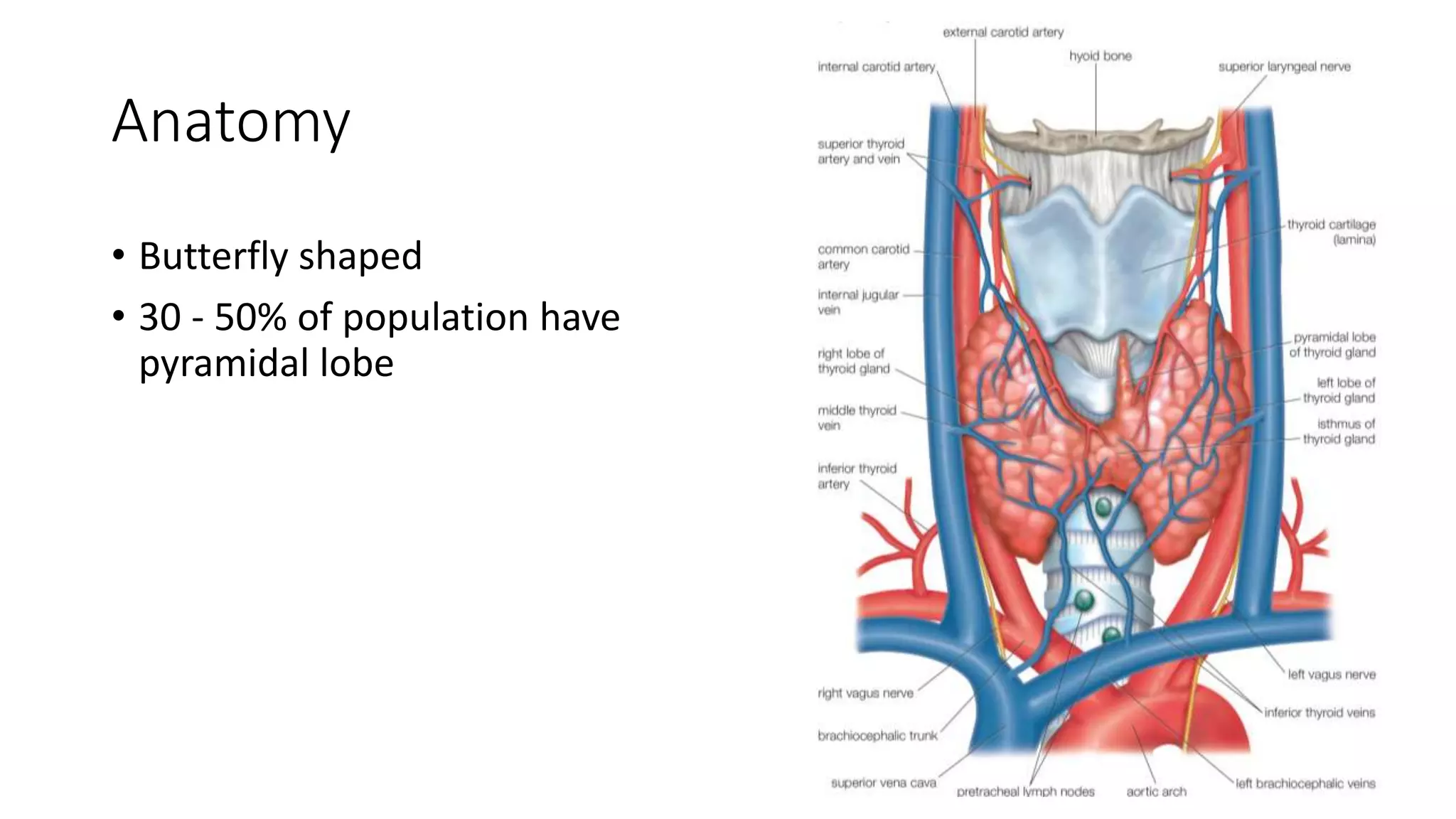
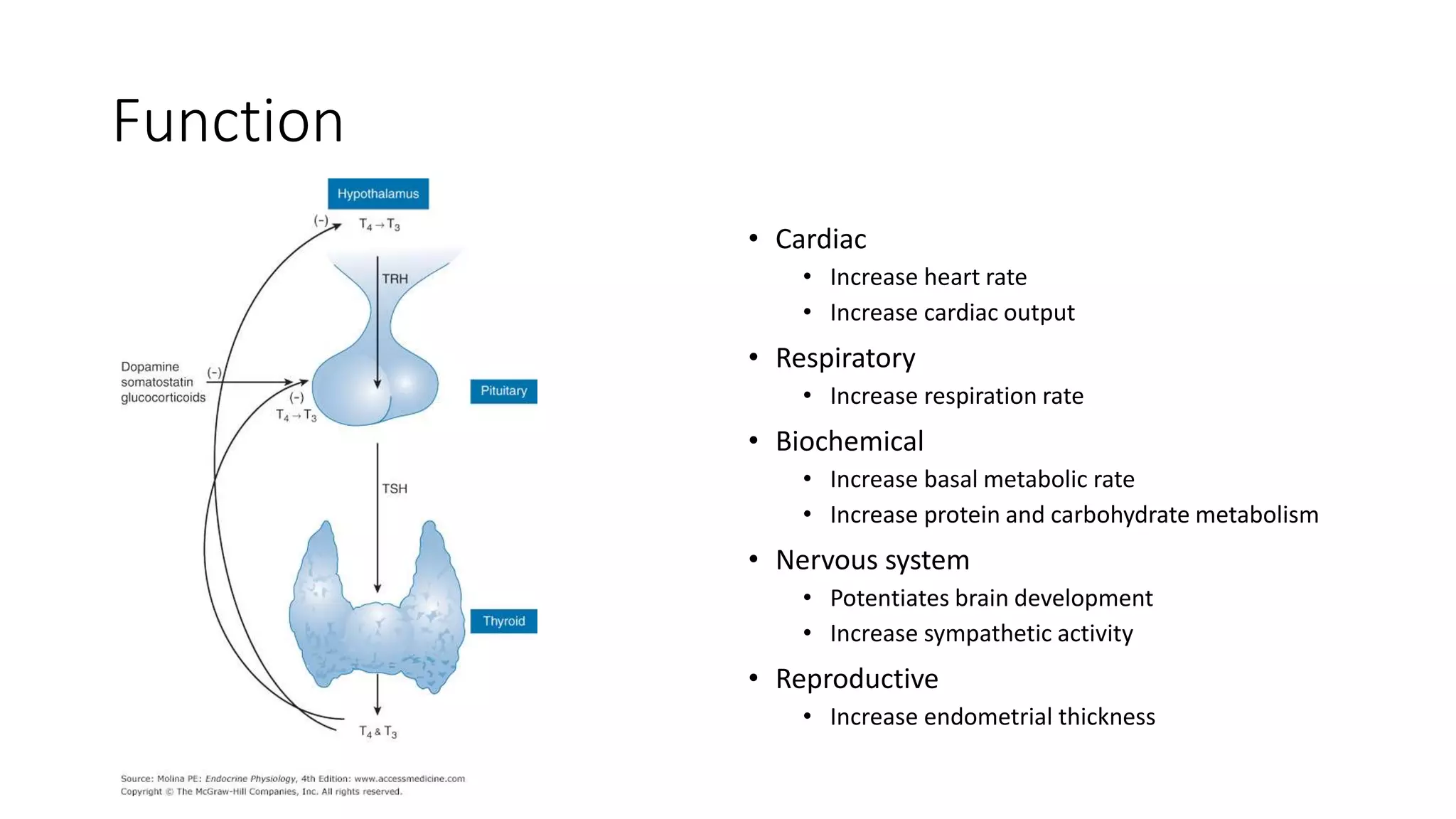
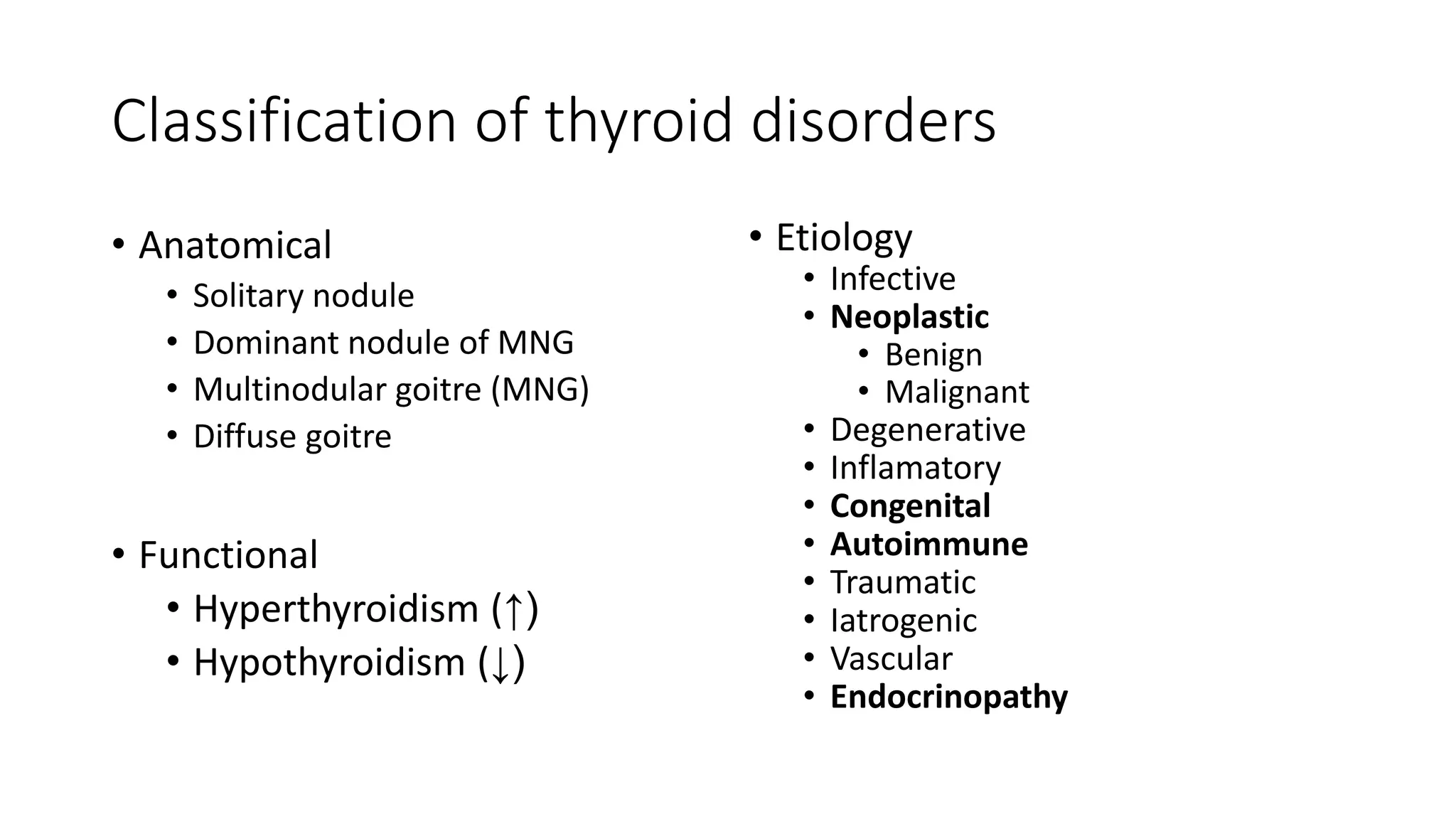
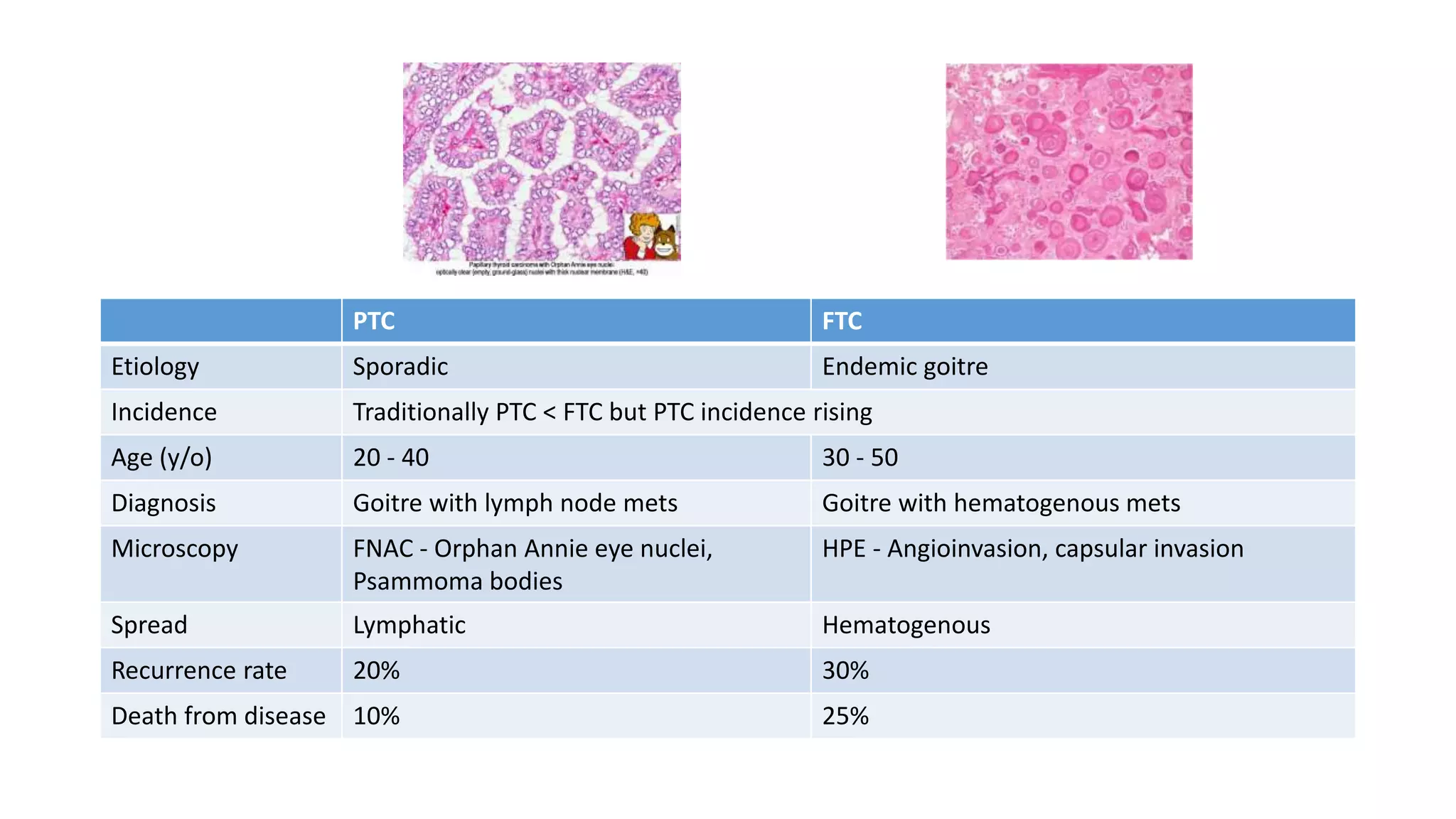
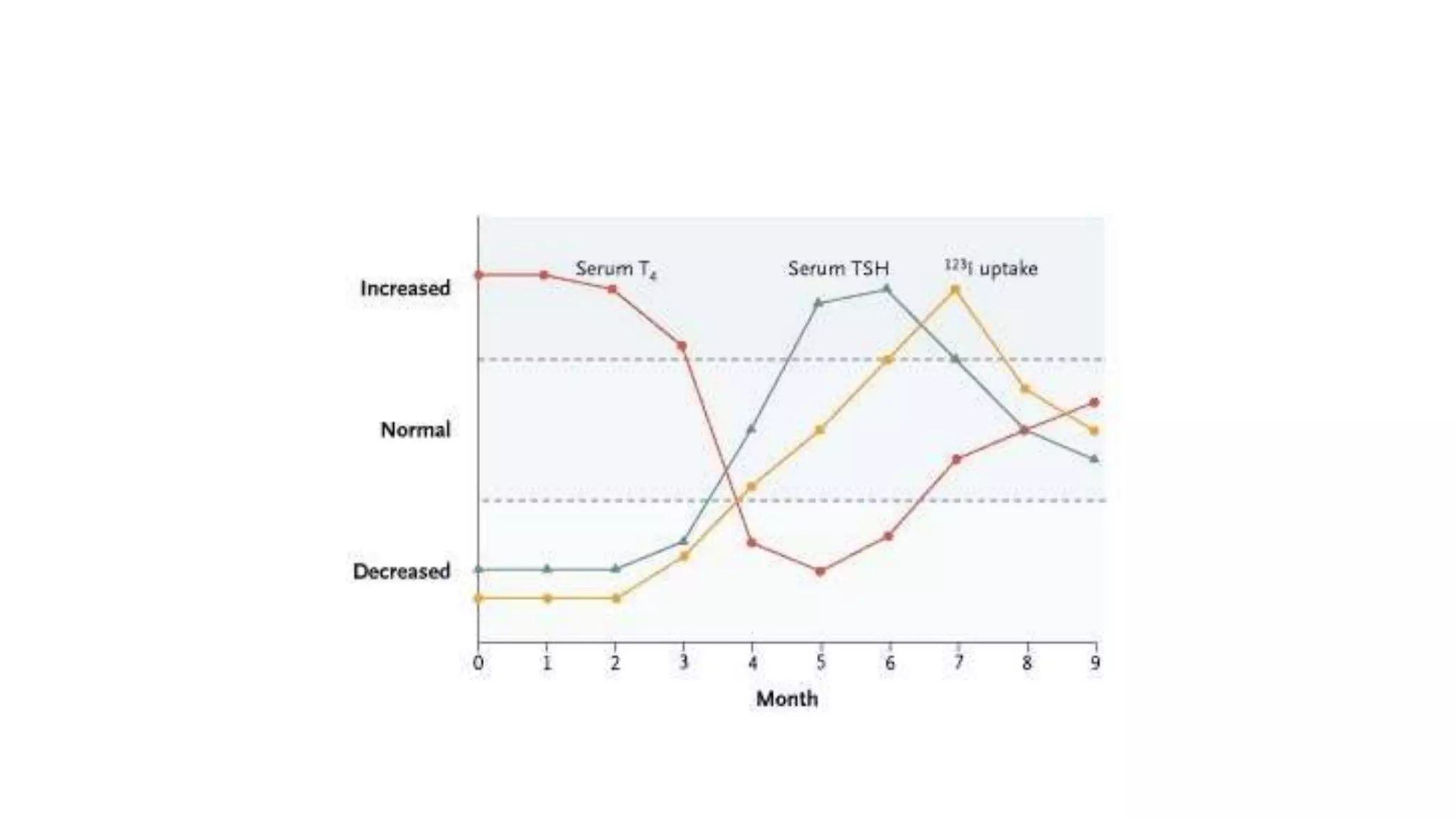
