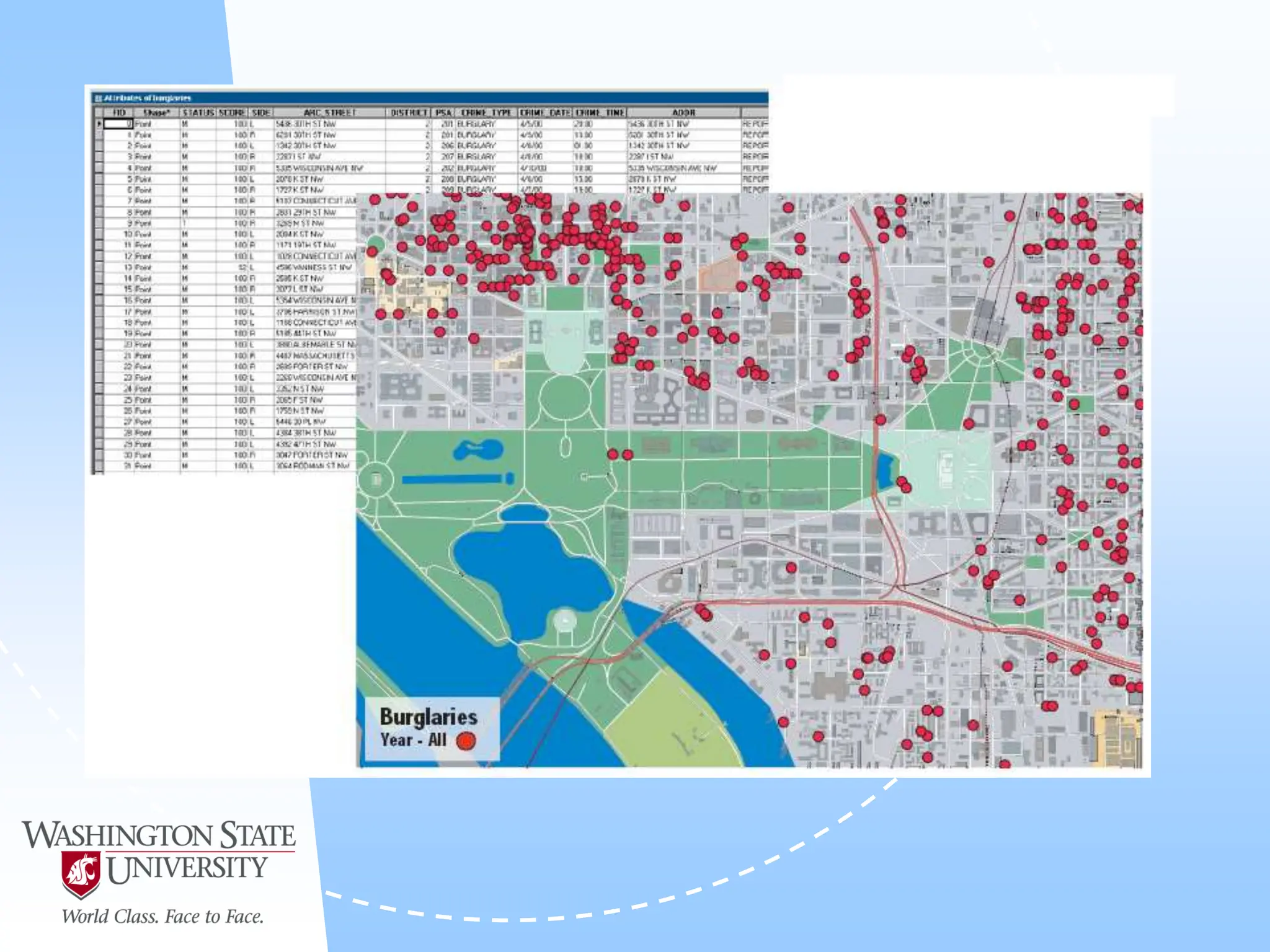
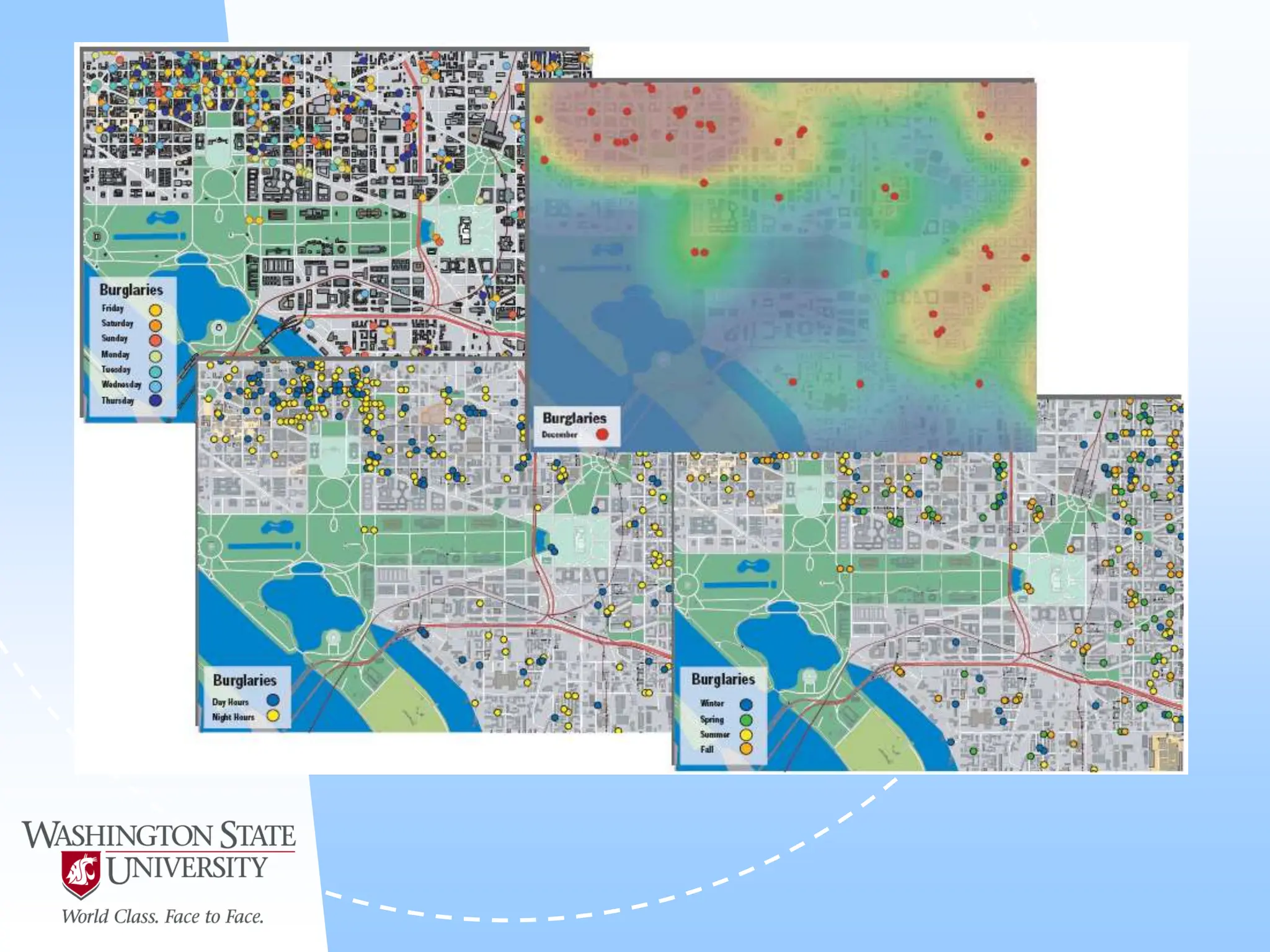
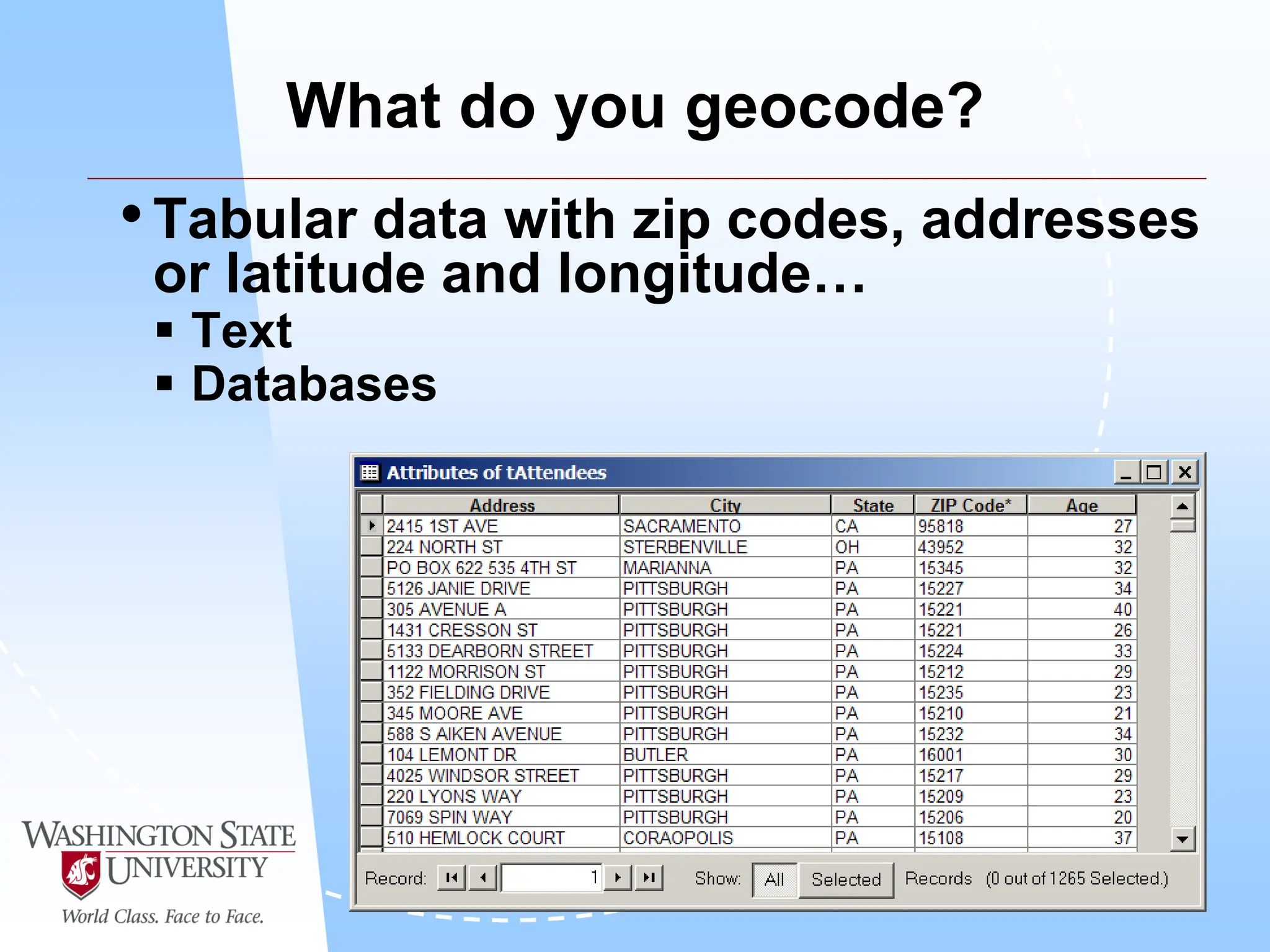
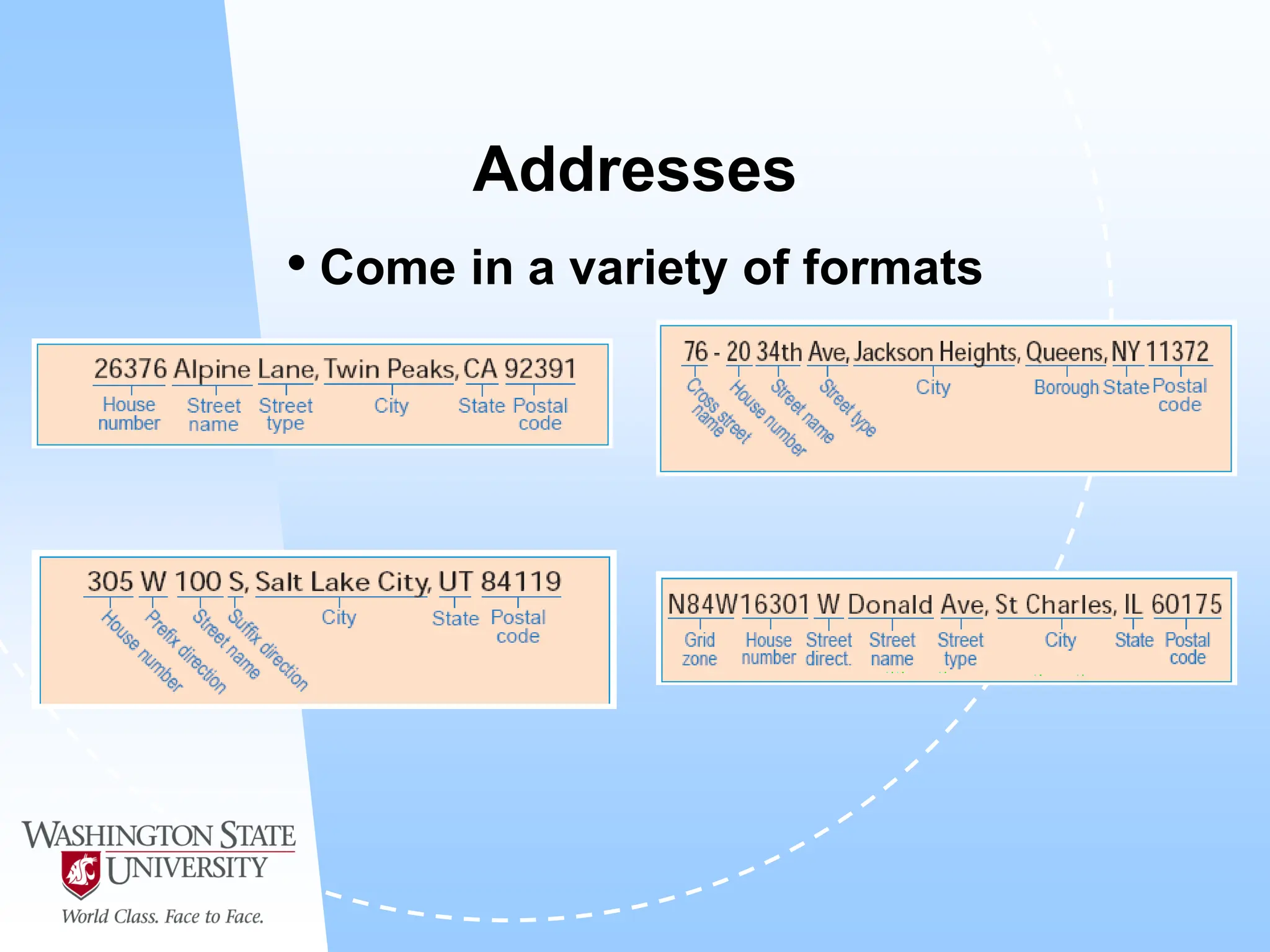
