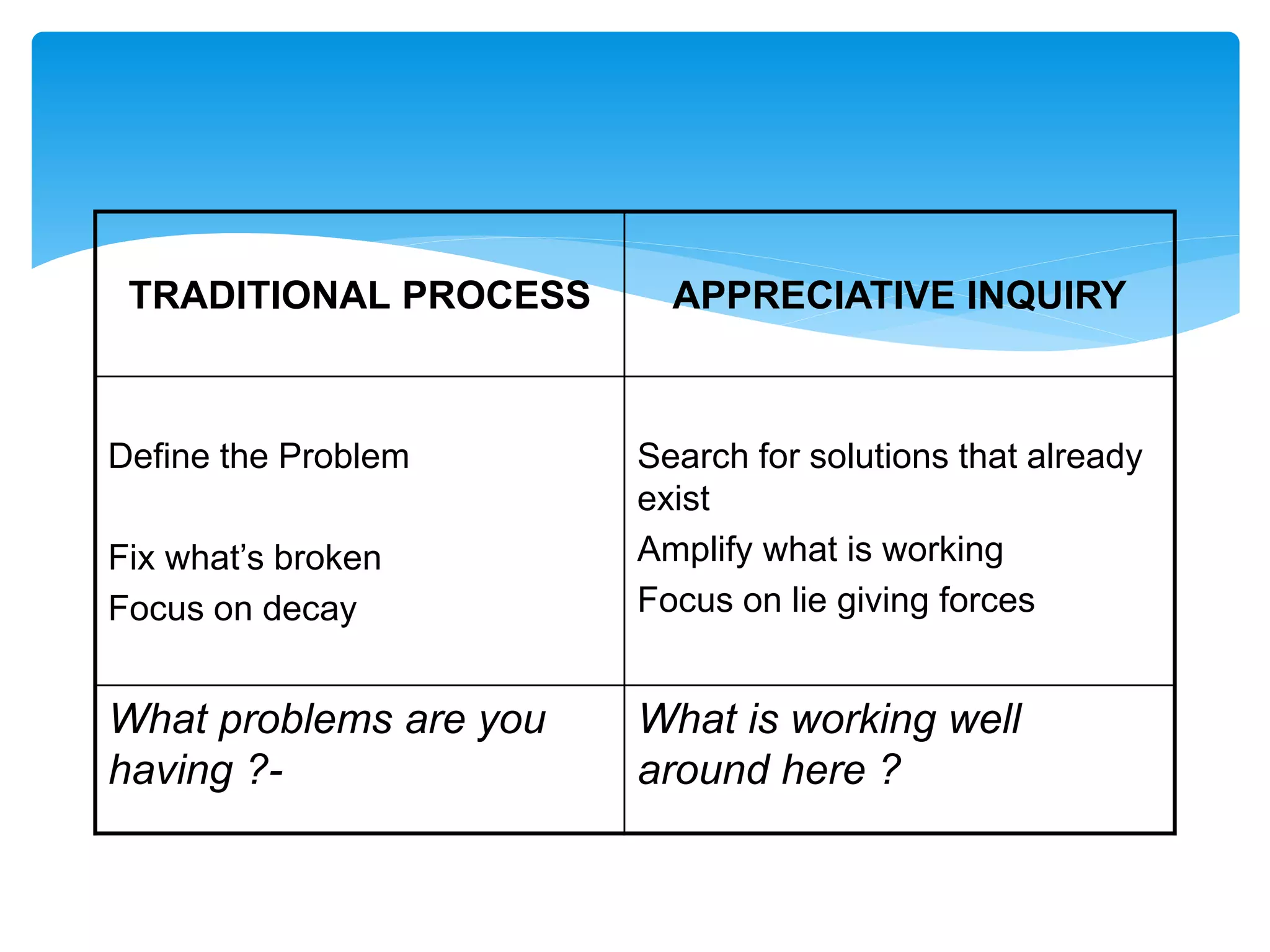
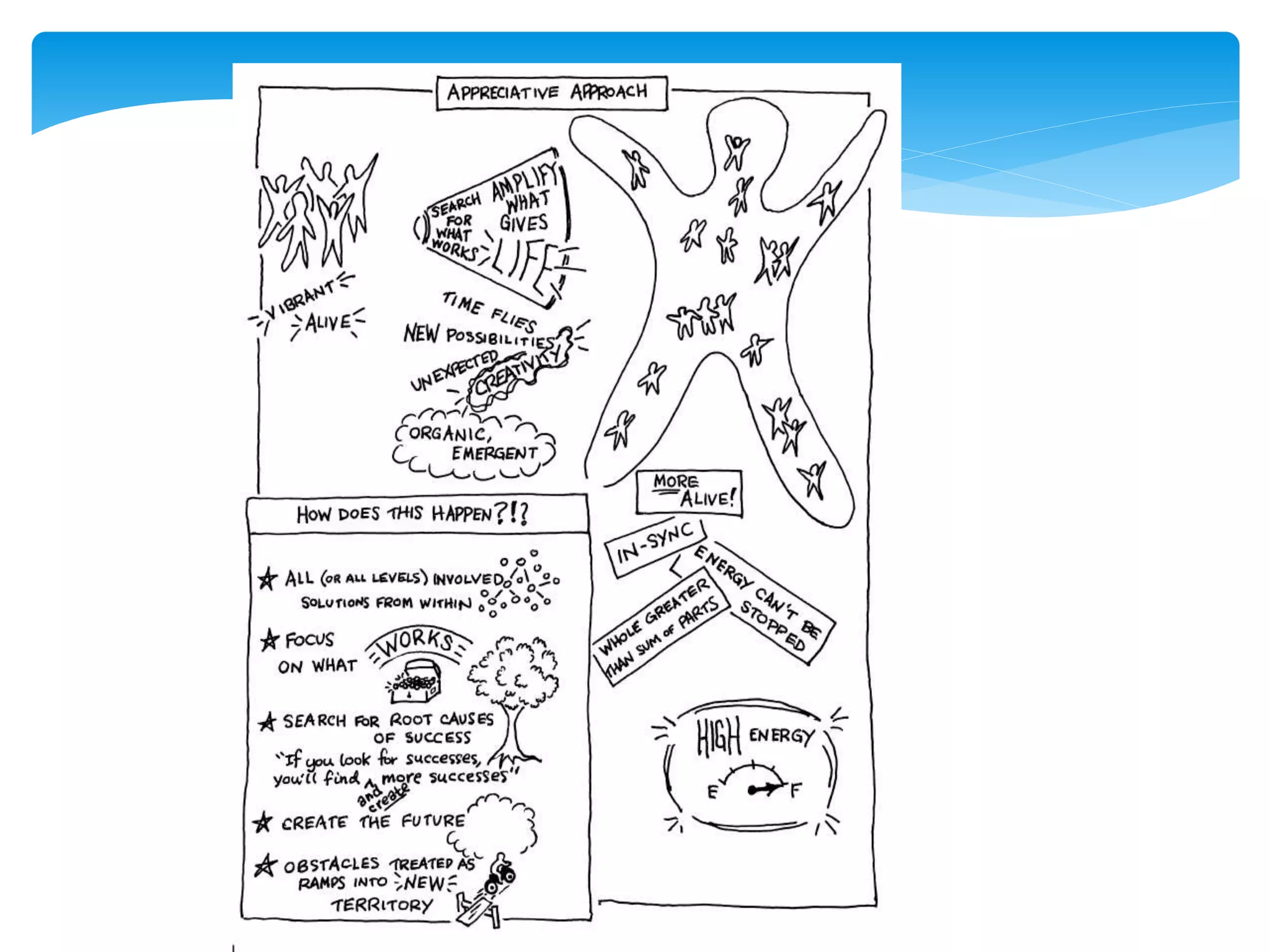
Appreciative Inquiry is a new approach to organizational change that focuses on amplifying an organization's strengths rather than fixing its problems. It involves identifying what is already working well through collaborative dialogue. The conversations uncover successful experiences and positive aspects to build a shared vision of the organization's future. Rather than examining what is wrong, Appreciative Inquiry concentrates on possibilities, capabilities, and assets to generate energy and enthusiasm for change.