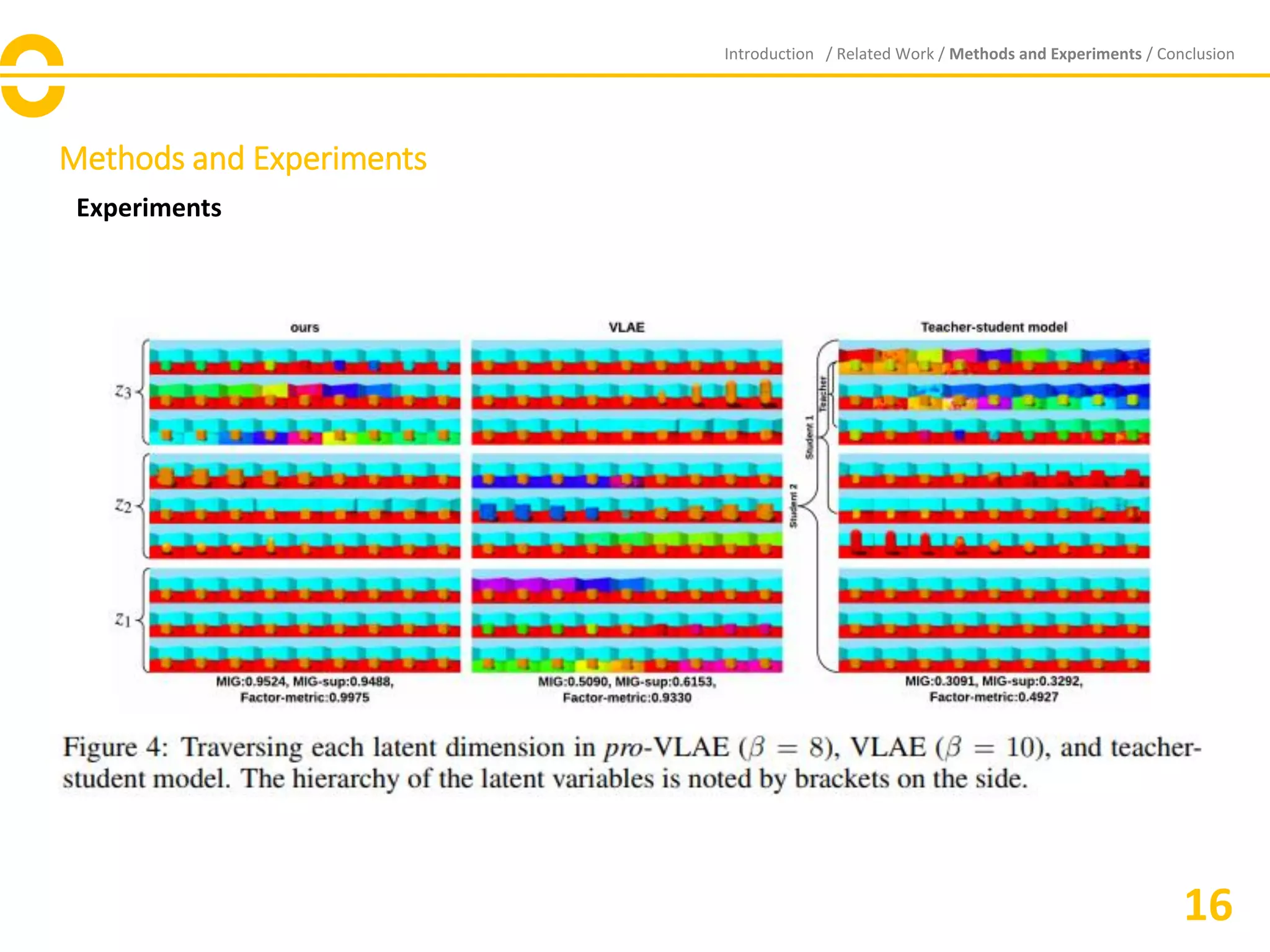
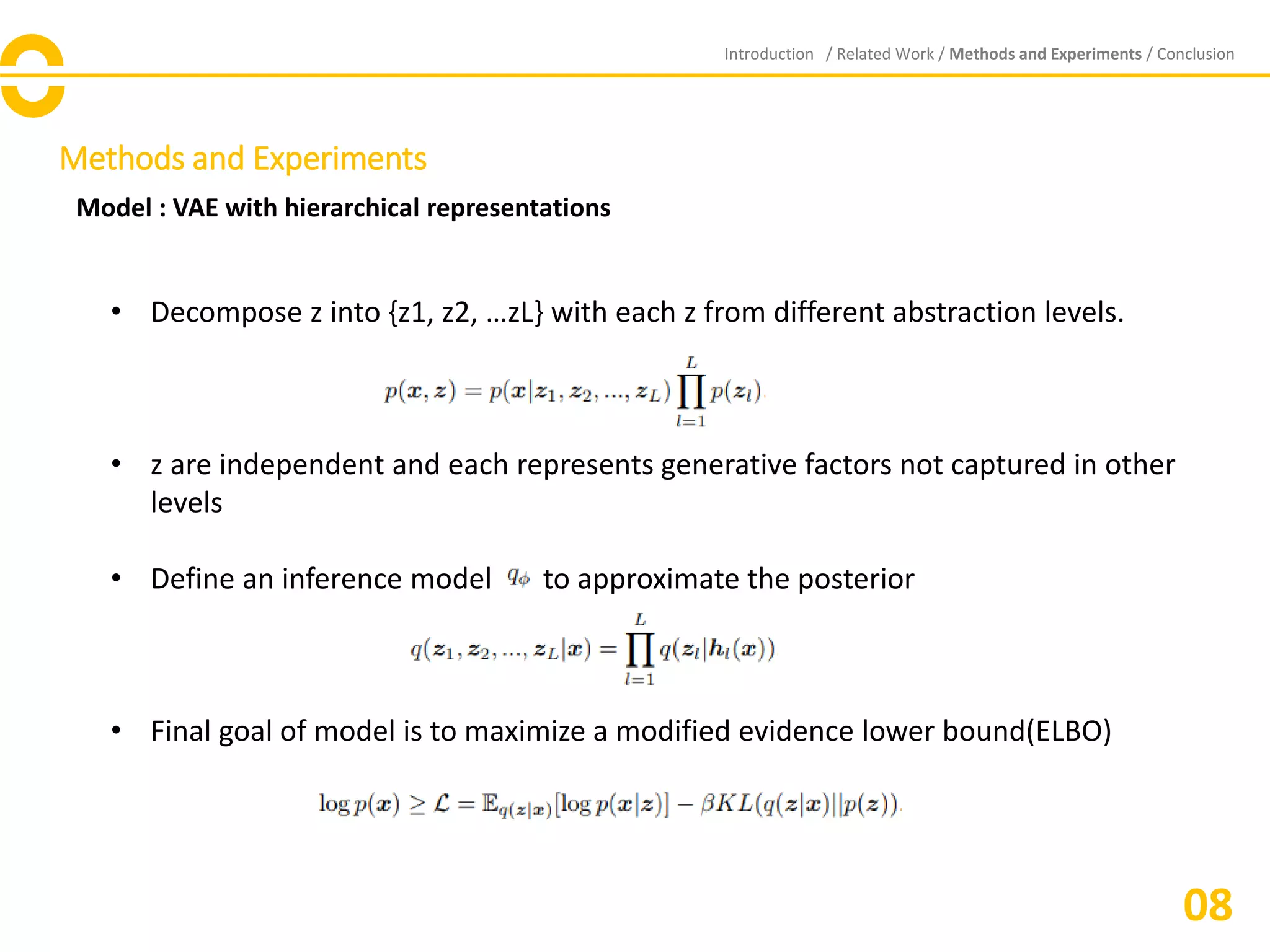
The document discusses the proposal of 'pro-VLAE', a progressive learning approach to enhance the learning and disentangling of hierarchical representations in variational autoencoders (VAEs). It demonstrates improved disentanglement metrics and superior performance compared to existing models like B-VAE and VLAE by progressively growing the network's capacity. Future work aims to strengthen guidance for information allocation across different abstraction levels.