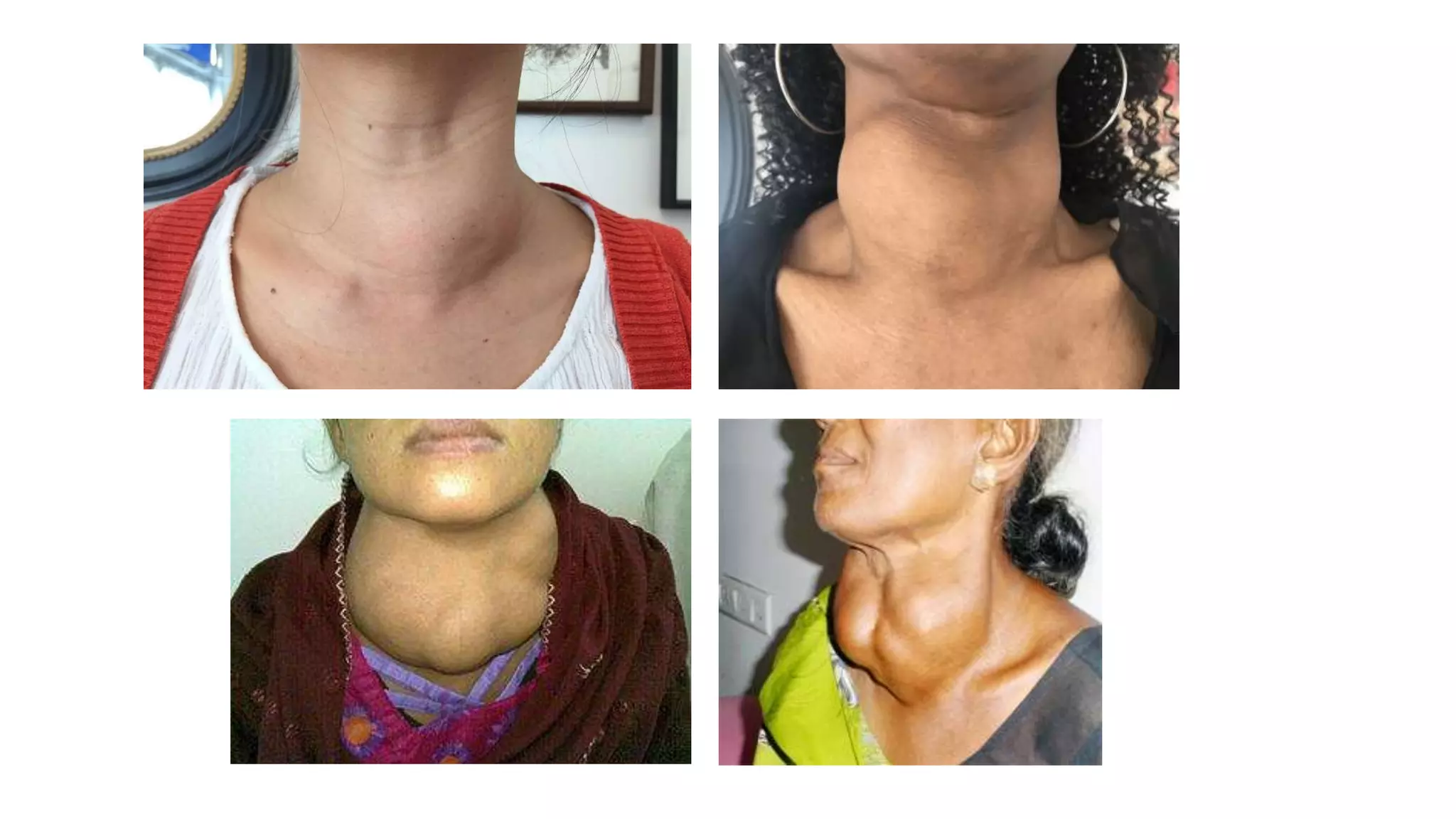
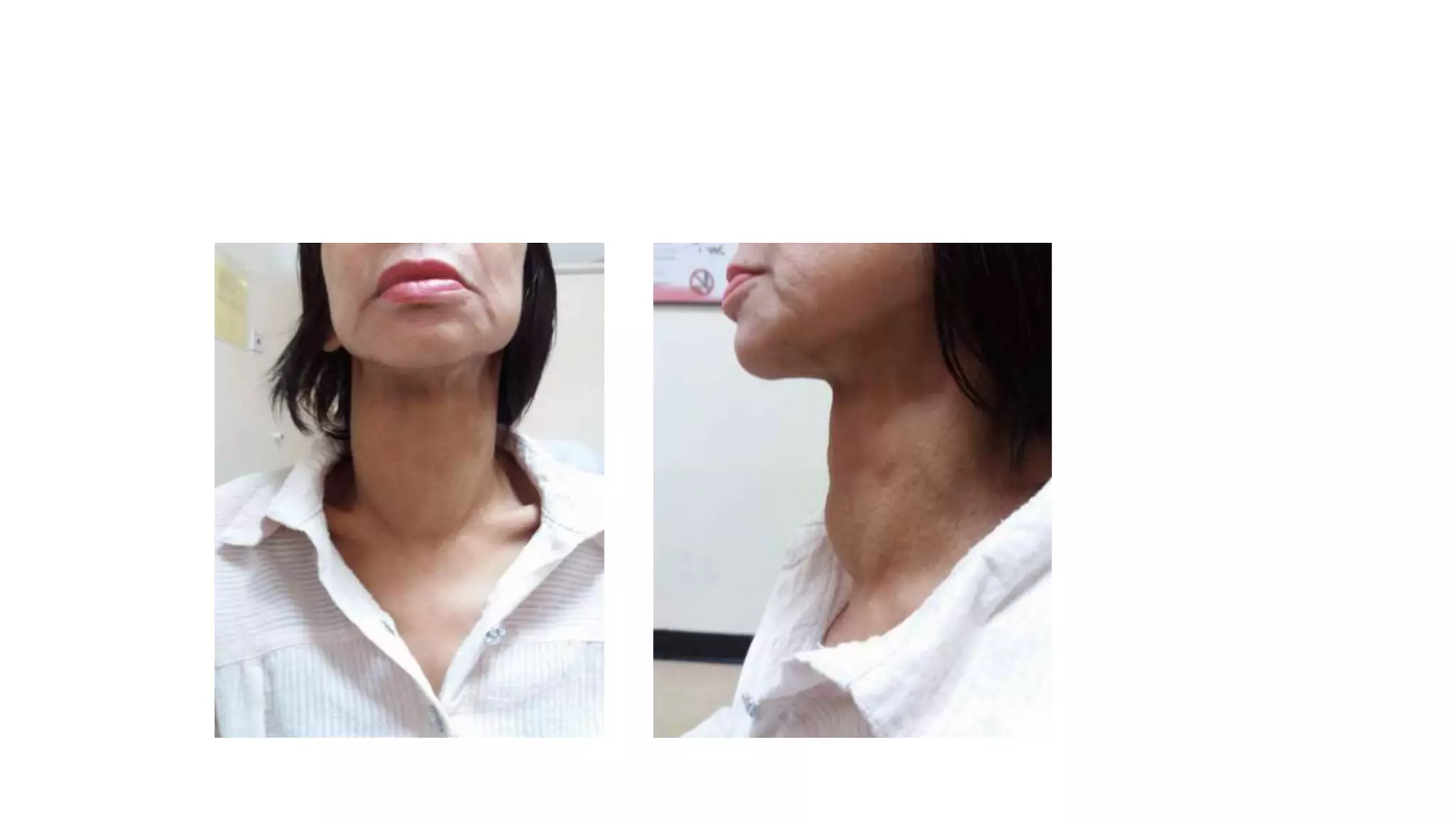
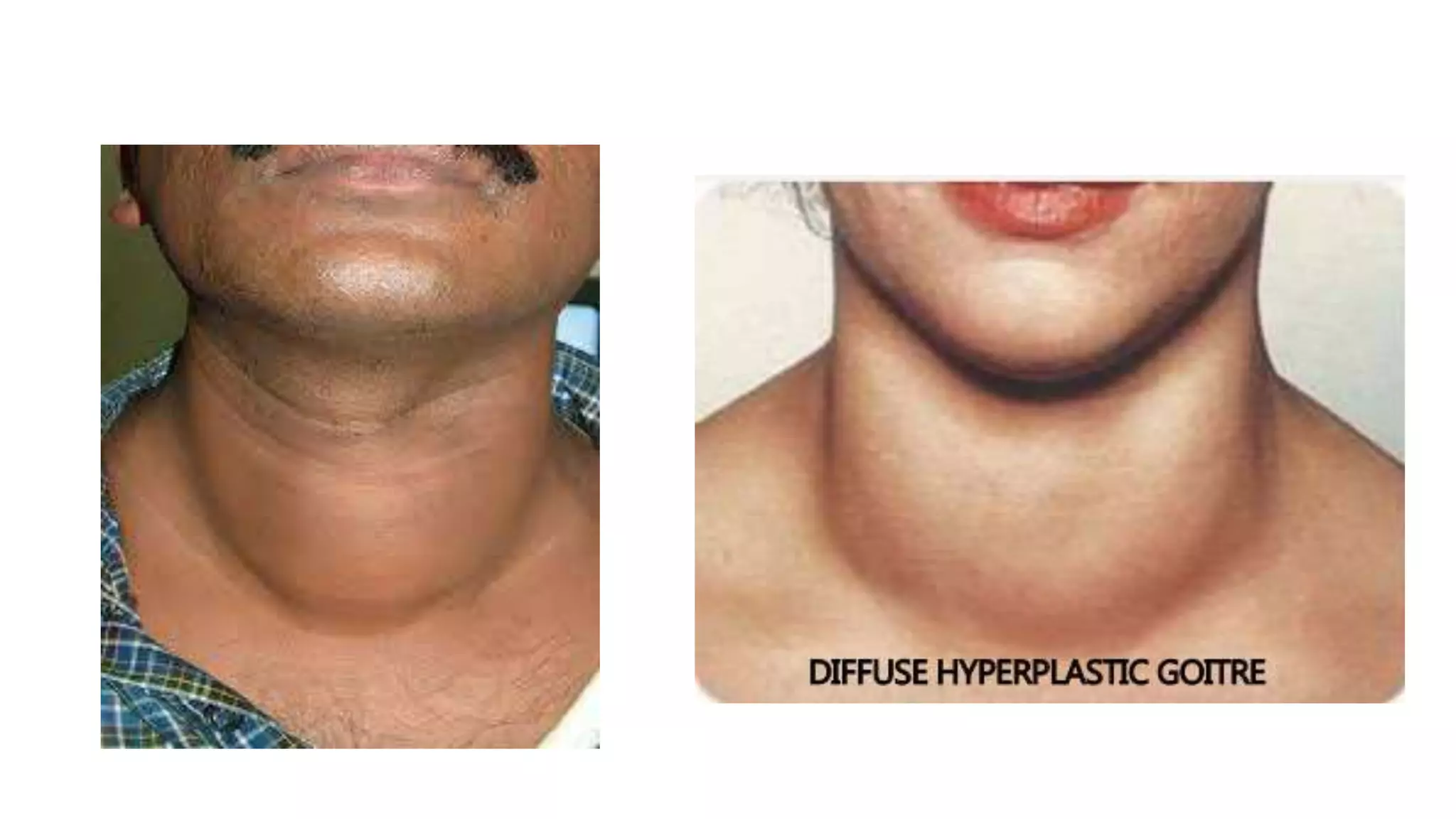
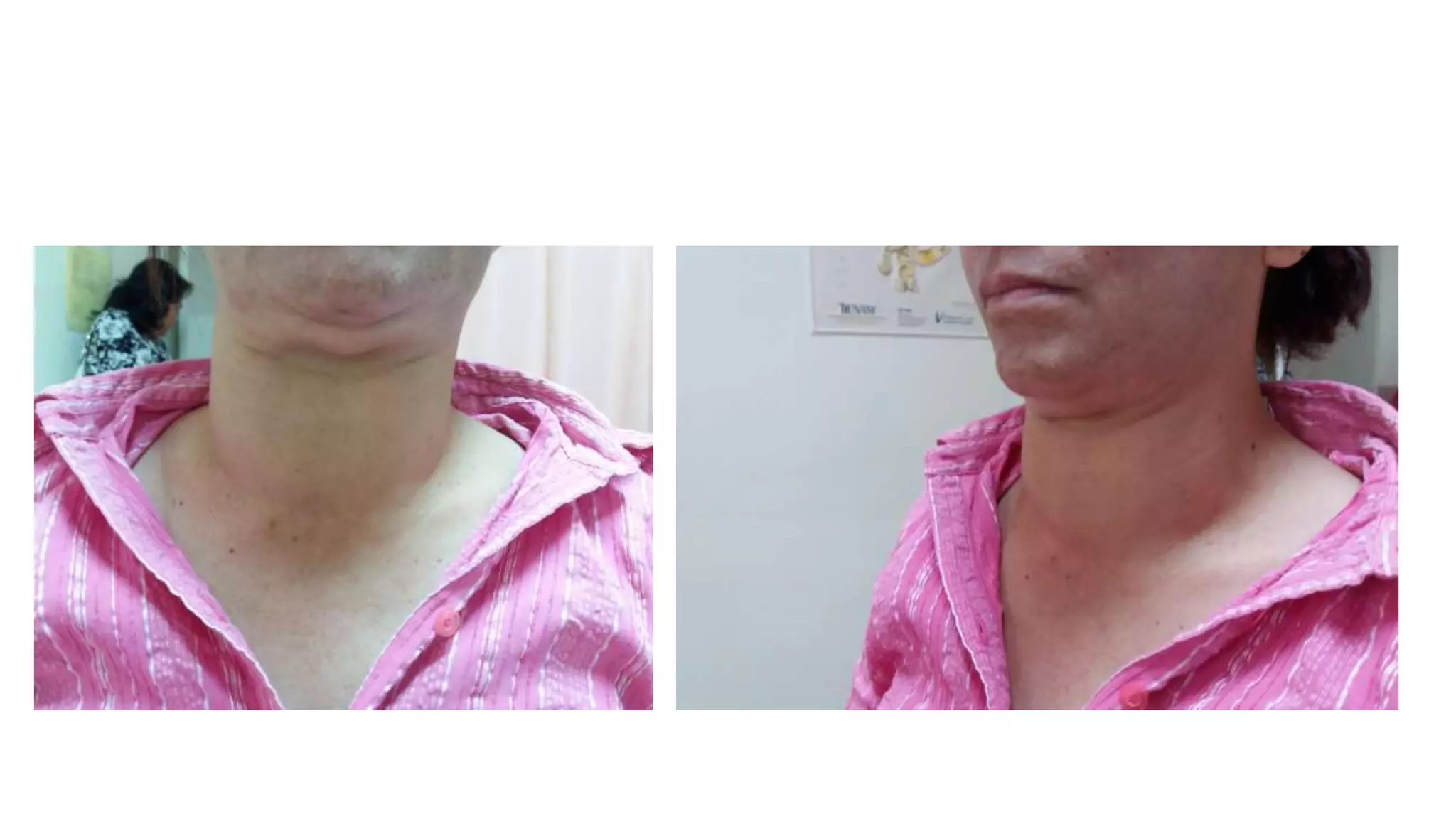
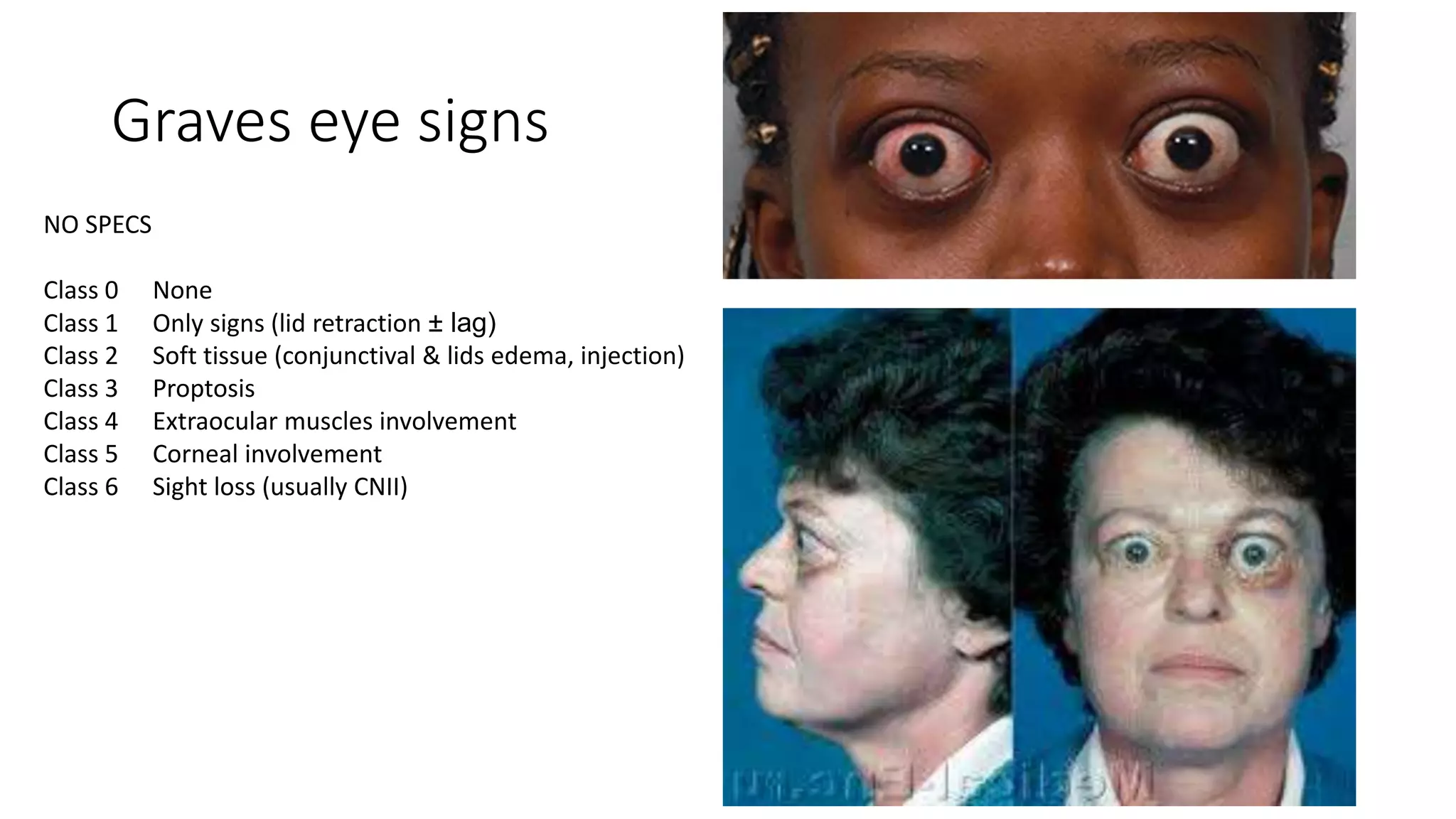
