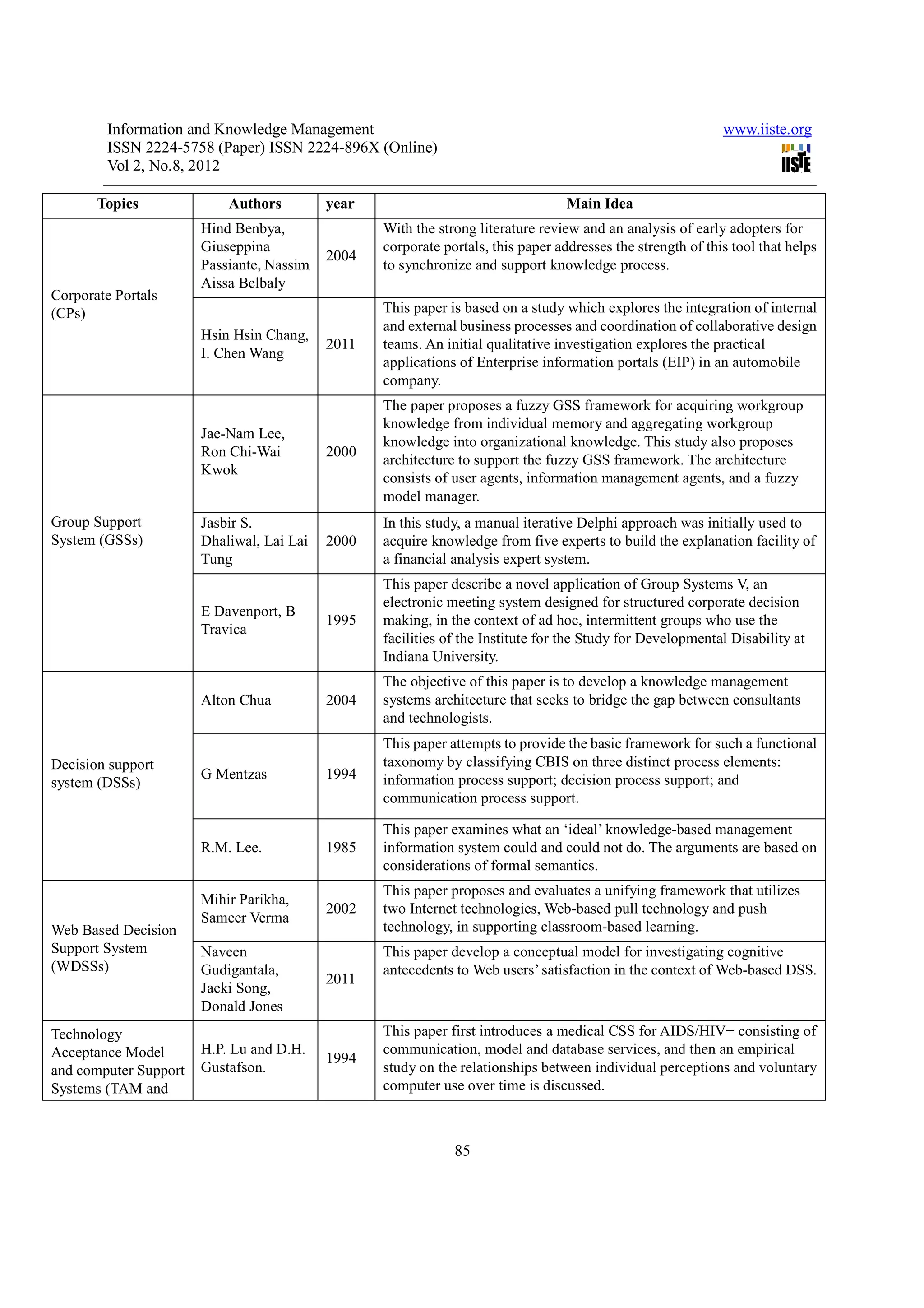
1. The document discusses various types of software support systems used for decision making, including corporate portals, decision support systems, group decision support systems, web-based decision support systems, and adaptive decision support systems.