![Pro-VLAE
Introduction – Background
• Learning rich representation from data is
important for deep generative models like
VAE
• VAE has not been able to fully utilize the
depth of NNs → Encoder is able to extract
high-level representations helpful for
discriminative tasks, but generation requires
the preservation of all generative factors at
different abstraction levels
• It is difficult to extract and disentangle all
generative factors at once, especially at
different abstraction levels
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
01
[Variational Auto Encoder]
[Latent space Disentanglement]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provlaereview-201025124105/75/Progressive-learning-and-Disentanglement-of-hierarchical-representations-3-2048.jpg)
![Pro-VLAE
Introduction – Proposal
• Use progressive learning strategies to improve learning and disentangling of
hierarchical representations
- Hierarchical representations are latent representations from different depths of the
inference(encoder) and generation(decoder) model [1] VLAE
- Progressively grow the capacity of the network.
→ Named it pro-VLAE
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
02[1] Shengjia Zhao, Jiaming Song, and Stefano Ermon. Learning hierarchical features from deep generative models. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 4091–
4099, 2017.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provlaereview-201025124105/75/Progressive-learning-and-Disentanglement-of-hierarchical-representations-4-2048.jpg)

![Related Work
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
04
Variational Autoencoder
[Encoder]
[Decoder]
* Images imported from https://itrepo.tistory.com/48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provlaereview-201025124105/75/Progressive-learning-and-Disentanglement-of-hierarchical-representations-6-2048.jpg)
![Related Work
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
05
Variants of VAE
VLAE [1]
B-VAE [2]
[1] Shengjia Zhao, Jiaming Song, and Stefano Ermon. Learning hierarchical features from deep generative models. In International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 4091–
4099, 2017.
[2] Irina Higgins, Loic Matthey, Arka Pal, Christopher Burgess, Xavier Glorot, Matthew Botvinick, Shakir Mohamed, and Alexander Lerchner. beta-vae: Learning basic visual
concepts with a constrained variational framework. In International Conference on Learning Representations, 2017.
• Learn independent hierarchical representation
from different levels of abstraction
[Variational Ladder AutoEncoder]
[Beta - VAE]
• When B>1, applies a stronger constraint on the latent bottleneck
and limits the representation capacity of z
• Higher ‘B’ value encourages more efficient latent encoding and
disentanglement, in change of reconstruction quality.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provlaereview-201025124105/75/Progressive-learning-and-Disentanglement-of-hierarchical-representations-7-2048.jpg)
![Related Work
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
06
Progressive Learning
[3] Tero Karras, Timo Aila, Samuli Laine, and Jaakko Lehtinen. Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation. In International Conference on Learning