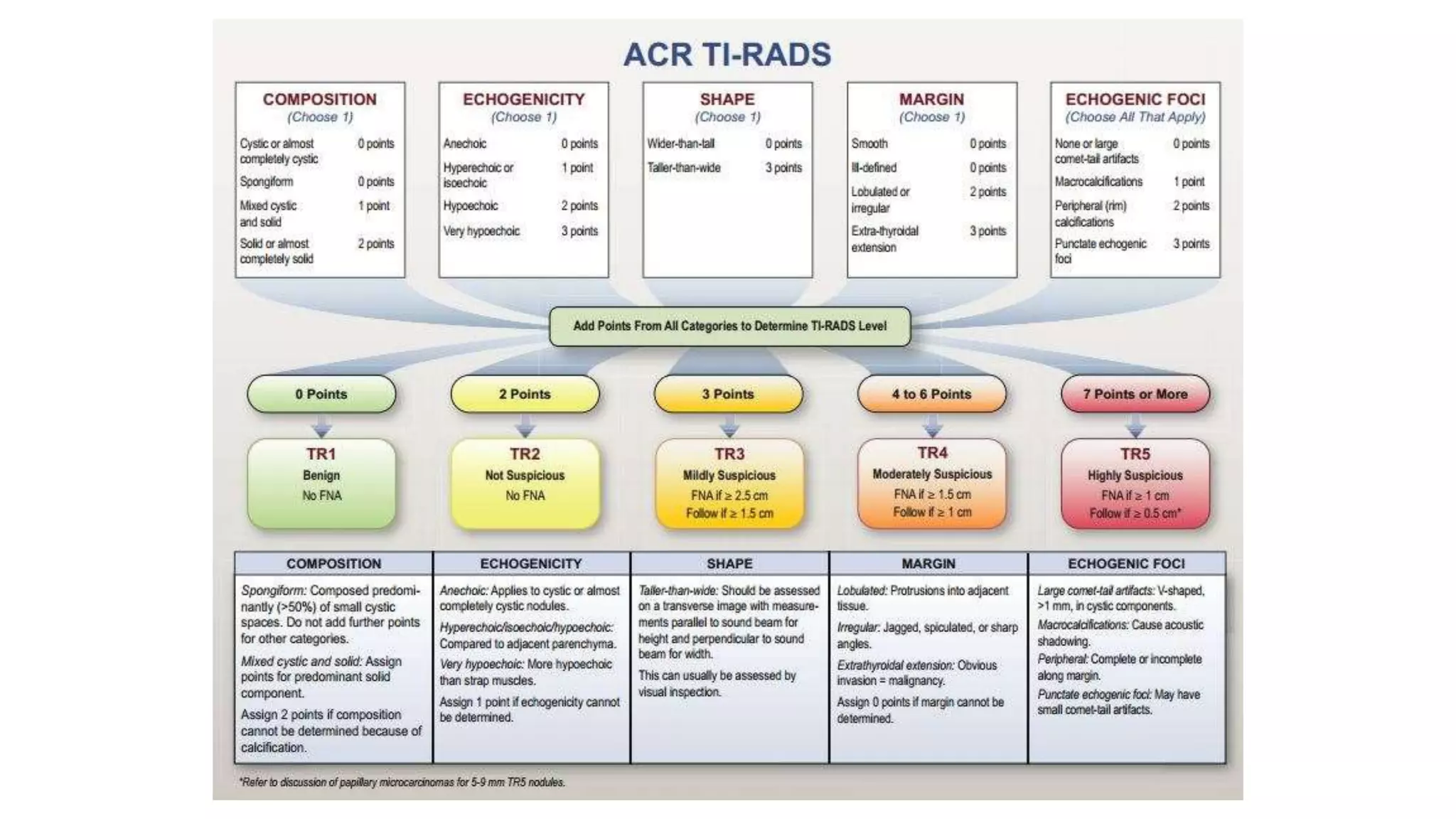
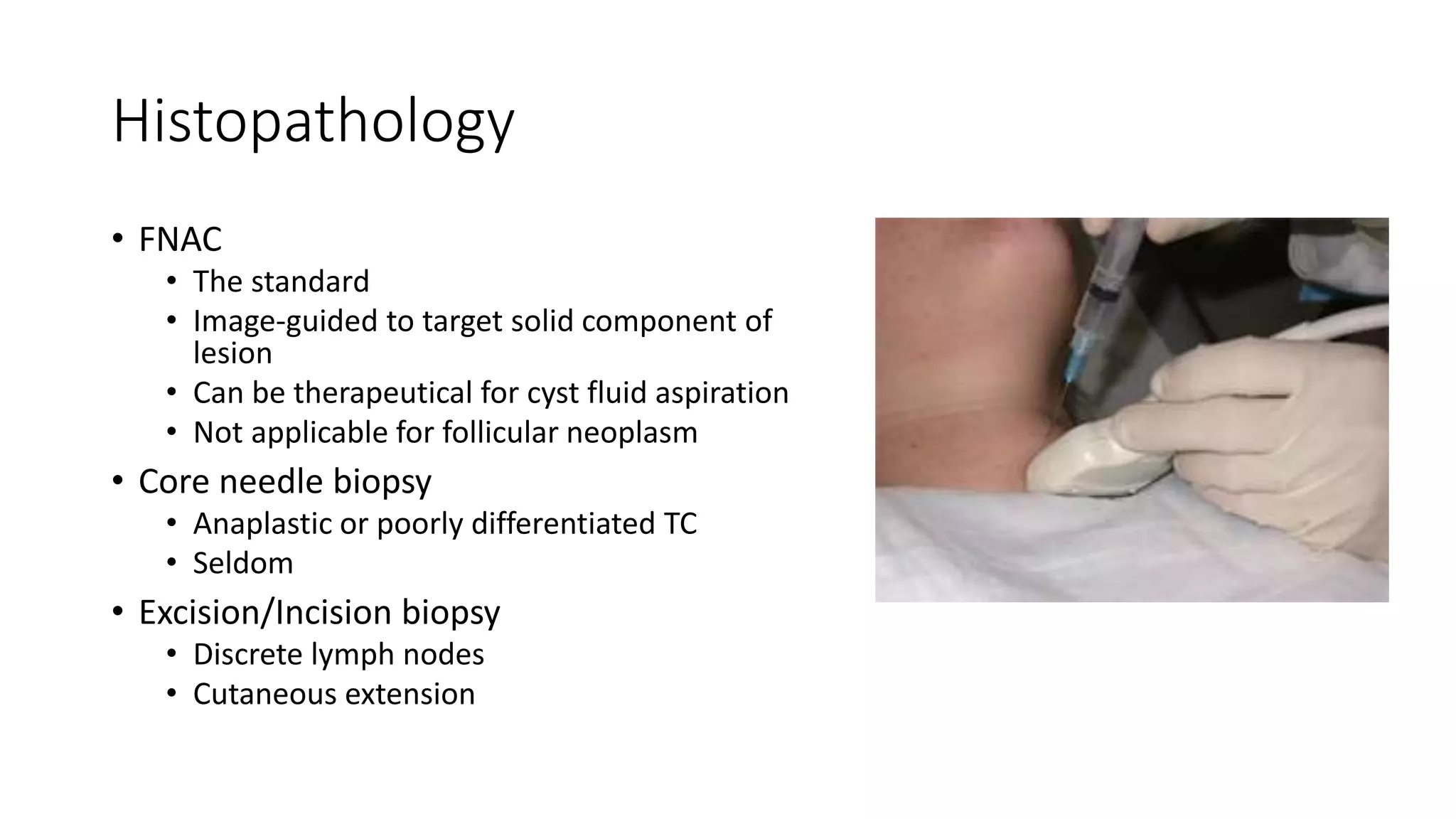
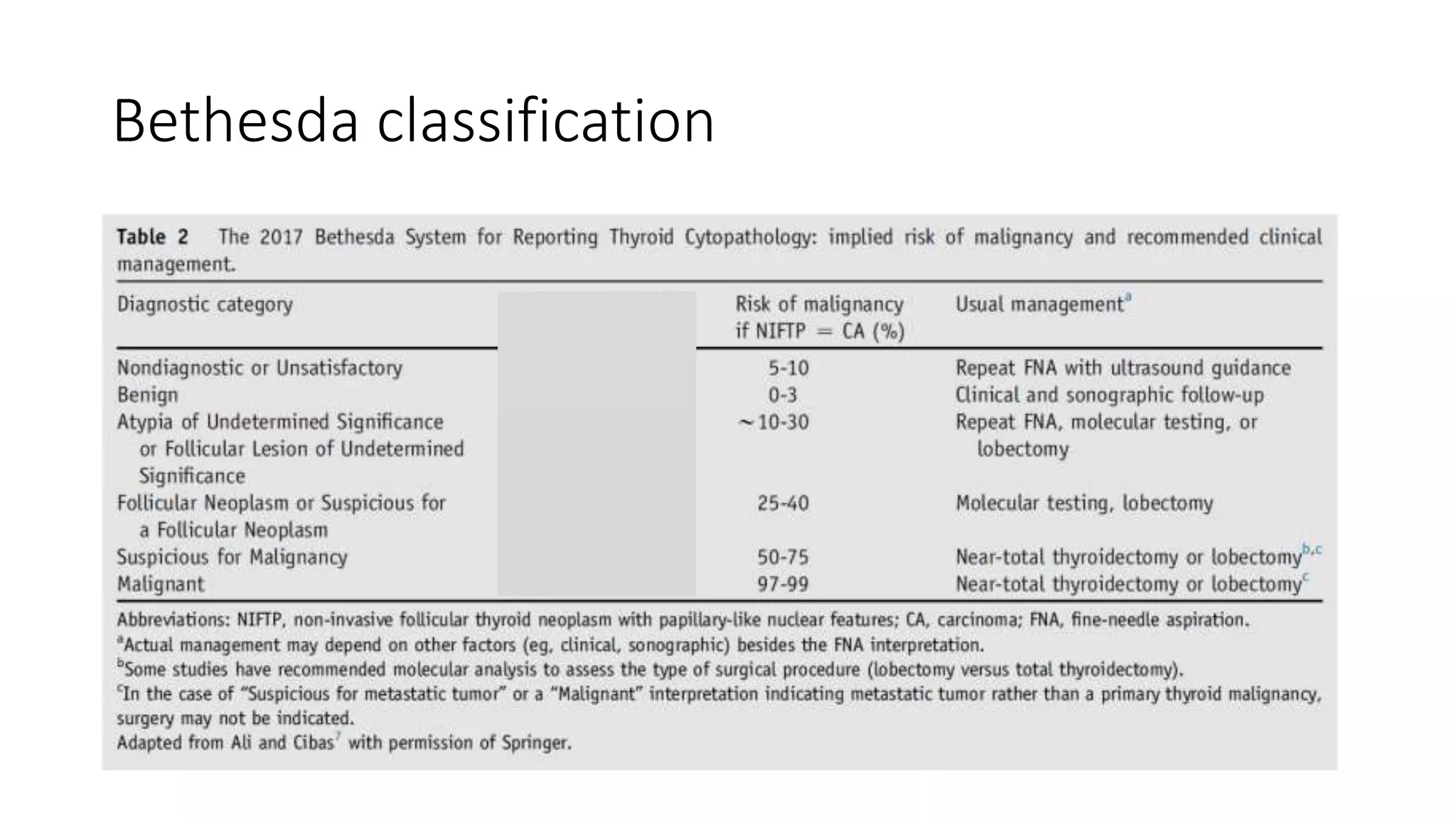
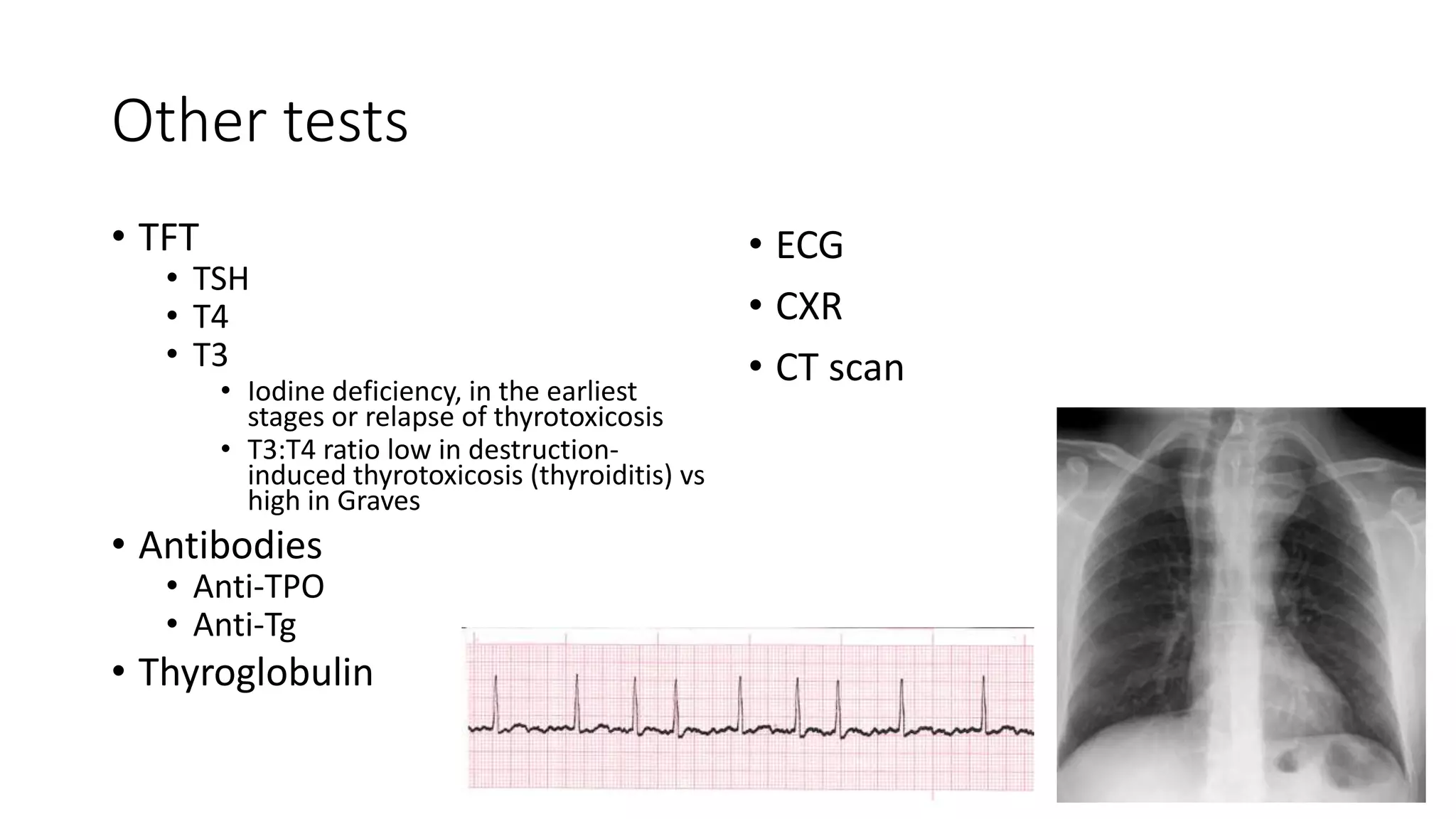
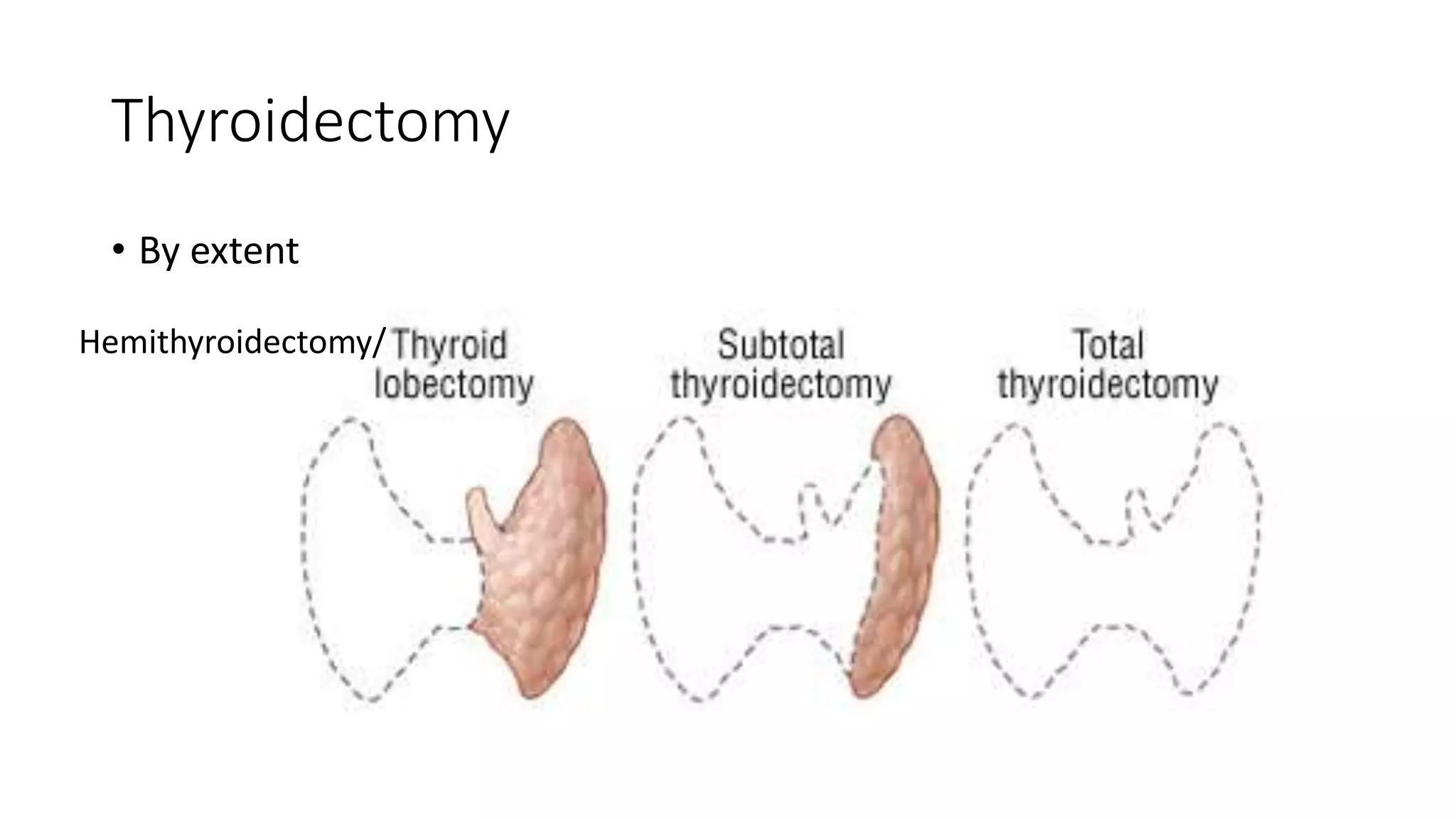
