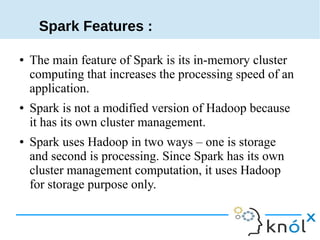
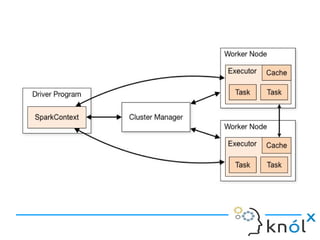
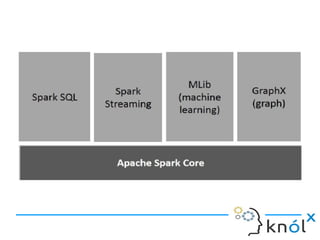
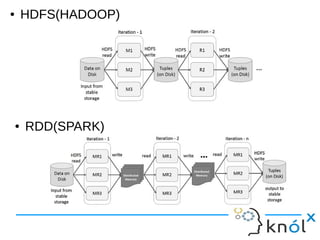
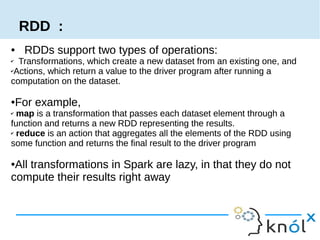
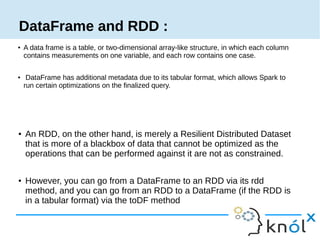
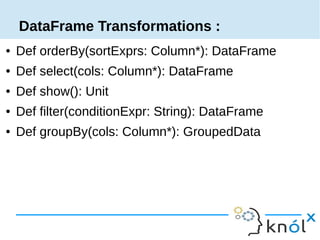
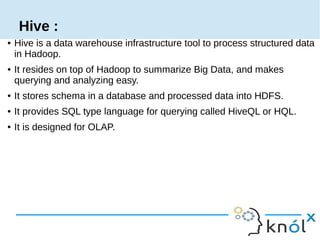
Spark is an in-memory cluster computing framework that can access data from HDFS. It uses Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) as its fundamental data structure. RDDs support transformations that create new datasets and actions that return values. DataFrames are equivalent to relational tables that allow for optimizations. HiveContext allows Spark to query data stored in Hive. Queries can be written using HiveQL, which is converted to Spark jobs.



![● Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDD) is a fundamental
data structure of Spark.
● It is an immutable distributed collection of objects.
● RDDs can contain any type of Python, Java, or Scala
objects, including user-defined classes.
● There are two ways to create RDDs: parallelizing an
existing collection in your driver program
● e.g. val data = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
val distData = sc.parallelize(data)
● val distFile = sc.textFile("data.txt")
distFile: RDD[String] = MappedRDD@1d4cee08
RDD :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparksqlknolx-160715124340/85/A-Step-to-programming-with-Apache-Spark-7-320.jpg)
![● A DataFrame is equivalent to a relational table
in Spark SQL.
DataFrame :
● Steps to create DataFrame :
Create SparkContext object :
– val conf = new
SparkConf().setAppName("Demo").setMaster("local[2]")
– val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
Create SqlContext object :
– val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
Read Data From Files :
– val df = sqlContext.read.json("src/main/scala/emp.json")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparksqlknolx-160715124340/85/A-Step-to-programming-with-Apache-Spark-10-320.jpg)
![●Def collect(): Array[Row]
●Def collectAsList(): List[Row]
●Def count(): Long
●Def head(): Row
●Def head(n: Int): Array[Row]
●Def collect(): Array[Row]
●Def collectAsList(): List[Row]
●Def count(): Long
●Def head(): Row
●Def head(n: Int): Array[Row]
DataFrame Actions :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparksqlknolx-160715124340/85/A-Step-to-programming-with-Apache-Spark-13-320.jpg)
![1) first create a SqlContext instance,
val sqlContext = new SqlContext(sc)
2) submit the queries by calling the sql method on the HiveContext instance.
val res=sqlContext.sql("select * from employee")
To construct a HiveQL query,
1) first create a new HiveContext instance,
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Demo").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val hiveContext = new HiveContext(sc)
2) submit the queries by calling the sql method on the HiveContext instance.
val res=hiveContext.sql("select * from employee")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparksqlknolx-160715124340/85/A-Step-to-programming-with-Apache-Spark-17-320.jpg)