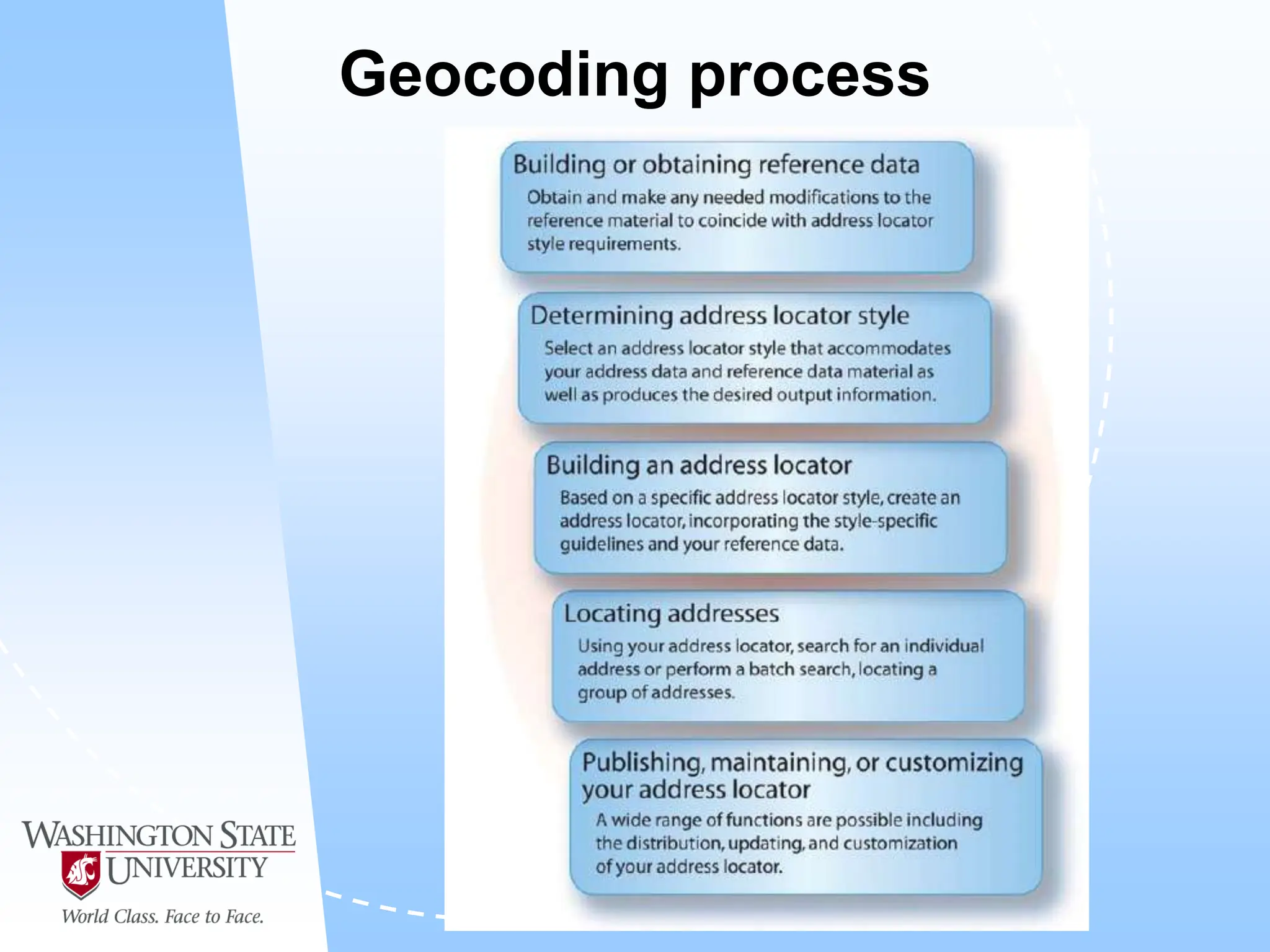
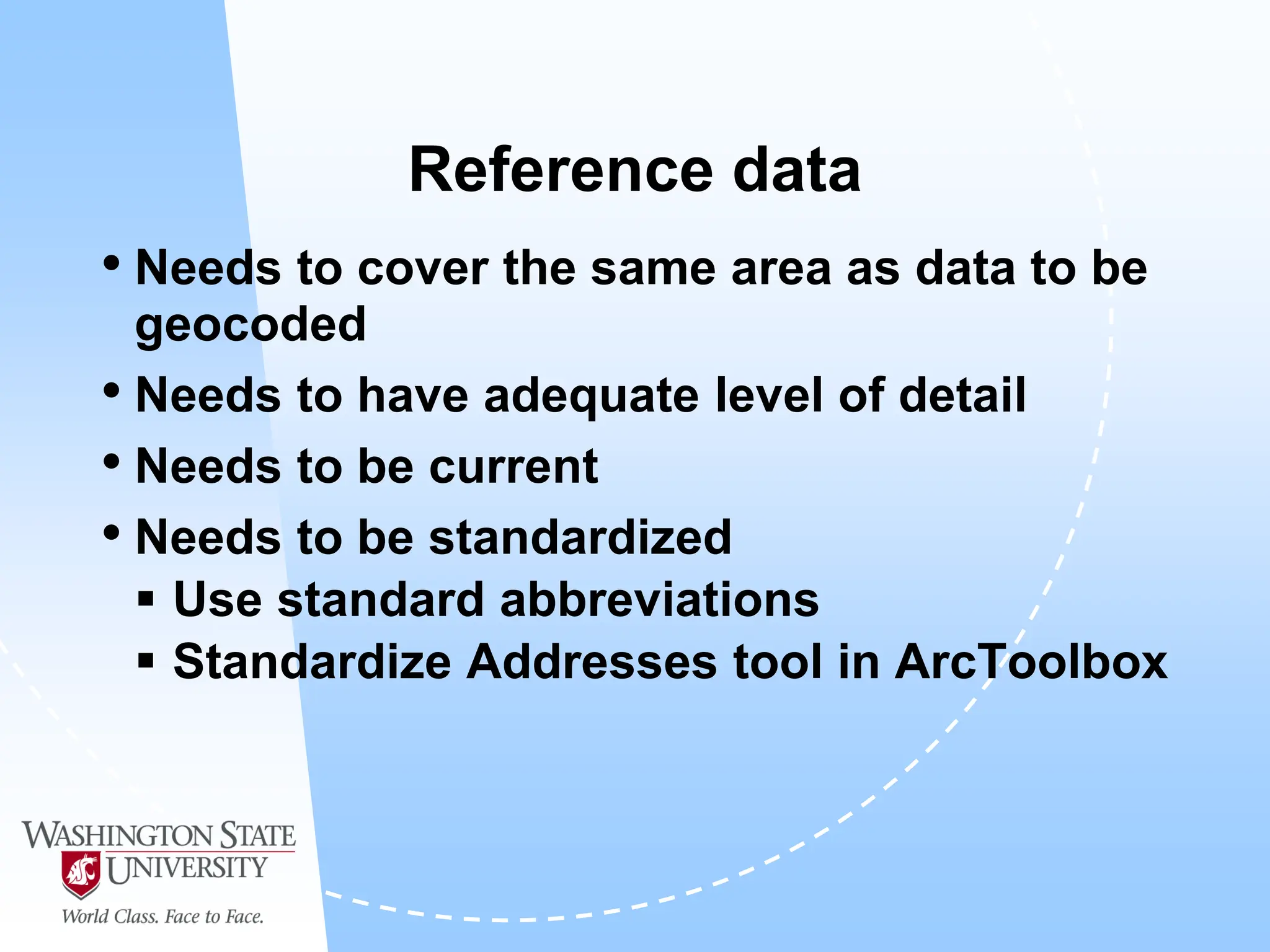
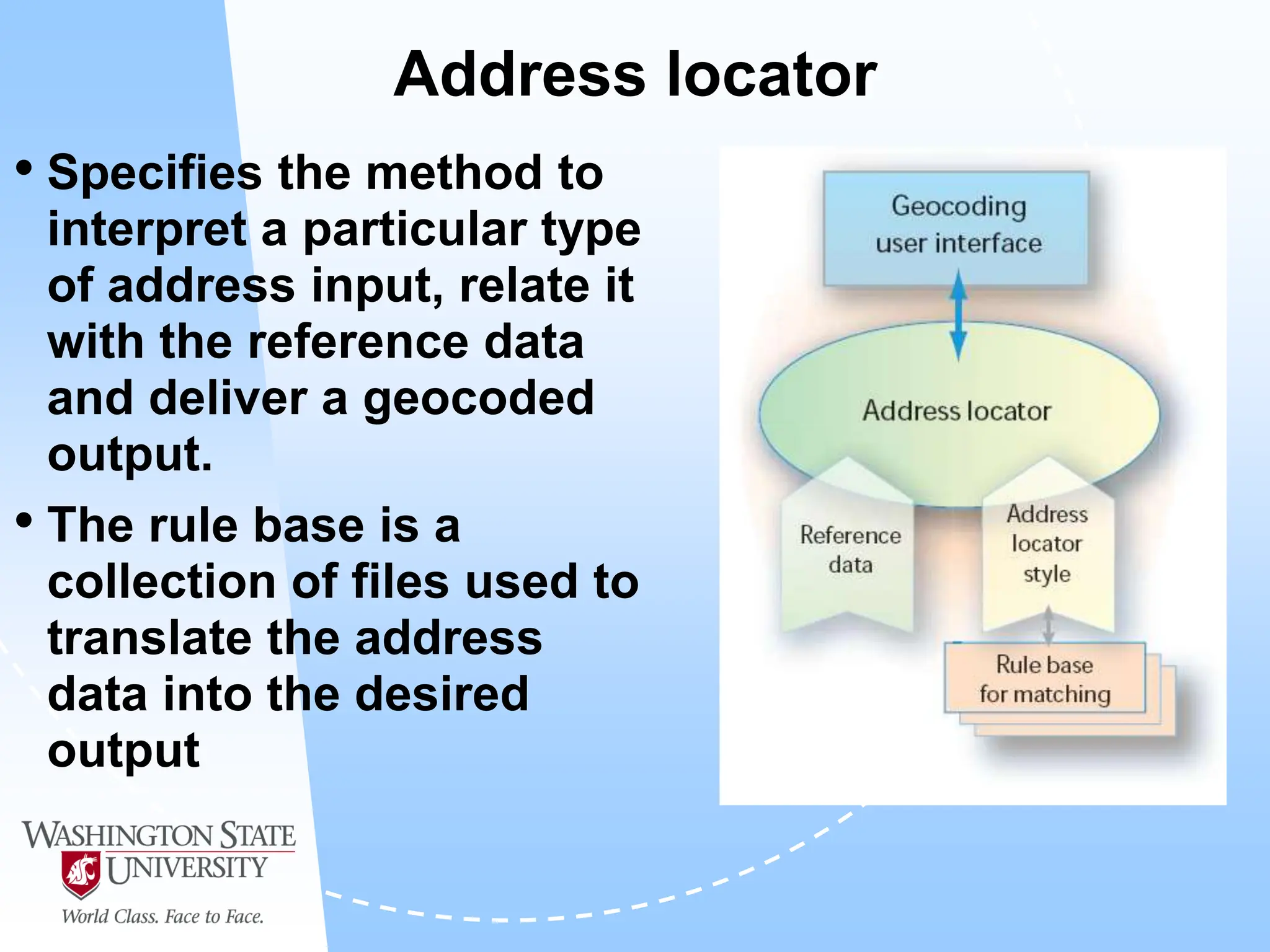
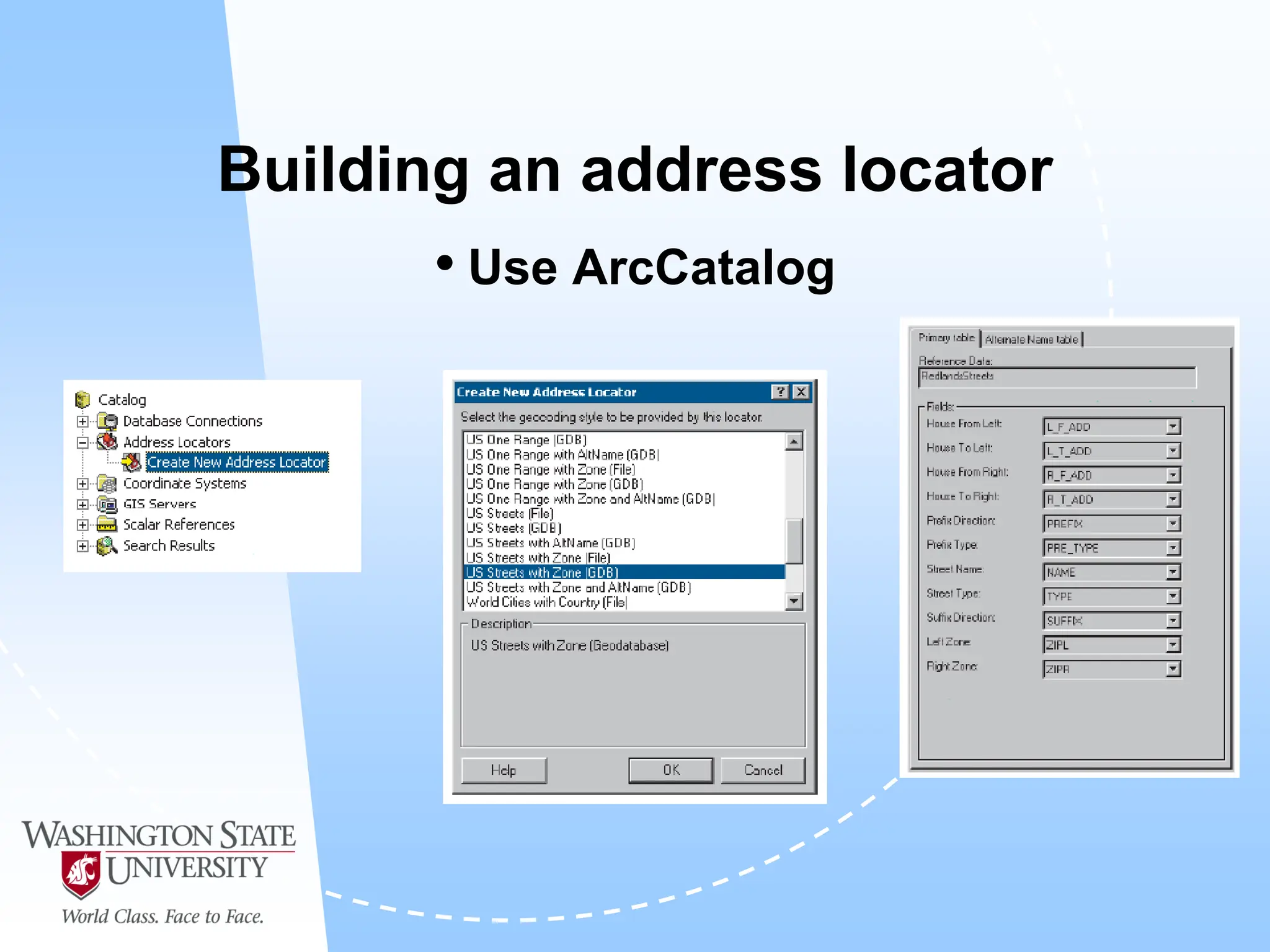
