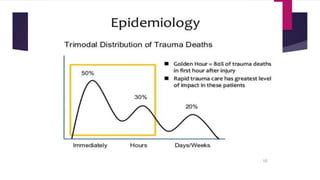
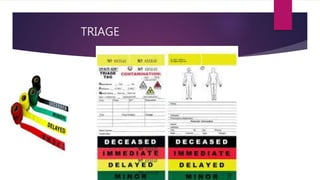
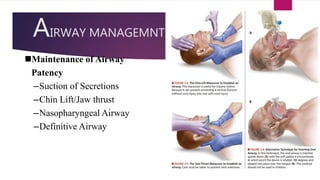
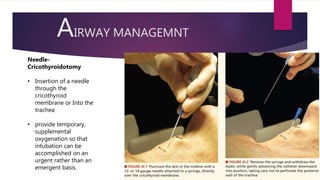
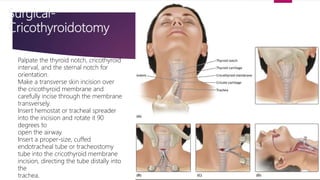
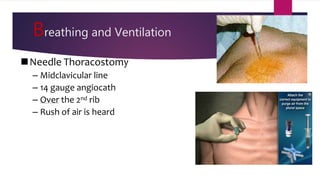
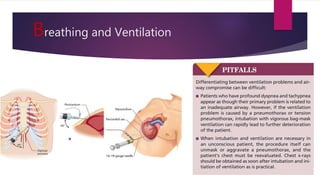
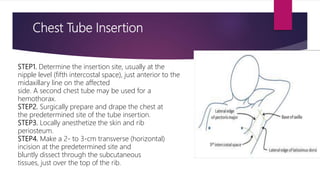
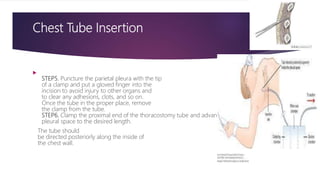
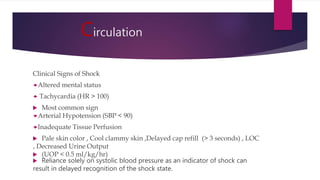
This document provides an overview of Advance Trauma Life Support (ATLS) principles from a presentation. It discusses the importance of the "golden hour" in trauma care. The objectives of ATLS are to prioritize patient assessment and management. It covers the basics of trauma assessment including preparation, triage, primary survey, resuscitation, secondary survey, and transfer to definitive care. The primary survey focuses on addressing life threats in order of airway, breathing, circulation, disability and exposure.