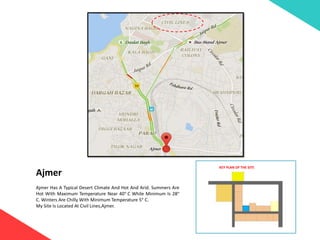
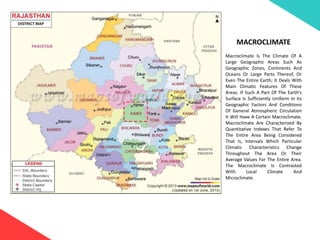
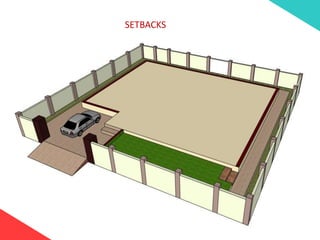
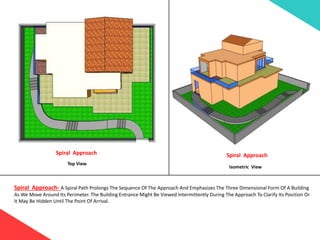
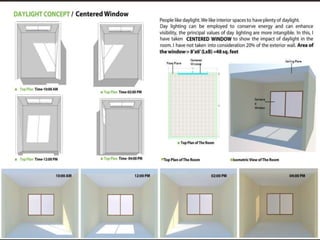
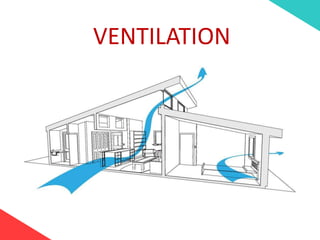
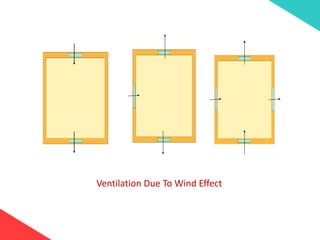
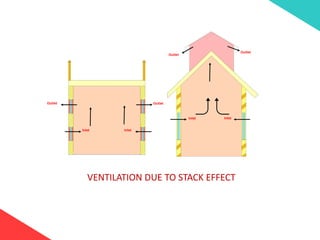
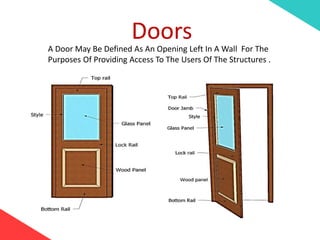
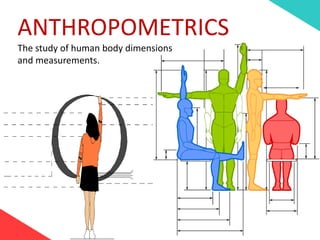
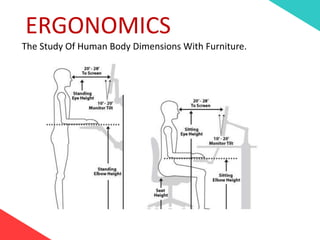
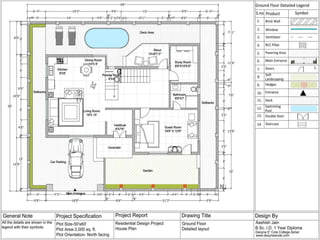
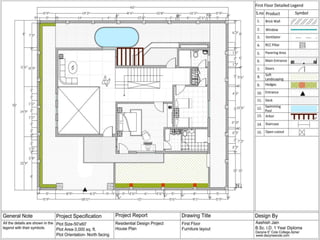
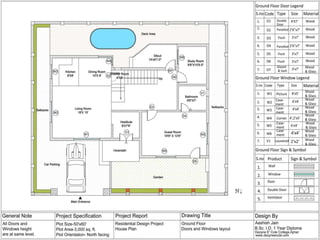
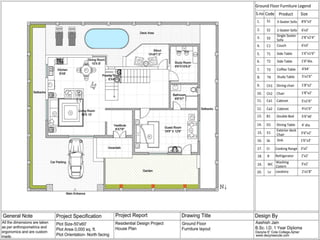
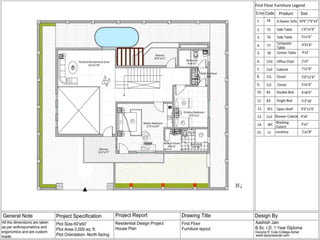
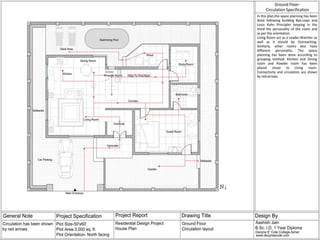
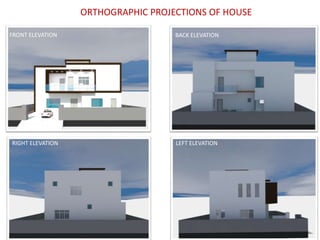
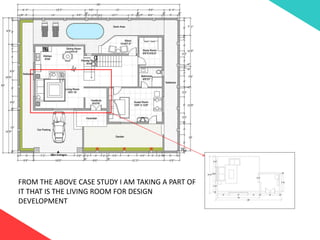
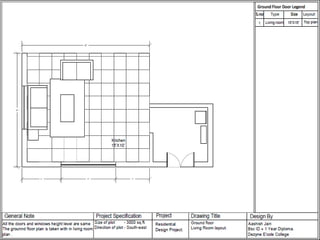
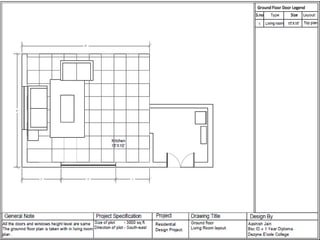
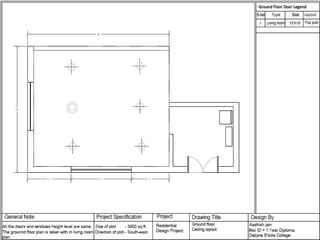
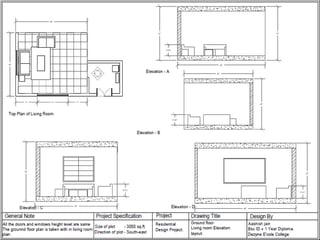
The document discusses the design requirements for a residential project for Mr. Khan's family, focusing on creating a functional and energy-efficient home on a 50'x60' plot in Ajmer, India. It details site considerations, macro and microclimate factors, and design elements such as room layout, building orientation, ventilation, and door/window specifications. The presentation also highlights key concepts learned during a diploma program in interior design, including ergonomics, building codes, and design principles.