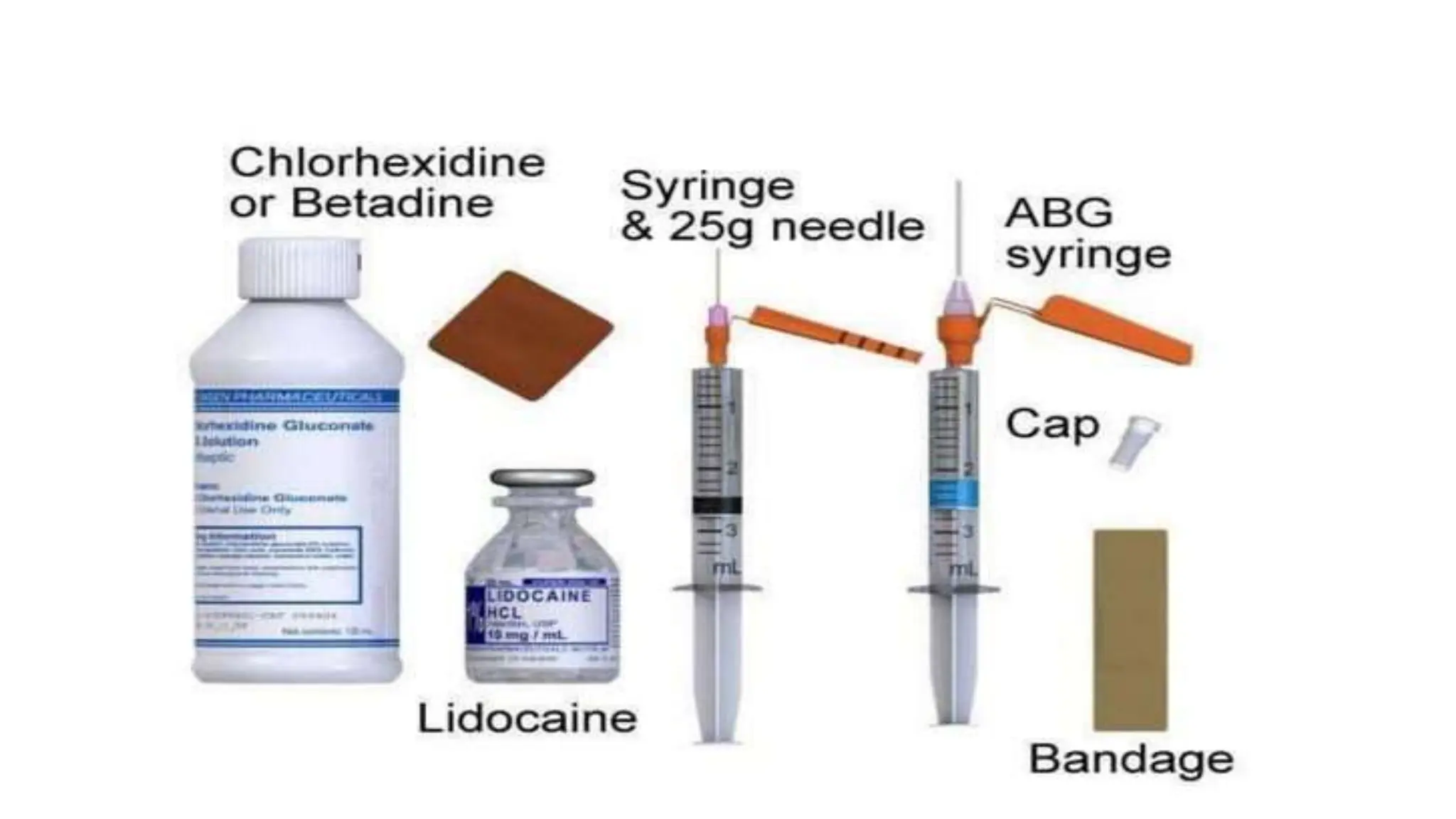
Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is crucial for assessing a patient's acid-base balance, oxygenation, and ventilation status and is performed via arterial puncture. Normal values and types of acid-base imbalances such as respiratory and metabolic acidosis/alkalosis are detailed, along with their causes and clinical manifestations. The document outlines the procedure for conducting ABG analysis, including necessary equipment, patient preparation, sample collection, and potential complications.