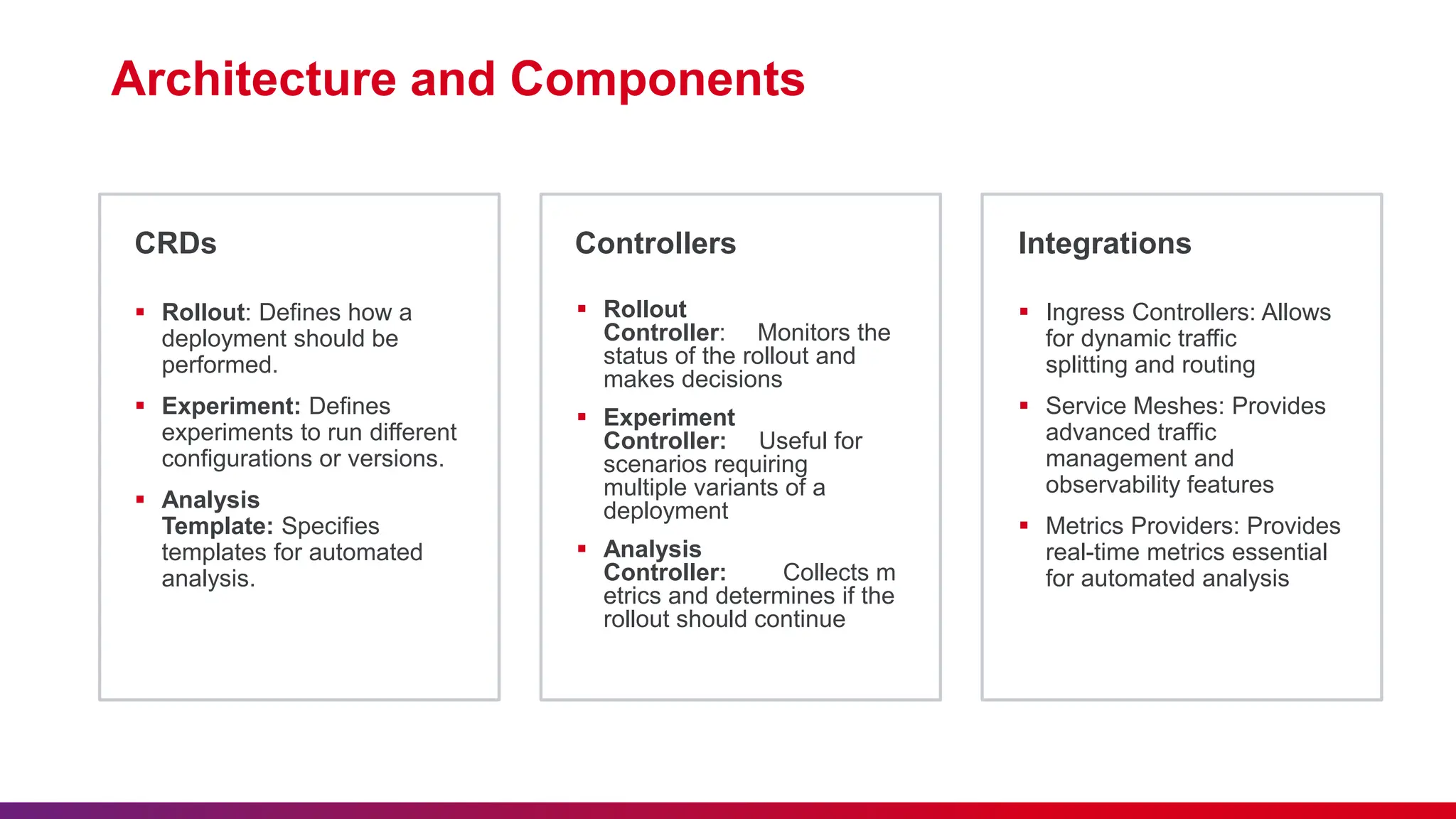
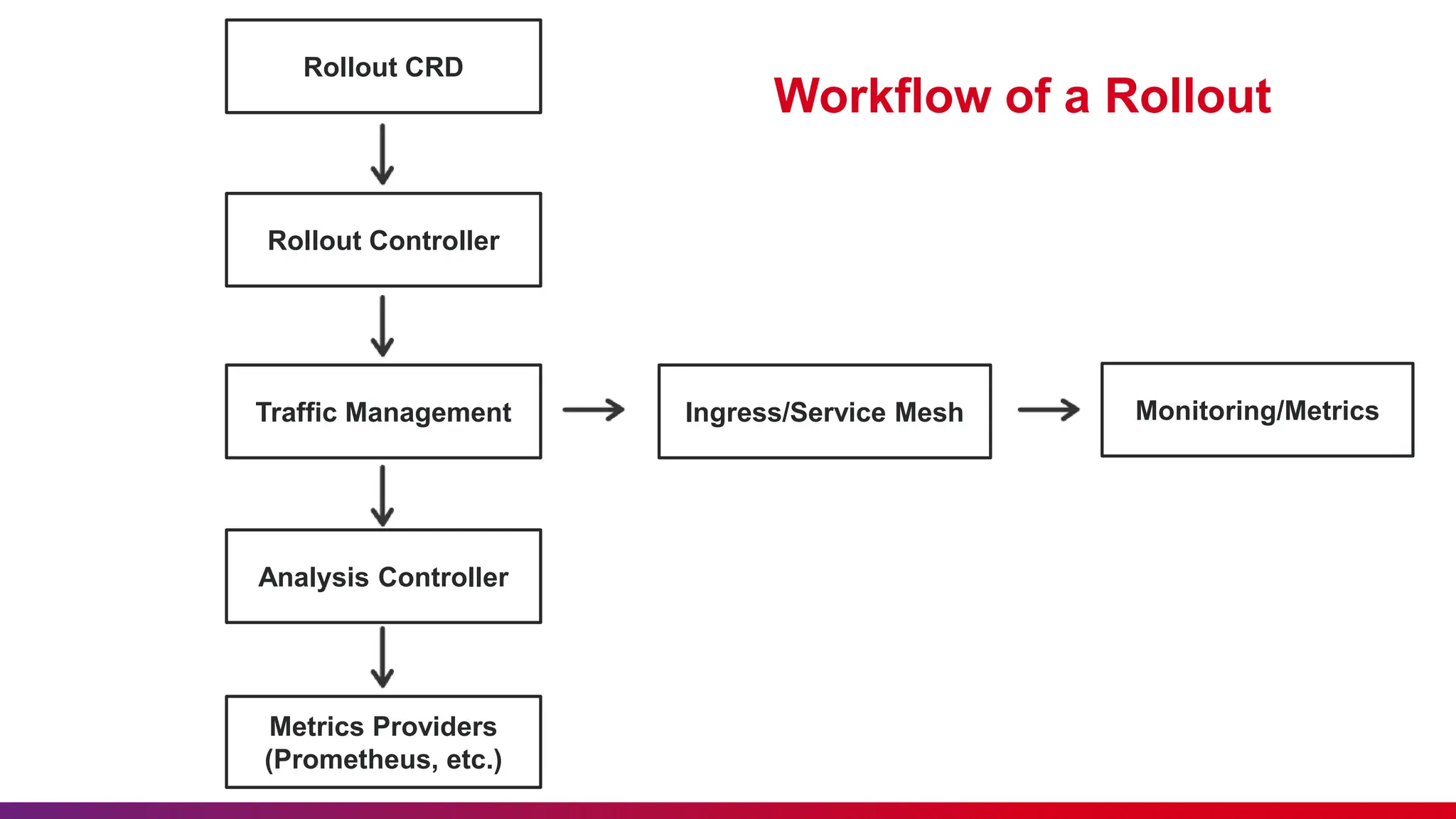
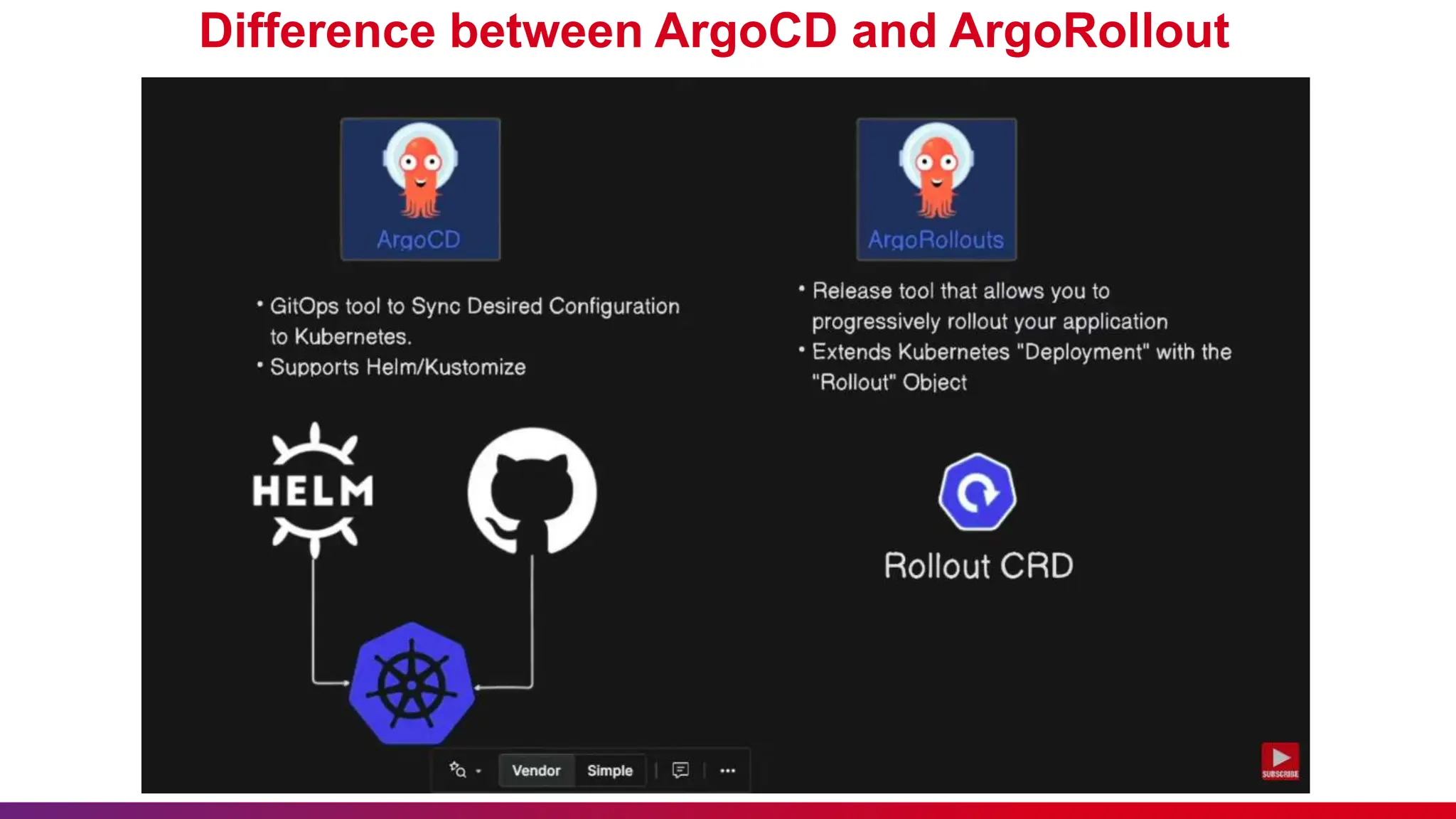
This document discusses Argo Rollouts, an advanced open-source Kubernetes controller that enhances deployment strategies such as canary and blue-green deployments. It emphasizes best practices for using these deployments, including feedback submission, punctuality, and minimizing disturbances during sessions. The benefits of Argo Rollouts include reduced deployment risk, incremental updates, and automated rollbacks.