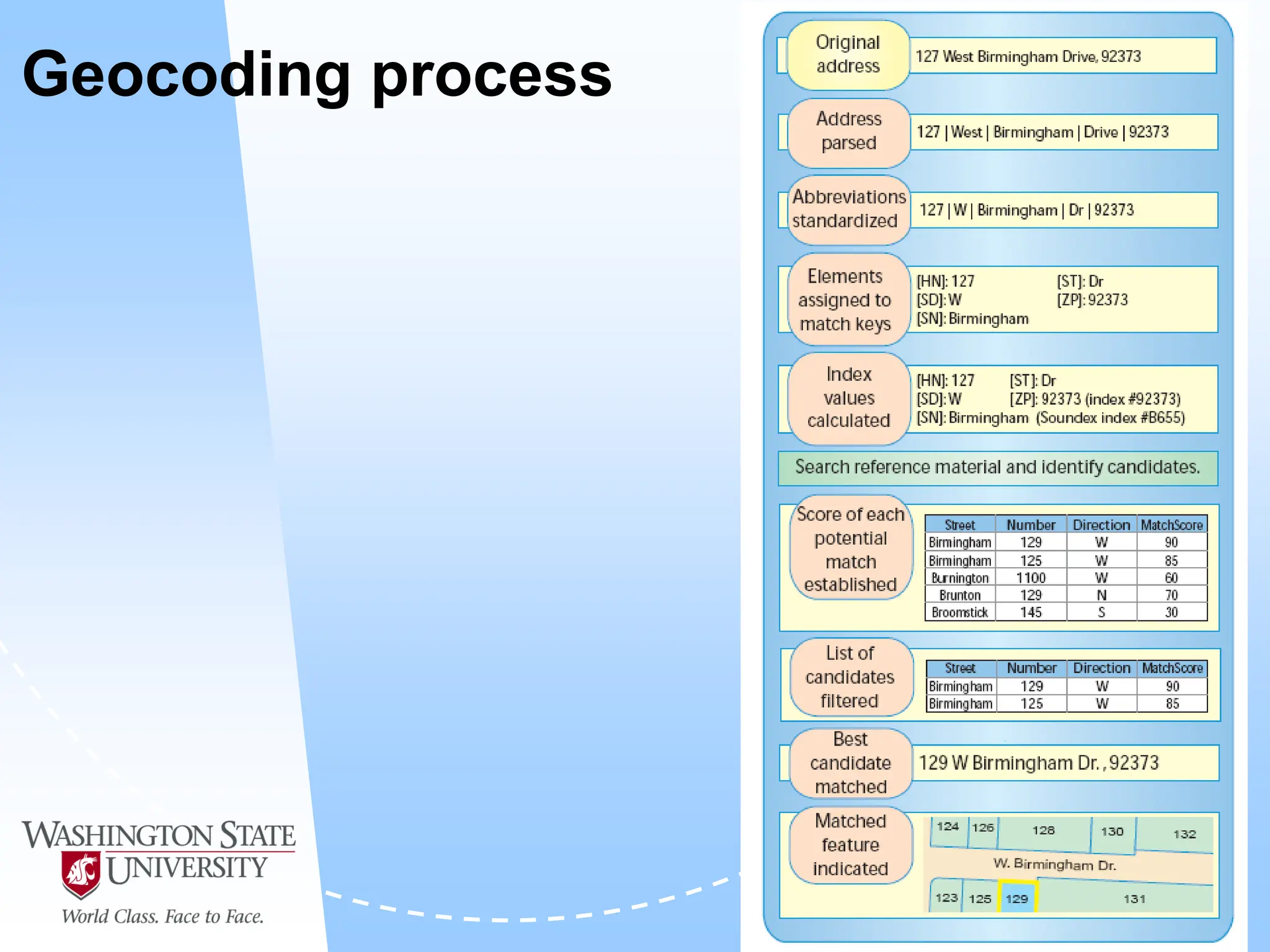
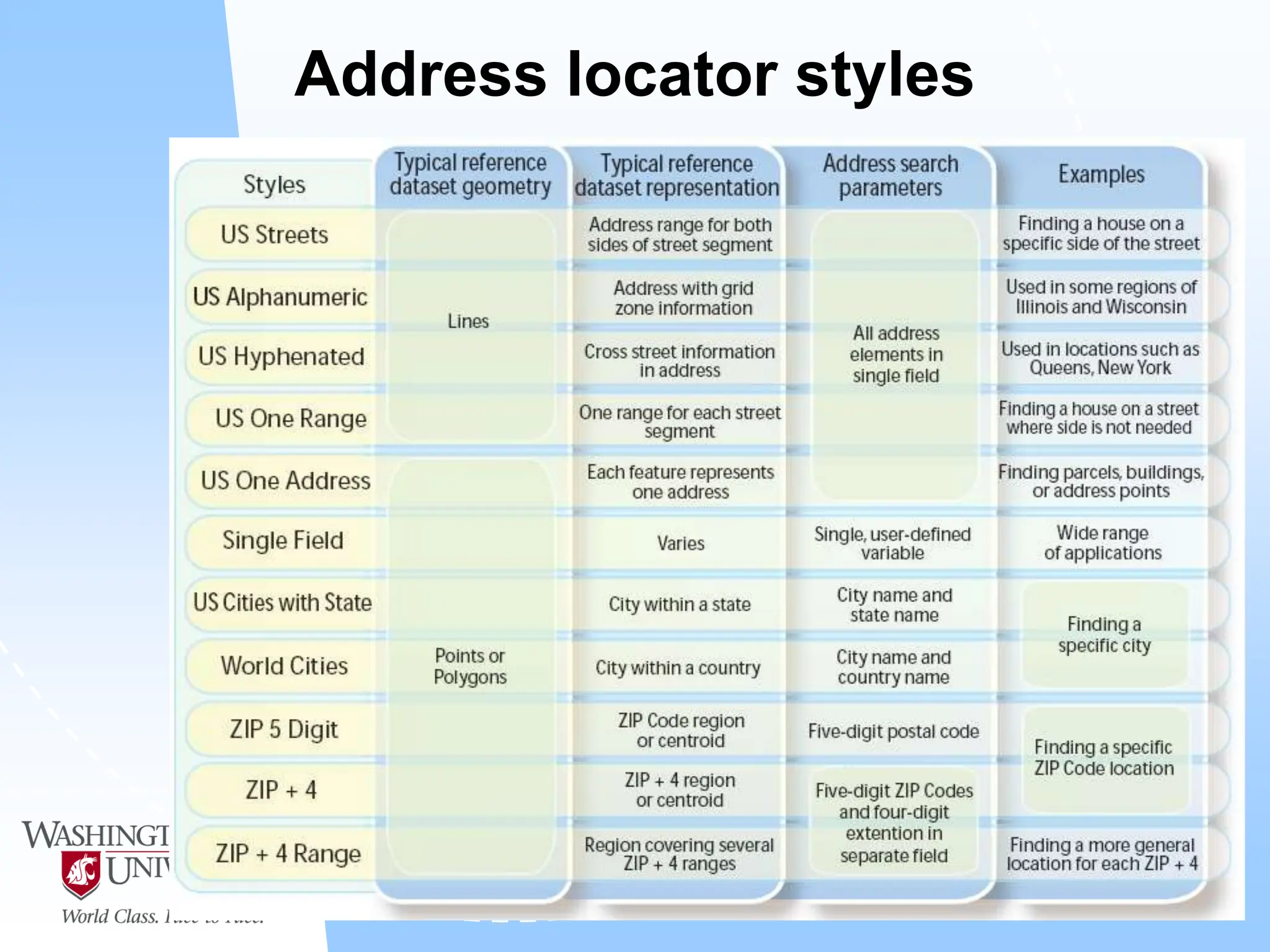
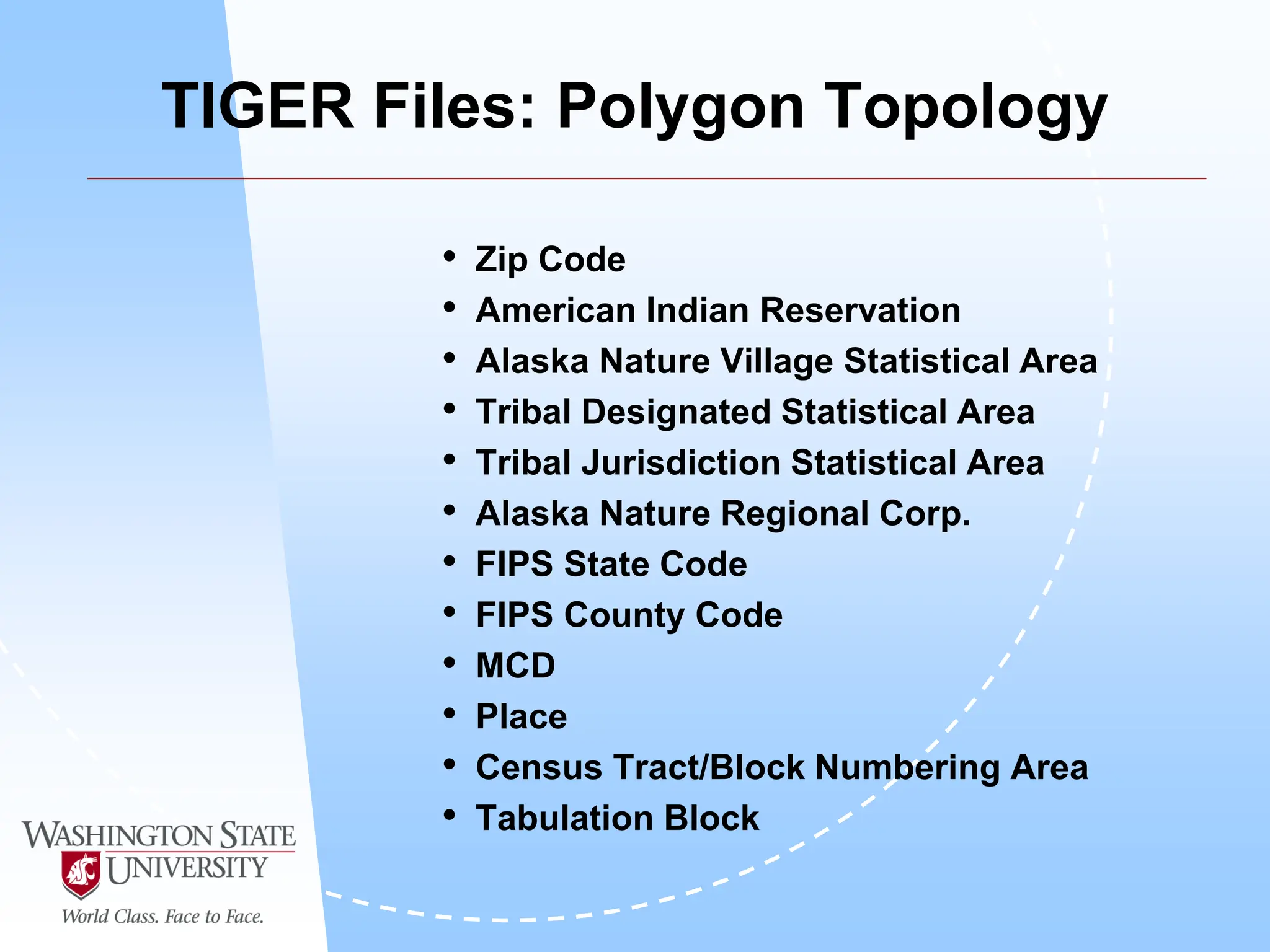
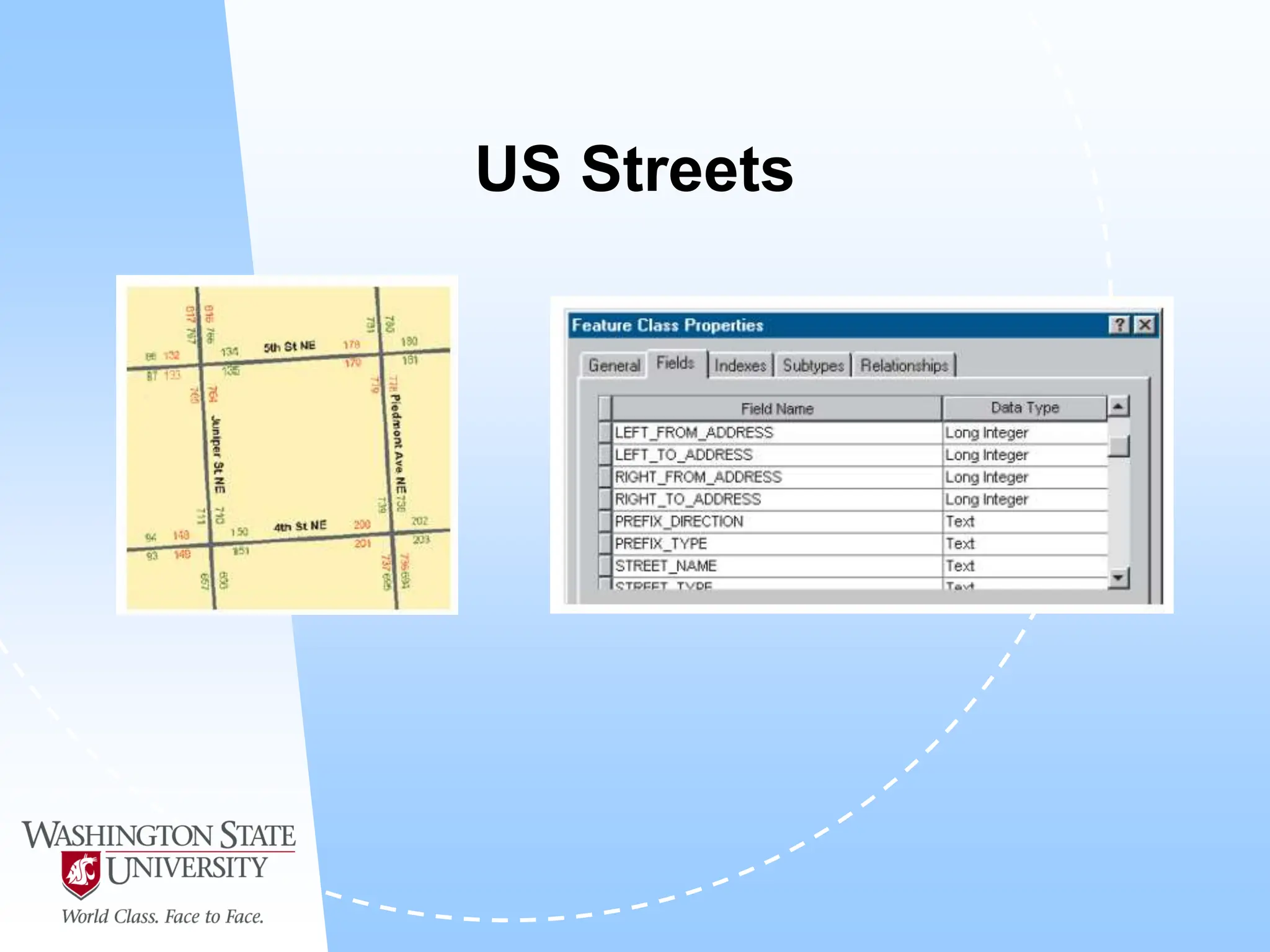