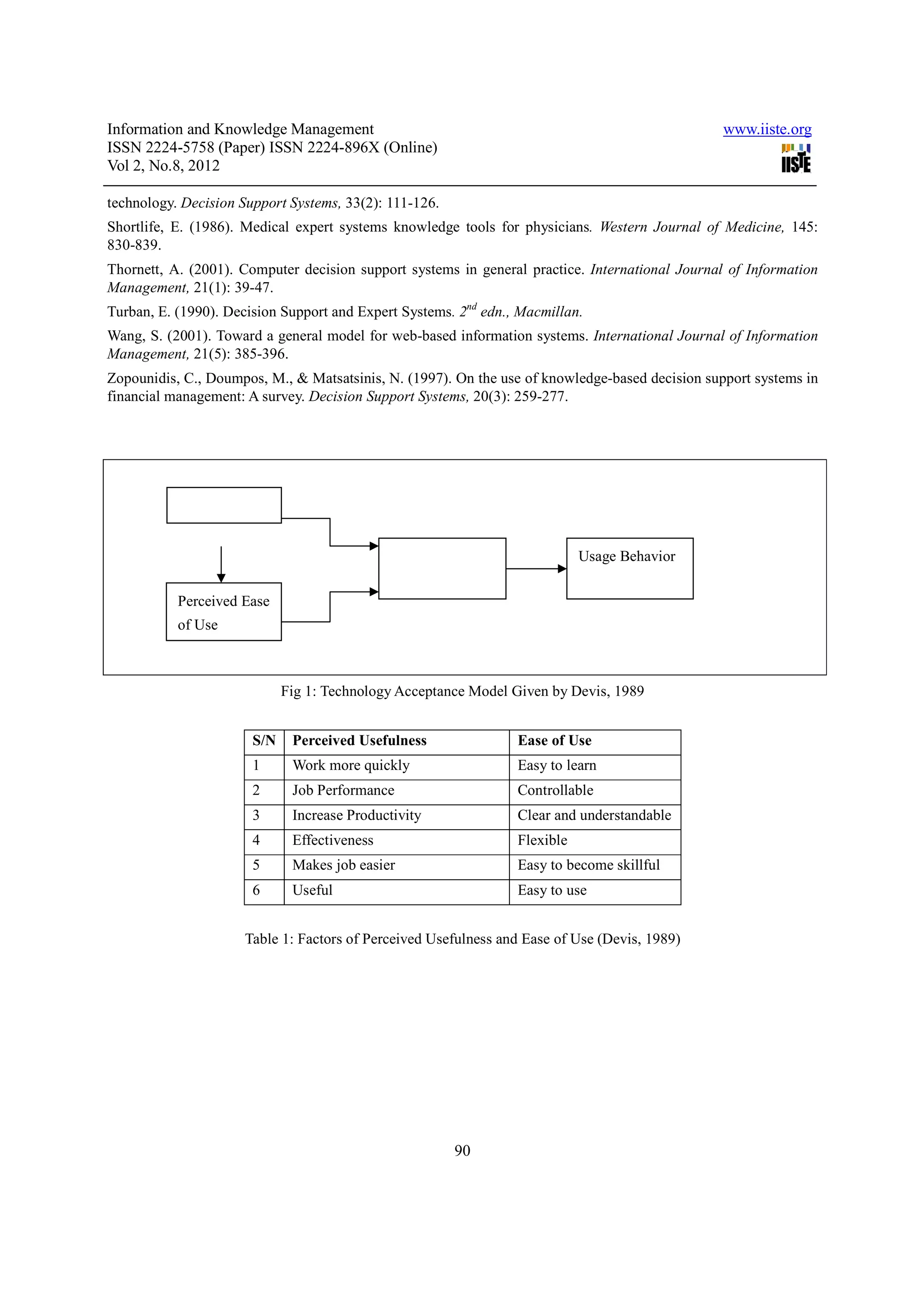
2. It also examines factors that influence the adoption of these systems, drawing from the technology acceptance model, which identifies perceived usefulness and ease of use as key determinants of whether users will adopt new technologies.
3. The document provides an overview of the evolution of these support systems and how knowledge management concepts can help organizations make more effective strategic decisions using information from internal and external sources.