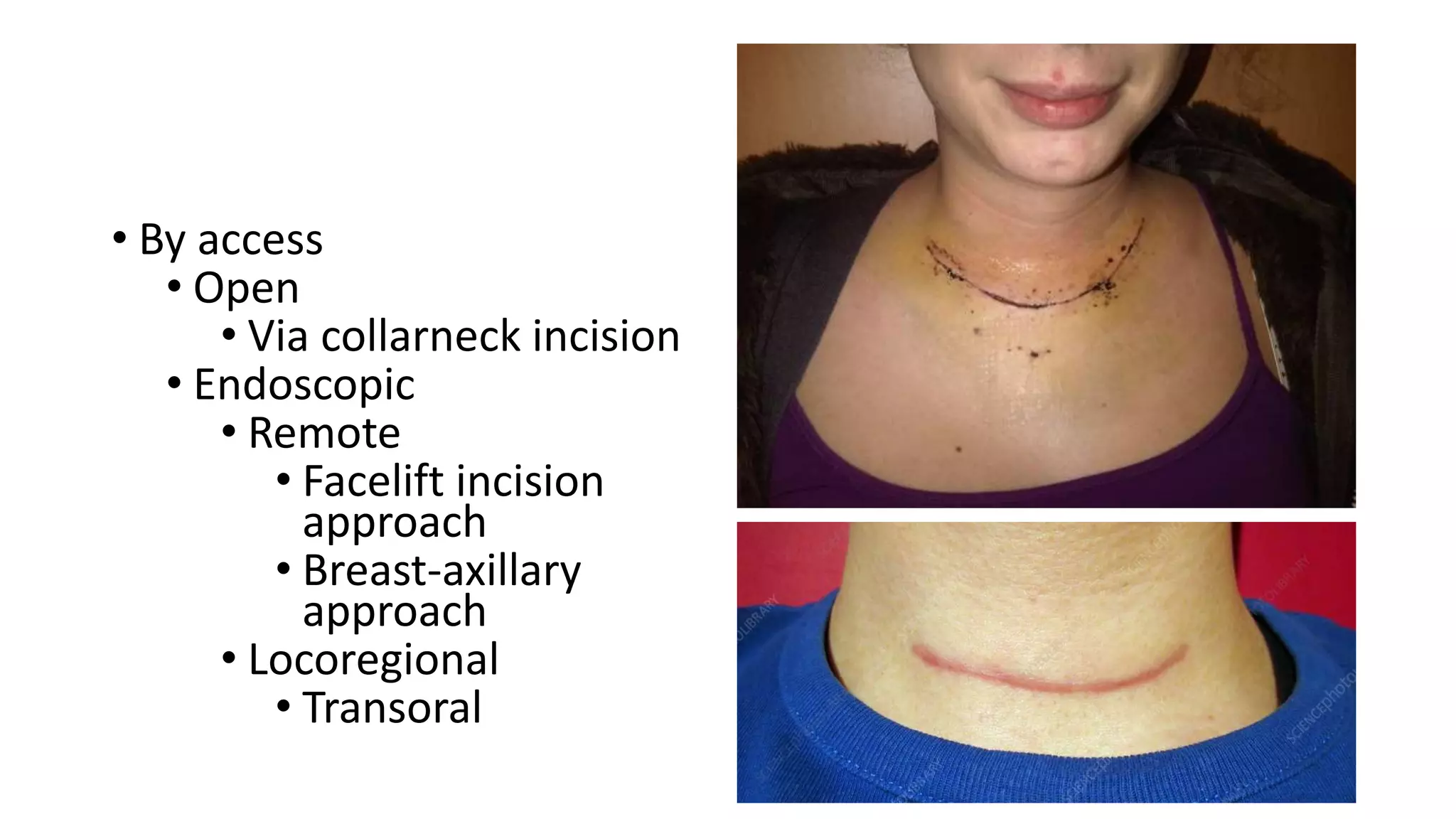
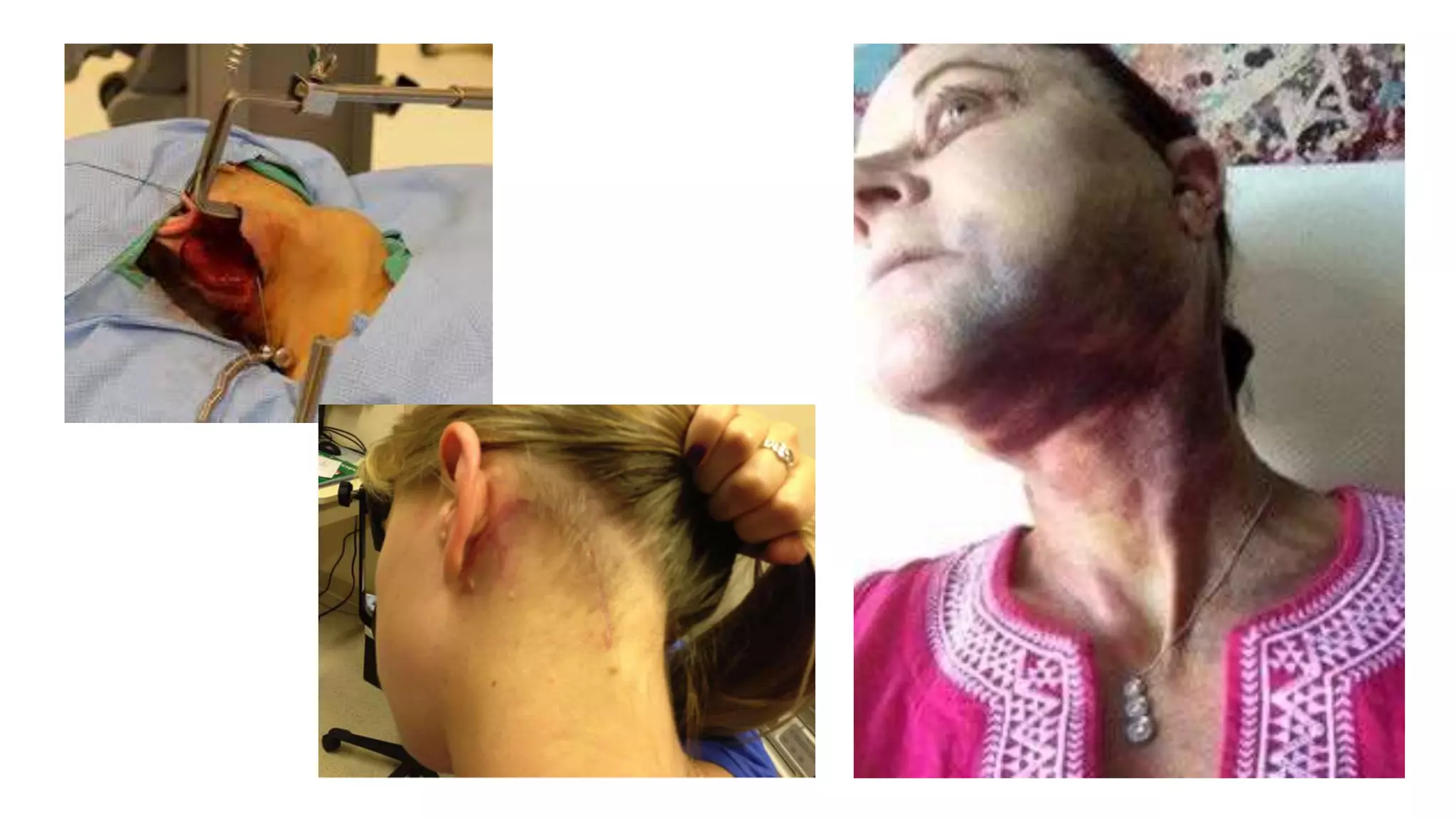
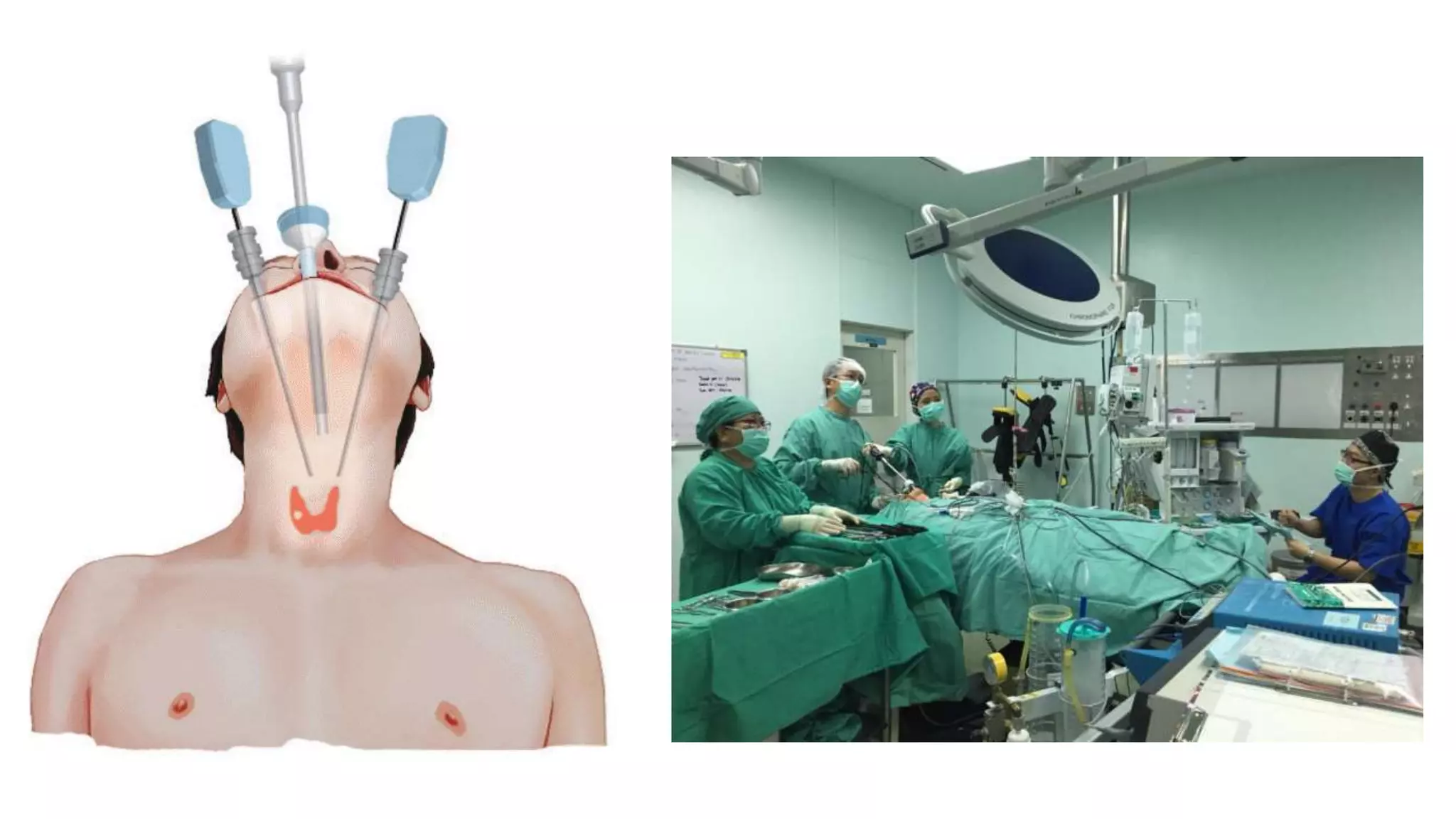
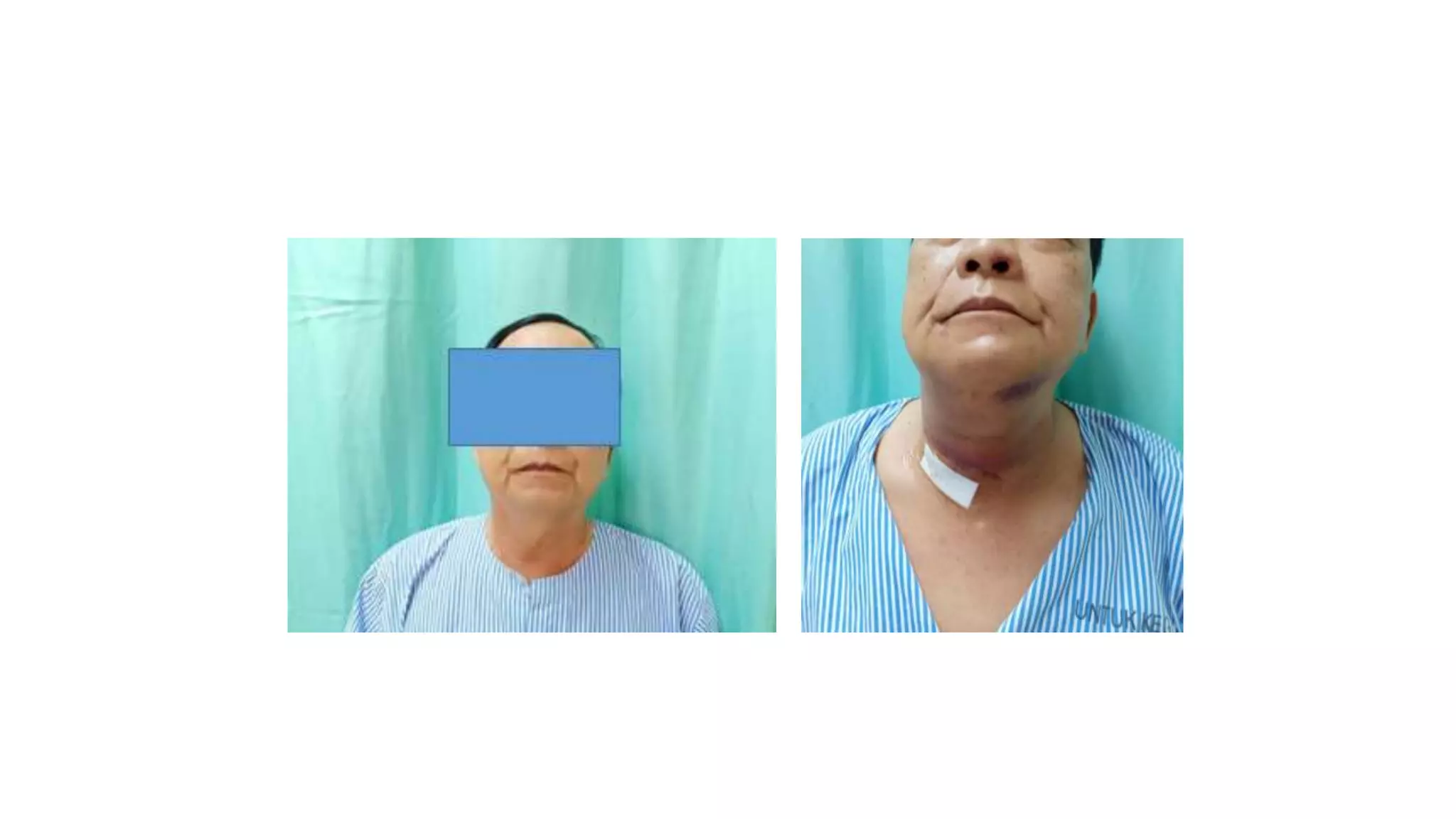