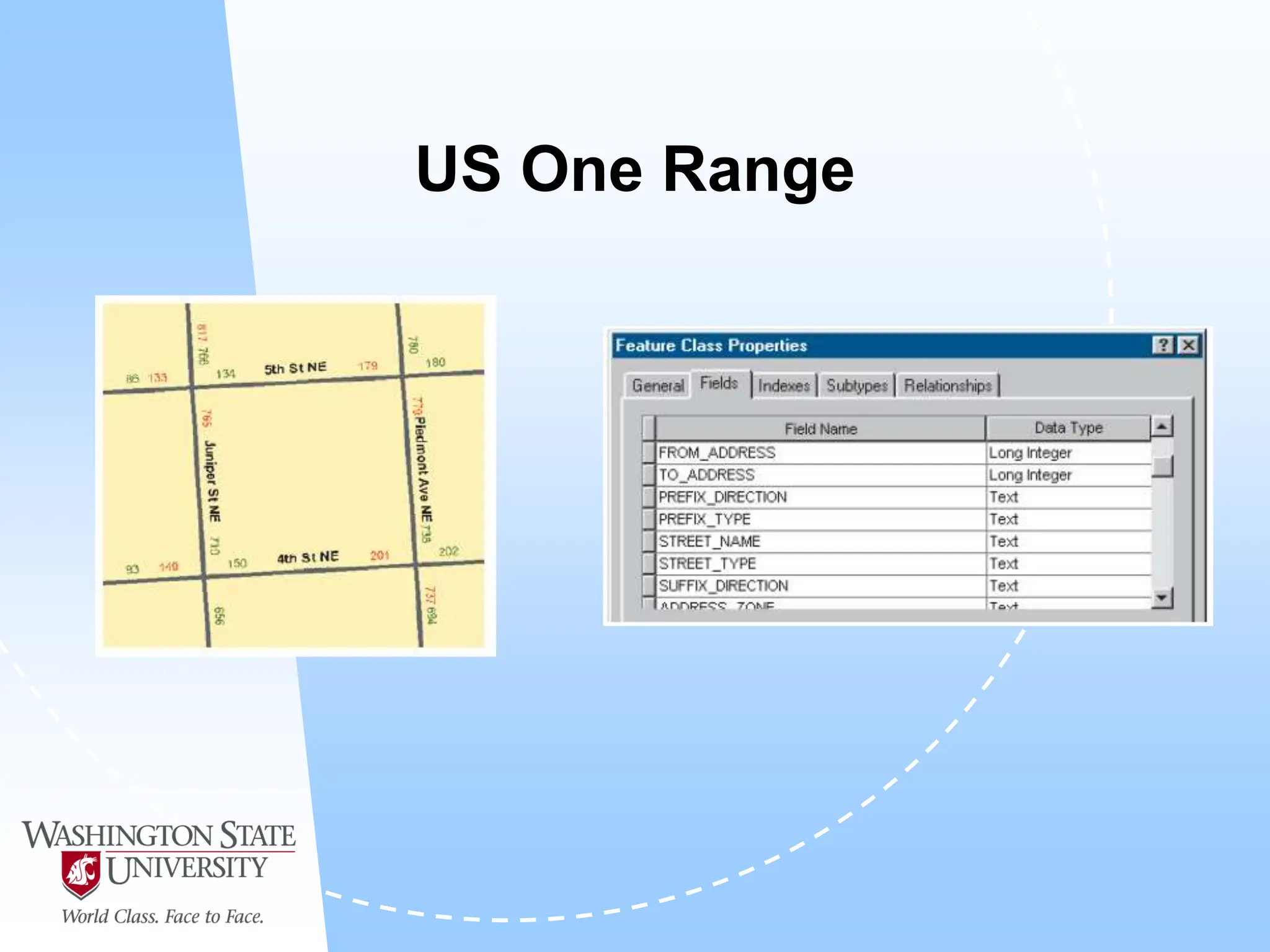
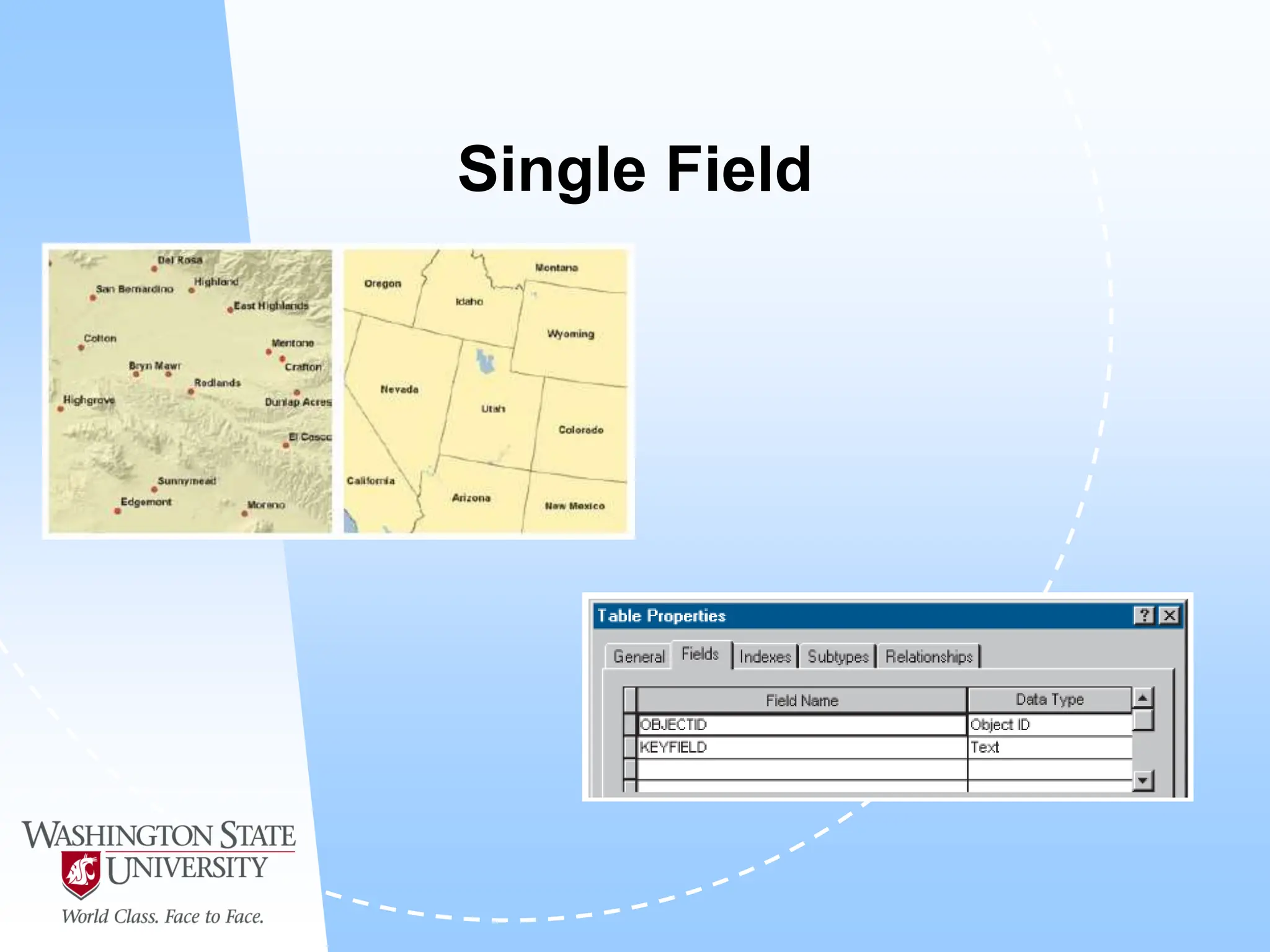
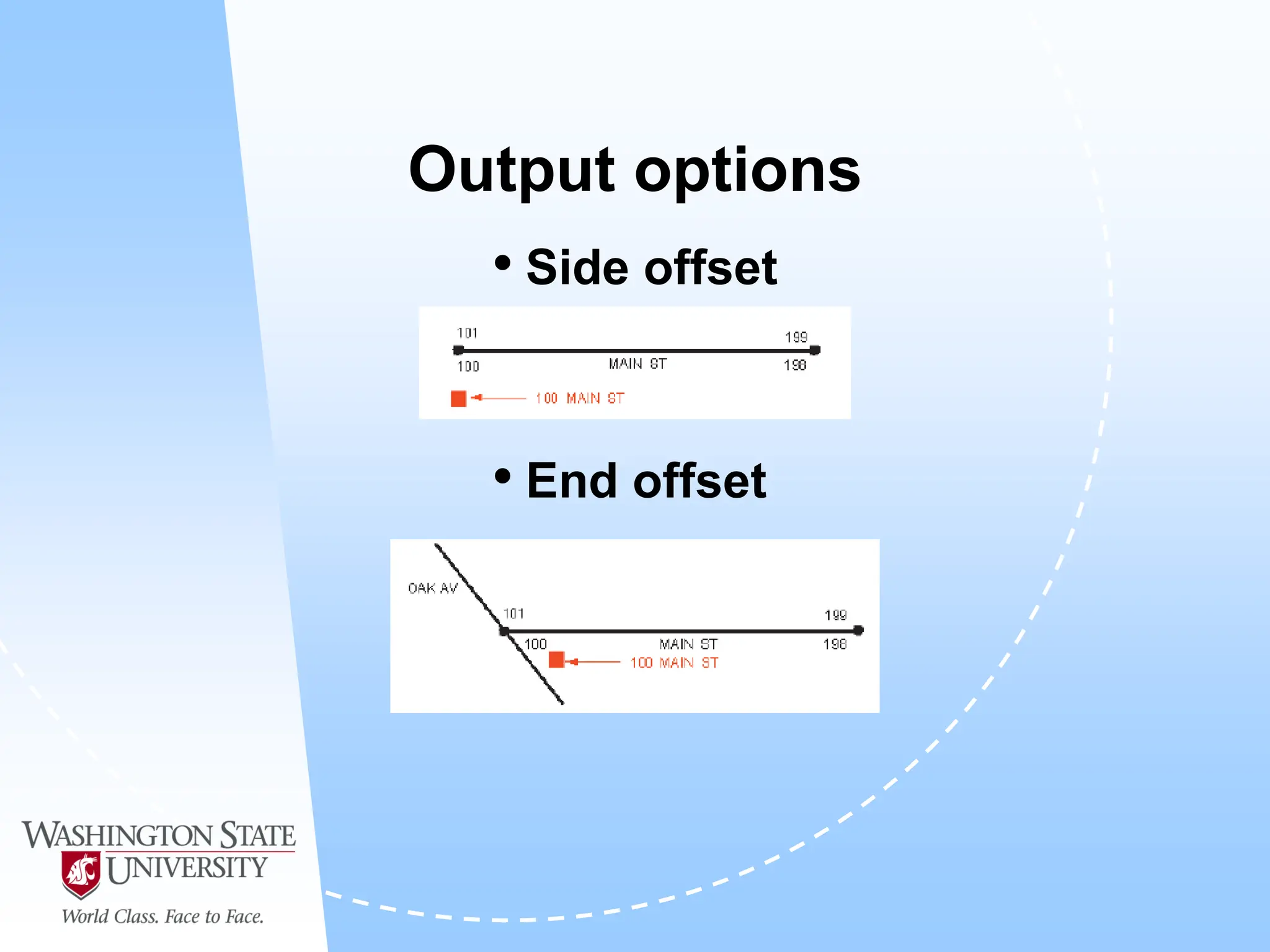
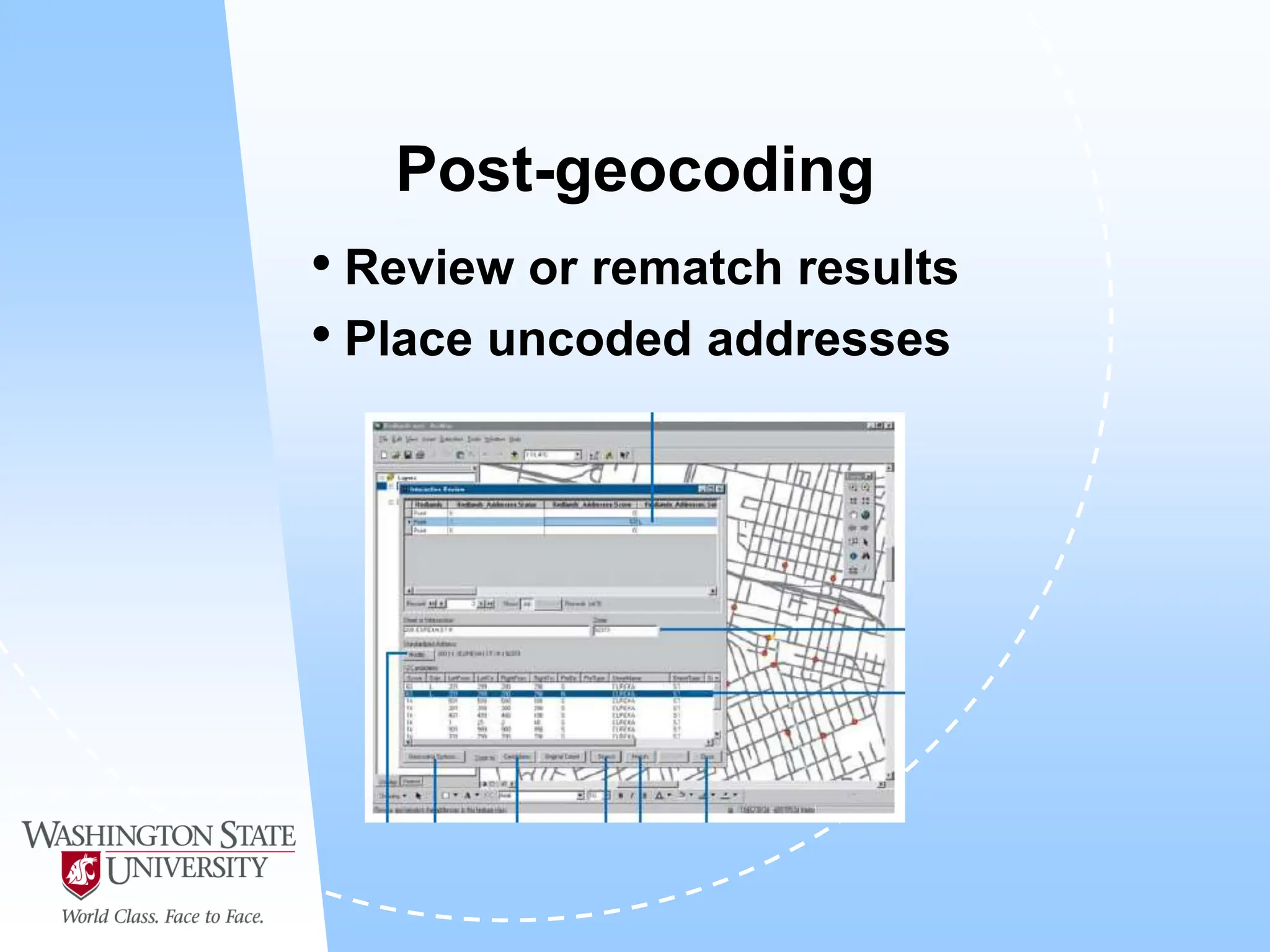
This document defines geocoding as assigning locations to addresses by comparing them to a reference layer. It discusses benefits like mapping customer locations for deliveries or expansion planning. Requirements include ArcGIS software, an address locator with rules to assign locations, and reference data covering the area. The geocoding process involves building an address locator specifying interpretation methods, relating inputs to reference data, and delivering geocoded outputs. The document provides examples of attribute and structure types that can be geocoded and discusses considerations for reference data, alternate names, and output options.