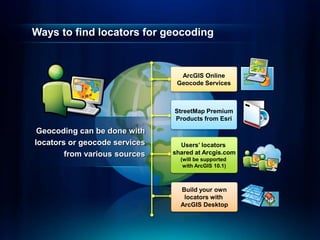
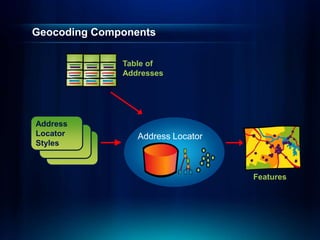
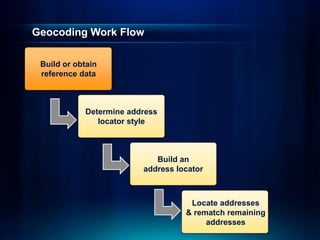
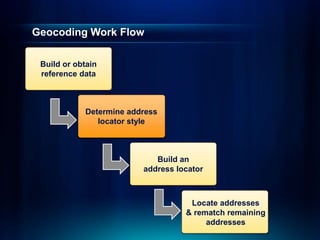
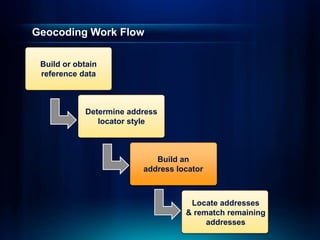
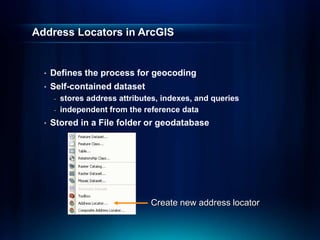
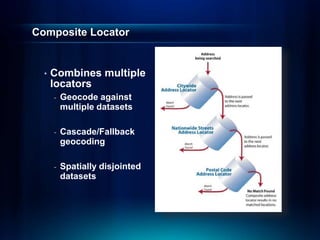
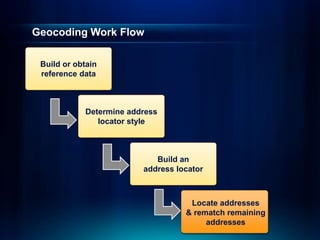
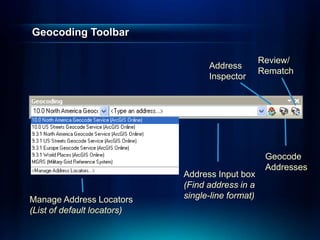
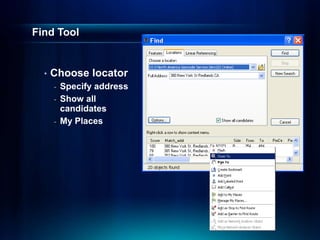
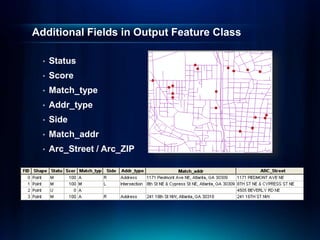
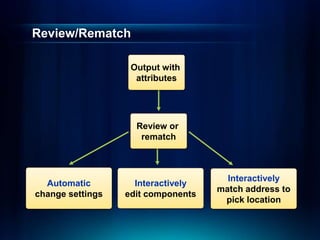
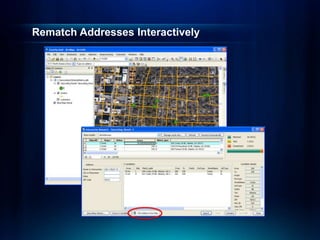
The document outlines a technical workshop at the Esri International User Conference focused on geocoding, including its definition, components, and workflow for transforming location descriptions into map locations. Key topics include developing address locators, utilizing reference data, and various methods for geocoding such as batch and interactive processes. Additionally, it offers resources for further learning and highlights related sessions at the conference.