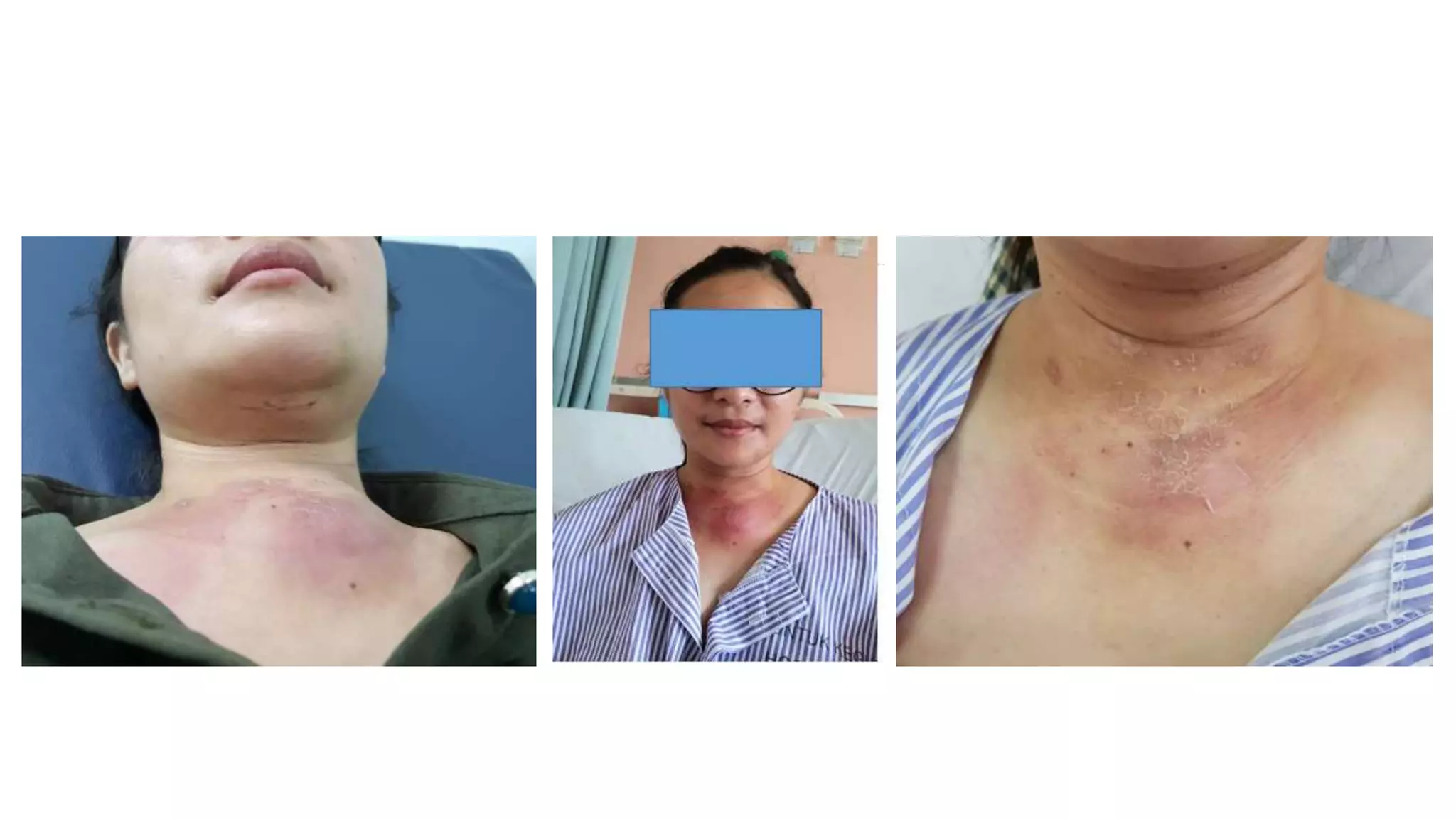
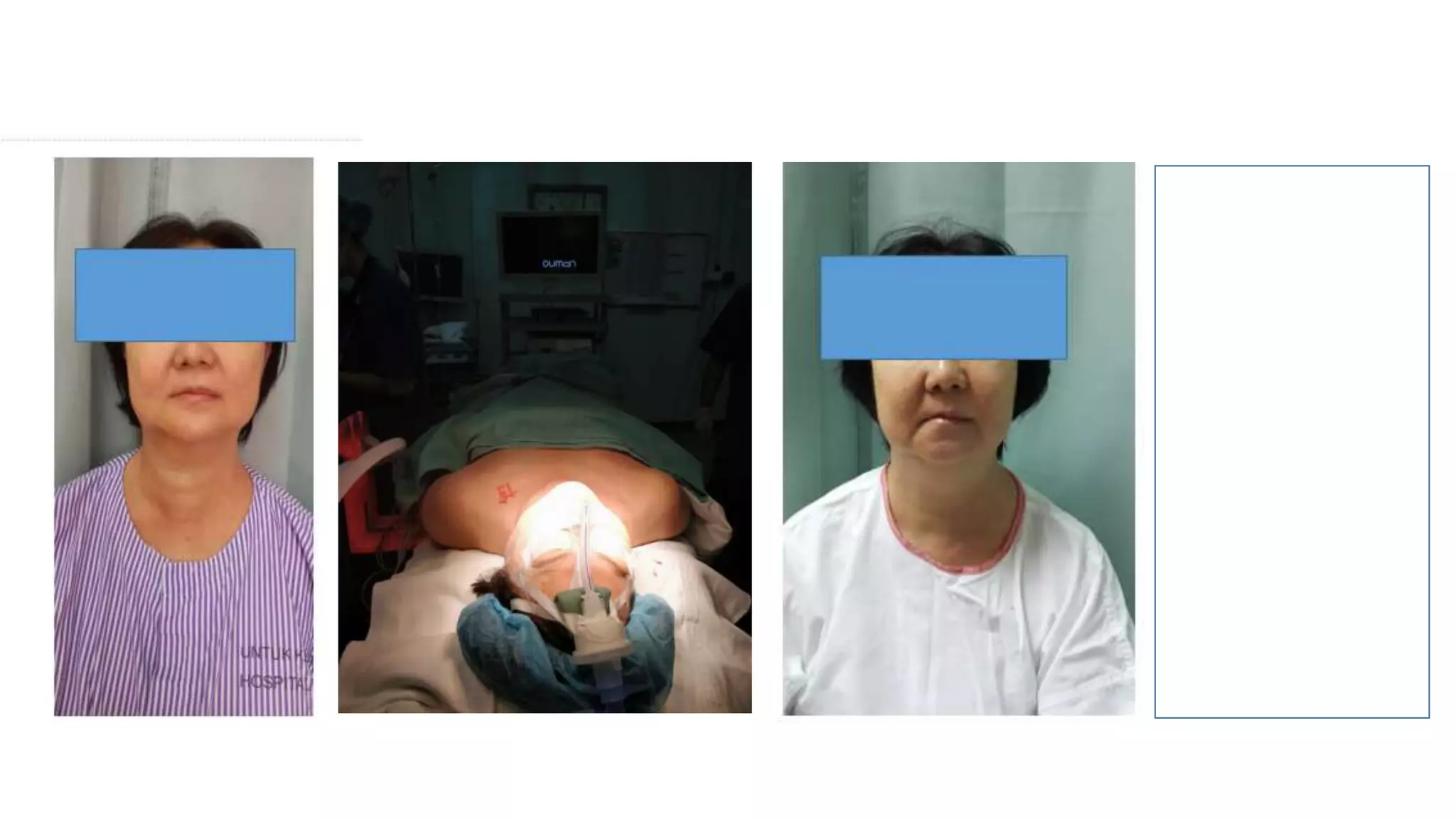
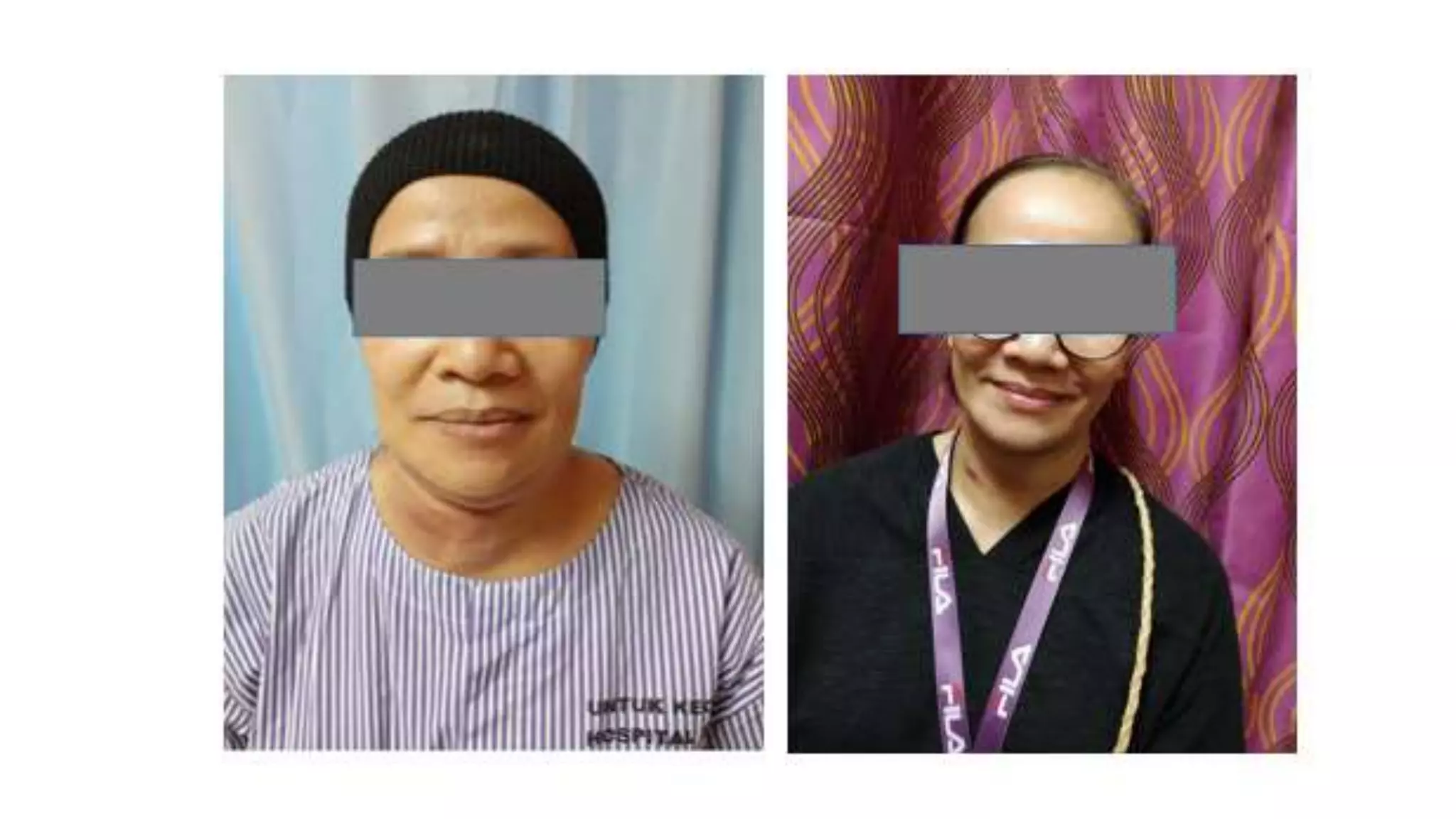
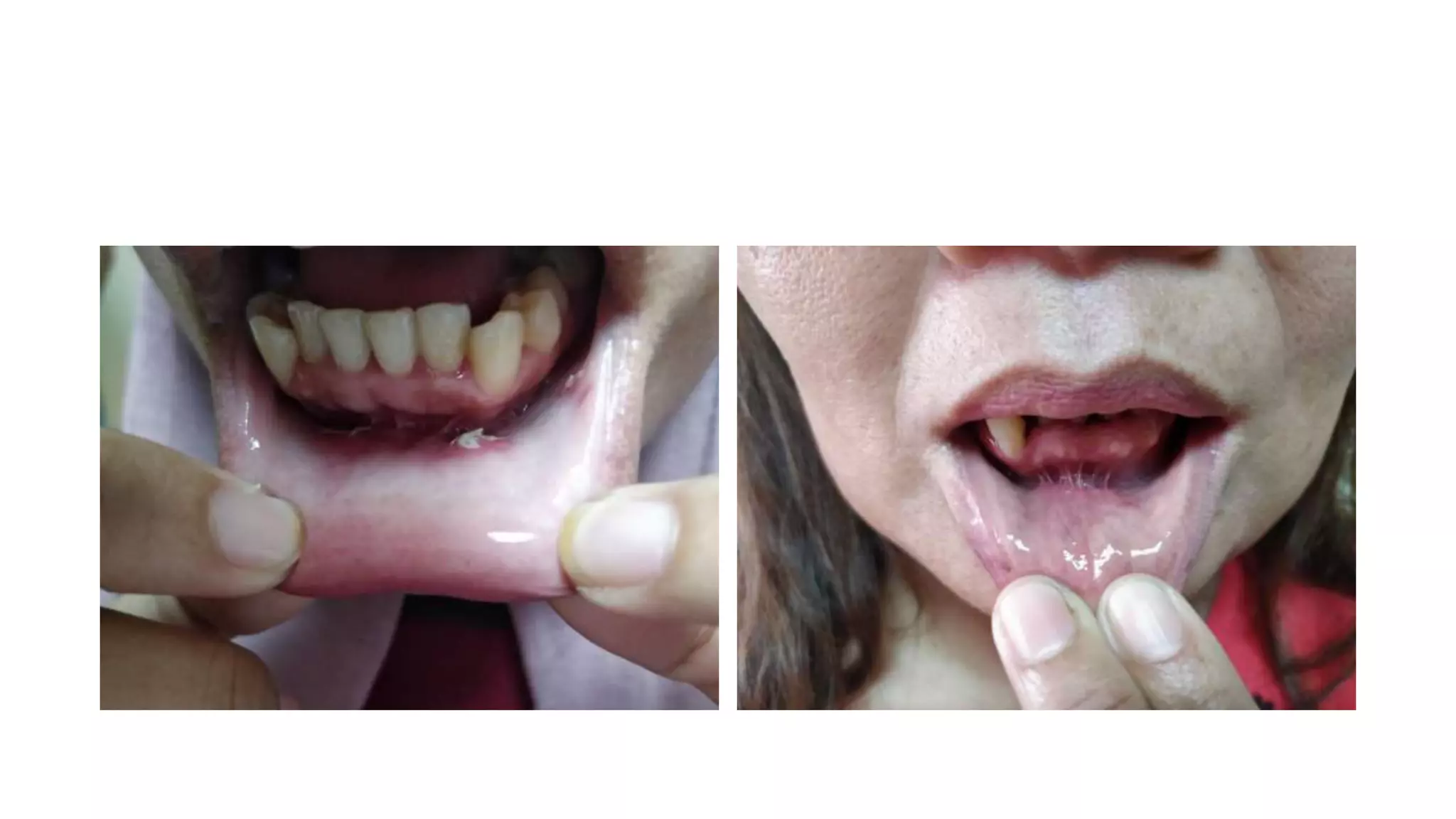
This document provides an overview of goitre (enlargement of the thyroid gland) including its definition, anatomy, functions, classifications, clinical features, investigations, and treatment options. It discusses the etiology, types and treatment of thyroid cancers. It also covers thyroiditis, imaging, histopathology, tests, and medical and surgical treatment approaches for hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism including anti-thyroid drugs, thyroidectomy, and radioiodine therapy. The document emphasizes the importance of a systematic clinical approach and awareness of red flags when evaluating patients with goitre.