Representations, 2018.
[4] Yifan Wang, Federico Perazzi, Brian McWilliams, Alexander Sorkine-Hornung, Olga SorkineHornung, and Christopher Schroers. A fully progressive approach to single-image
superresolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 864–873, 2018.
• A small number of works have demonstrated the ability to simply grow the
architecture of GAN’s from a shallow network with limited capacity for generating
low-resolution images, to a deep network capable of generating super-resolution
images. [3], [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provlaereview-201025124105/75/Progressive-learning-and-Disentanglement-of-hierarchical-representations-8-2048.jpg)
![Related Work
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
07
Teacher-student strategy
• Teacher-student strategy was used to progressively grow the dimension of the
latent representations in VAE [5]
• After a teacher is trained to correctly disentangle attributes, a student model will
be trained to improve the visual quality of the reconstruction
[5] Jose Lezama. Overcoming the disentanglement vs reconstruction trade-off via jacobian supervision. ´ In International Conference on Learning Representations, 2019.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provlaereview-201025124105/75/Progressive-learning-and-Disentanglement-of-hierarchical-representations-9-2048.jpg)
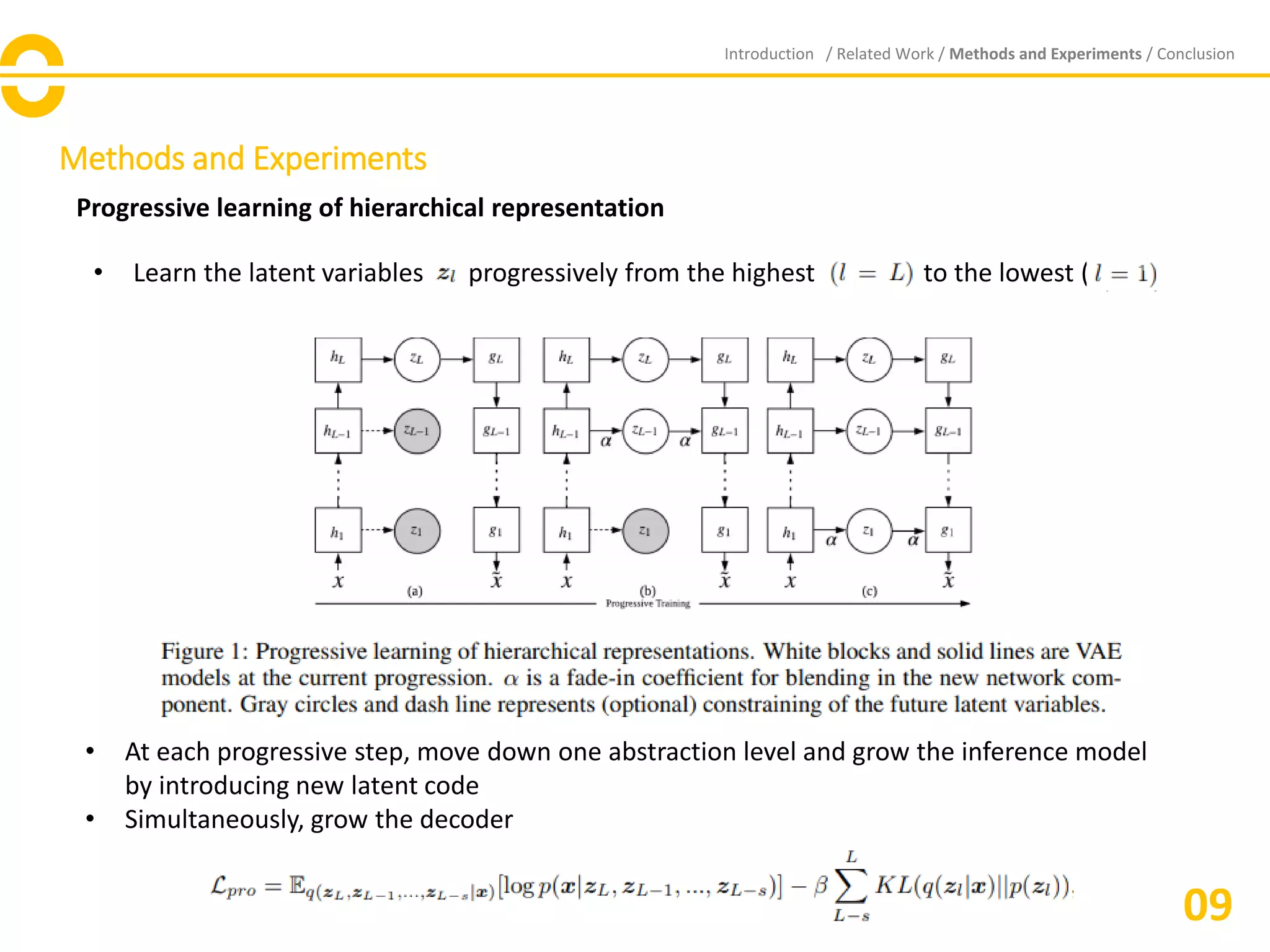

![Methods and Experiments
Code
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
11
[1] Inference [2] Sampling
