This document provides an overview of microprocessors including their definition, importance, components, registers, types, and applications. A microprocessor is an integrated circuit capable of carrying out computer program instructions by receiving, interpreting, and executing actions. It is important because it allows devices to have many functions by communicating with other parts like displays. A microprocessor contains millions of transistors on a small silicon chip and includes components like a control unit, arithmetic logic unit, and registers for temporary storage. Common types include PowerPC and Alpha. Microprocessors are used in general applications like personal computers as well as special applications like instrumentation, control systems, and communication devices.









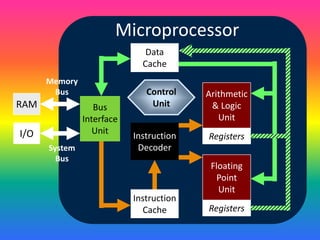
![Microprocessor Components
Bus interface unit]
Data & instruction cache memory
Instruction decoder
Arithmetic-Logic unit
Floating-point unit
Control unit
•
•
•
•
•
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aula-140224130809-phpapp02/85/Aula-10-320.jpg)