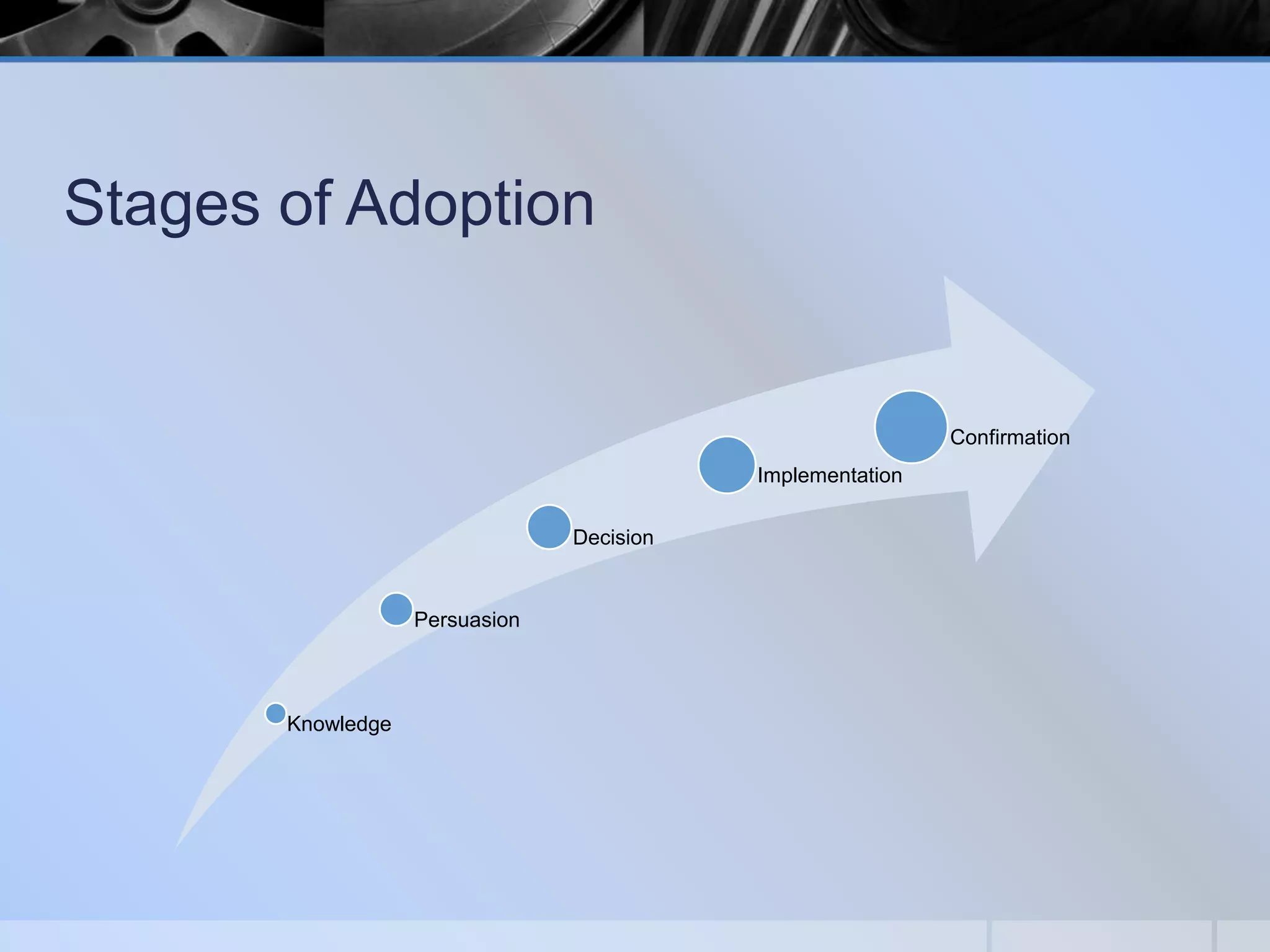
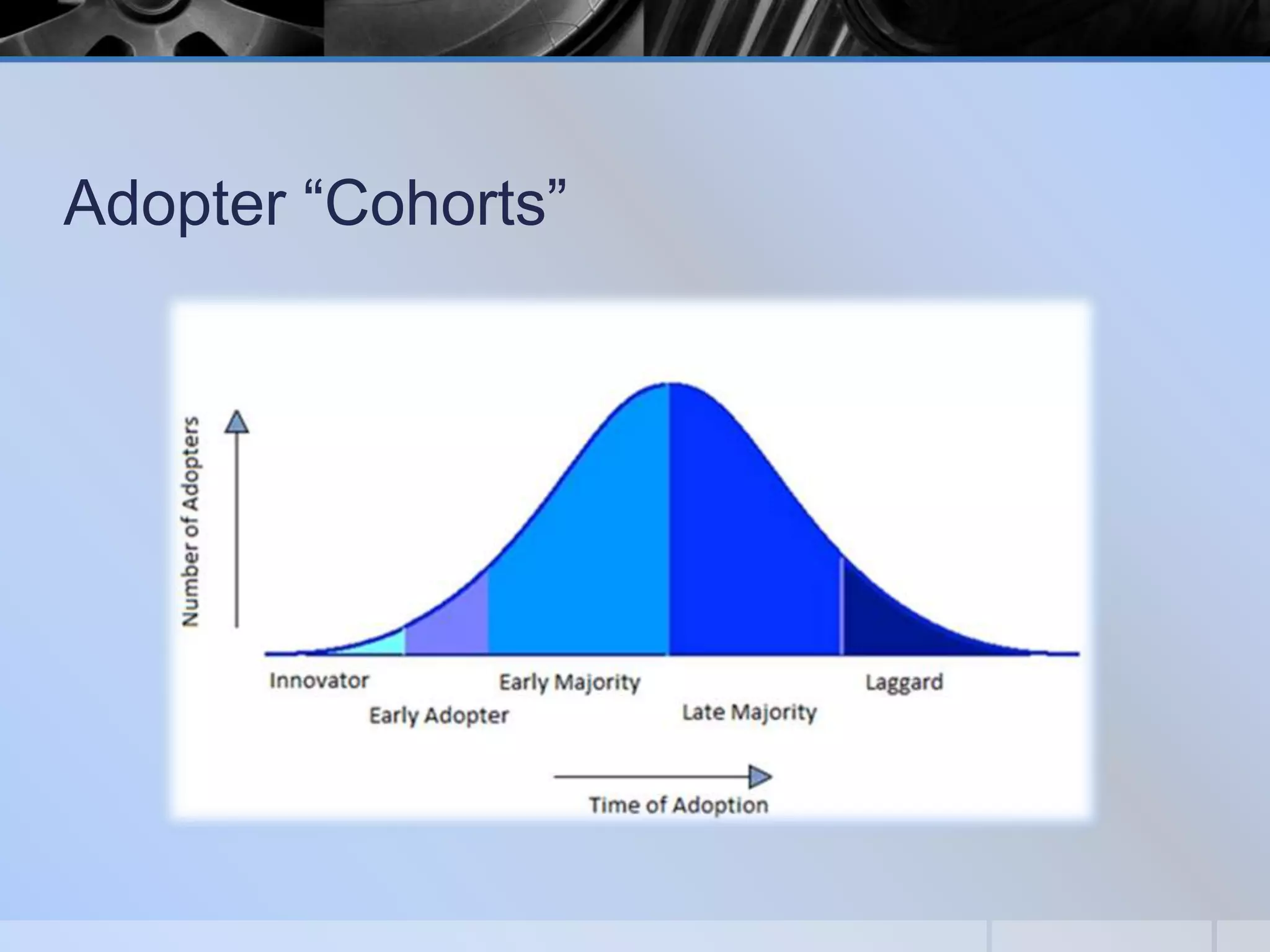
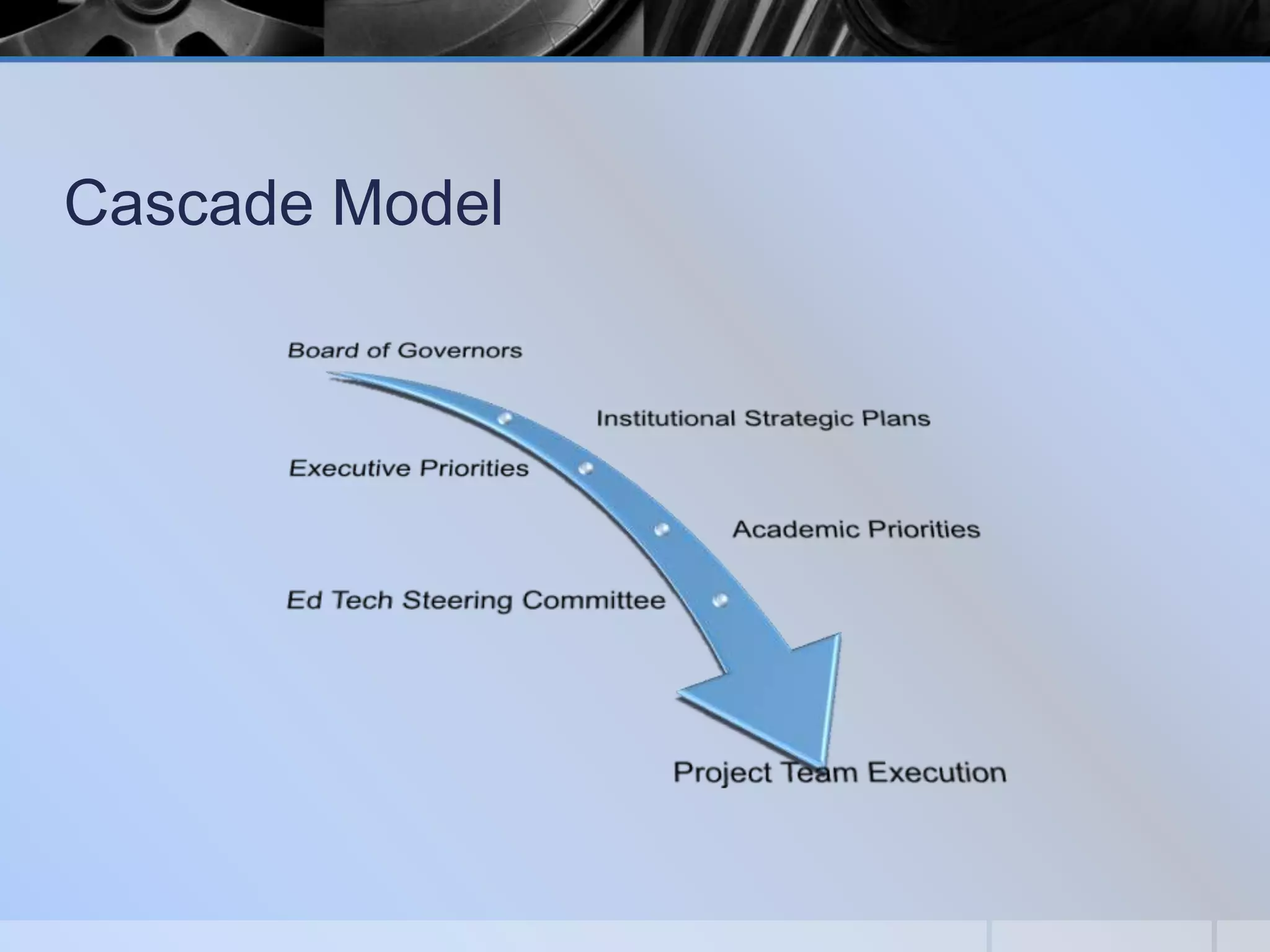
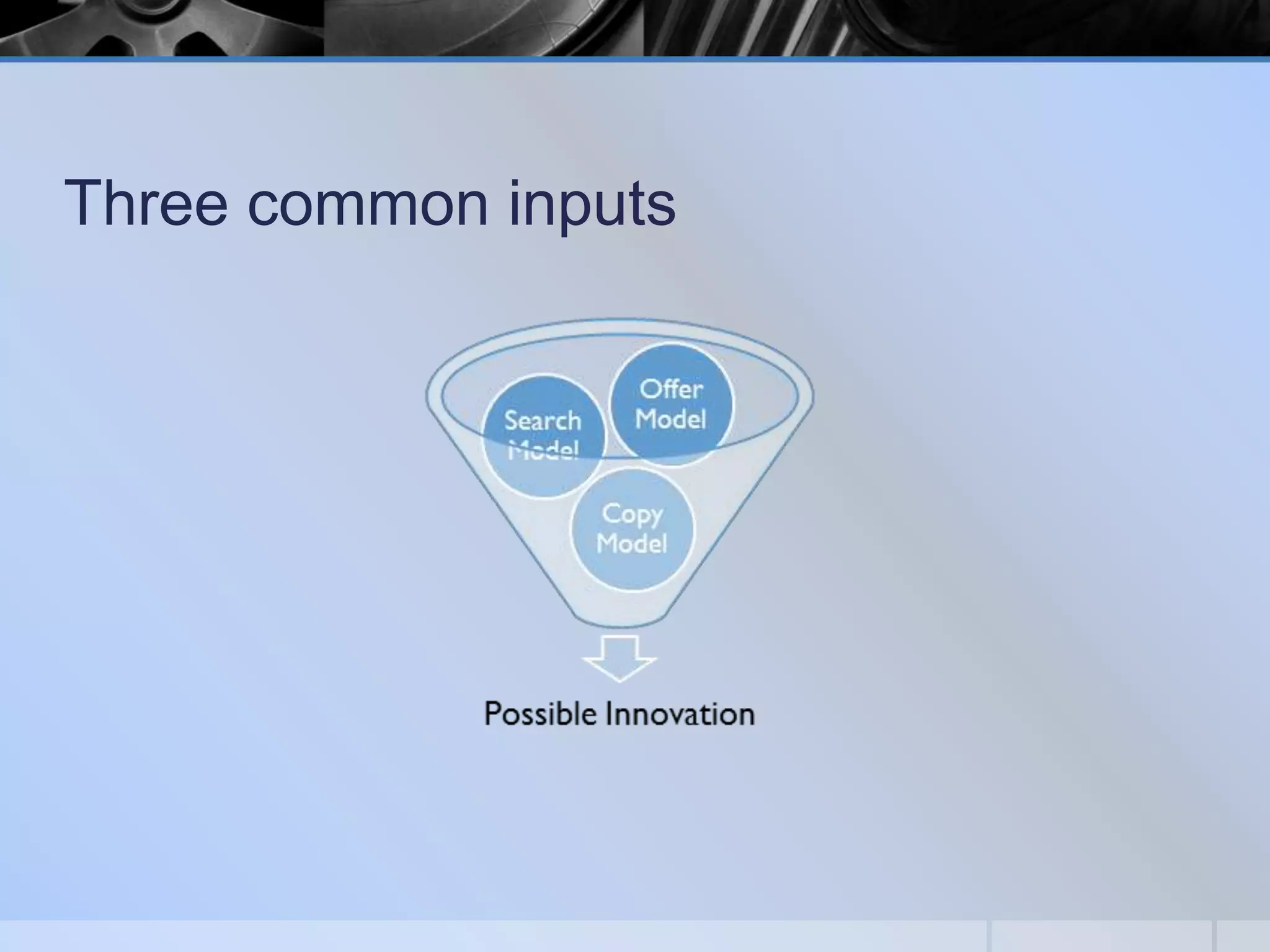
This document presents a methodology for choosing between different technology options described as "good, better, and best". It discusses stages of technology adoption including knowledge, persuasion, decision, implementation, and confirmation. It outlines factors to consider such as adopter cohorts, governance models, evaluation approaches, selection processes, implementation considerations, and lessons learned. The goal is to provide a framework to guide decision making when evaluating and adopting new educational technologies.