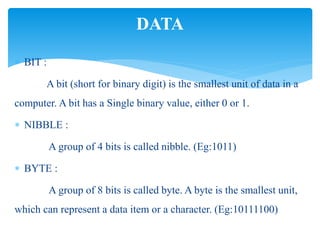
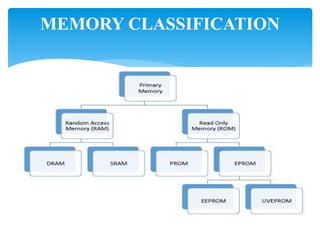
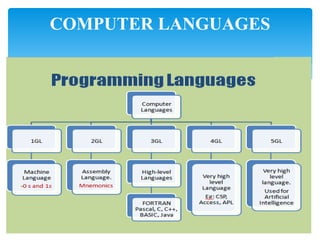
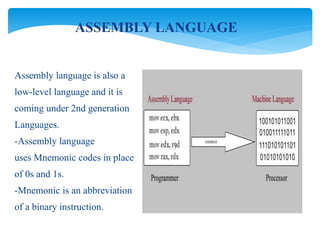
This document provides an overview of microprocessors and their applications. It consists of 5 units: (1) introduction to microcomputers and microprocessor architecture, (2) assembly language programming, (3) counters and timers, (4) conversions between numeric representations, and (5) interrupts and I/O interfaces. It also defines common hardware and software terms like bits, bytes, memory, and computer languages from machine code to fifth-generation languages. Translators like assemblers, compilers, and interpreters are discussed which convert programs to machine-executable code.