[3] Generation
[4] Latent Loss
[5] Reconstruction Loss](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provlaereview-201025124105/75/Progressive-learning-and-Disentanglement-of-hierarchical-representations-13-2048.jpg)
![Methods and Experiments
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
12
[7] Optimize
[6] Training
Code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provlaereview-201025124105/75/Progressive-learning-and-Disentanglement-of-hierarchical-representations-14-2048.jpg)
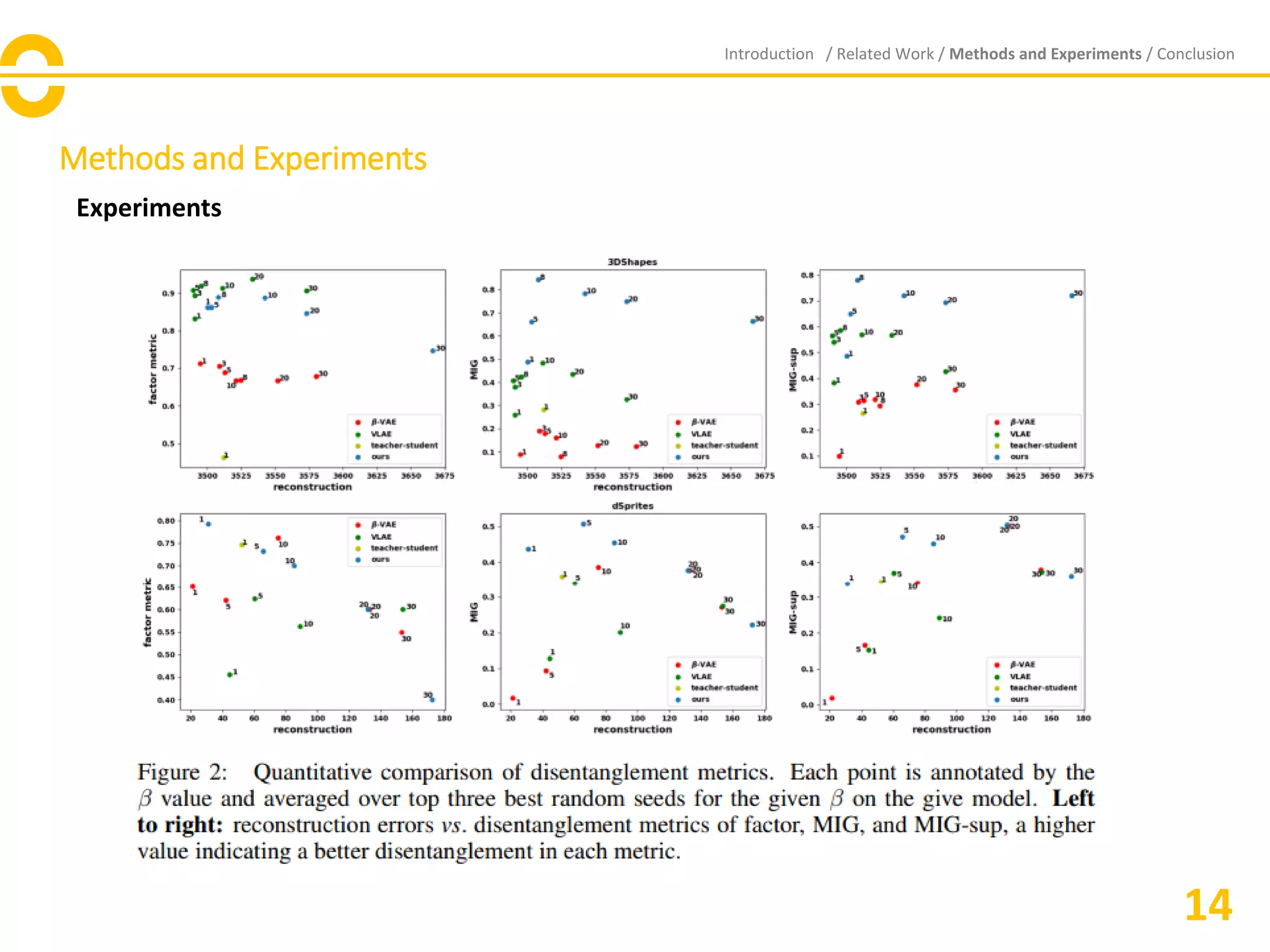
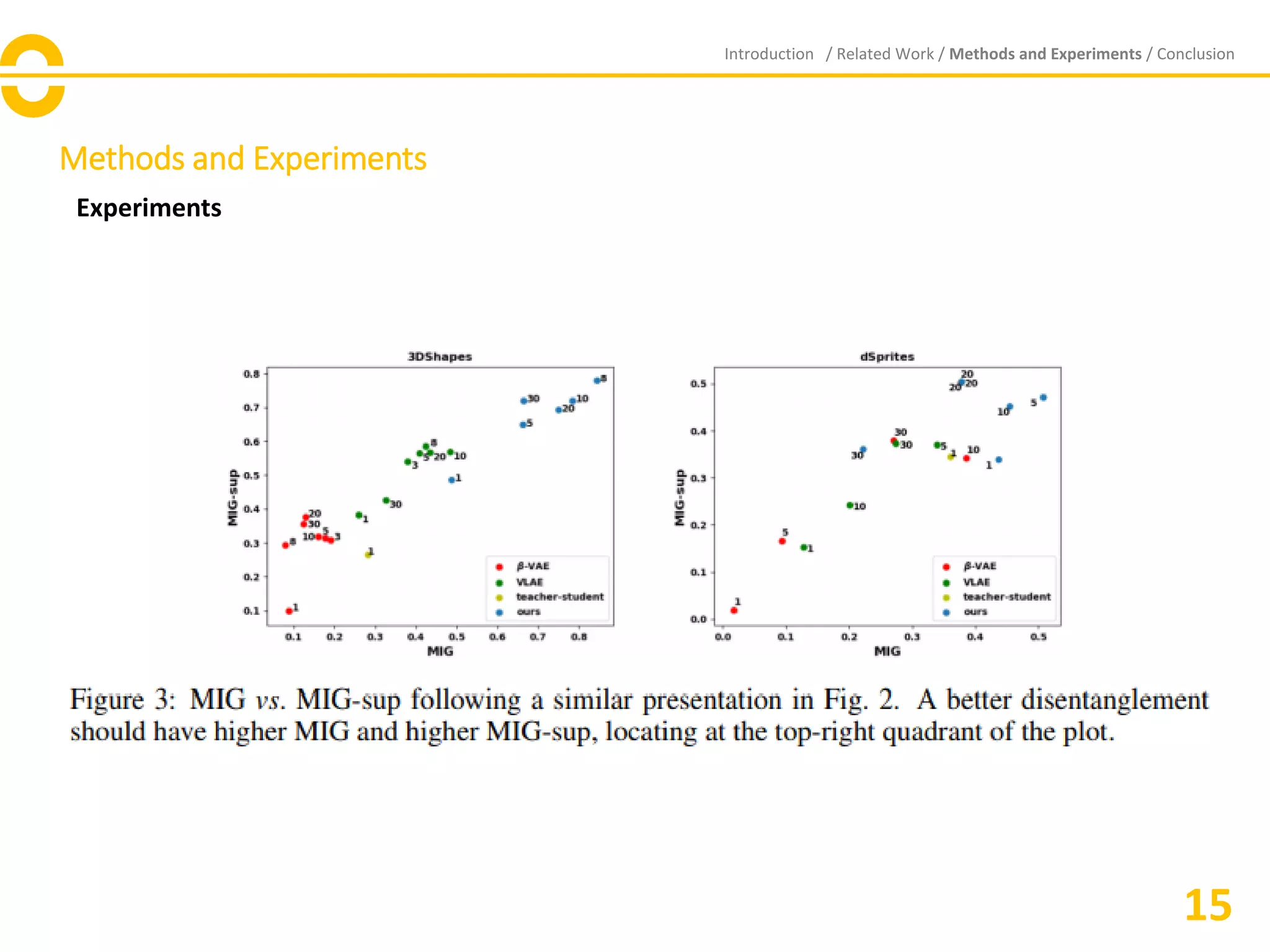
![Methods and Experiments
Disentanglement Metric
Introduction / Related Work / Methods and Experiments / Conclusion
13
(1) MIG (Mutual Information Gap) [6]
[6] Jose Lezama. Overcoming the disentanglement vs reconstruction trade-off via jacobian supervision. ´ In International Conference on Learning Representations, 2019.
(2) MIG-sup (supplement MIG)
• Single factor can have high mutual information with multiple latent variables
• Measure the difference between the top two latent variables with highest mutual information
• If different generative factors are entangled into the same latent dimension, MIG score doesn’t work
• Propose MIG-sup to recognize the entanglement of multiple generative factors in same latent
dimension
Latent A Latent B
Generative
factor A
Generative
factor B
[Generative Factor K]
[Latent Space J]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/provlaereview-201025124105/75/Progressive-learning-and-Disentanglement-of-hierarchical-representations-15-2048.jpg)