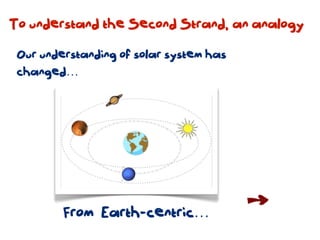
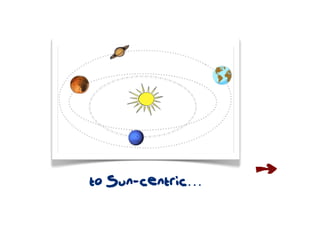
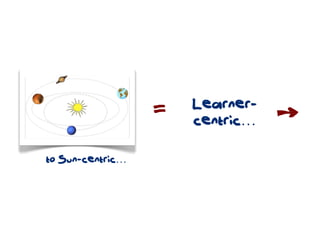
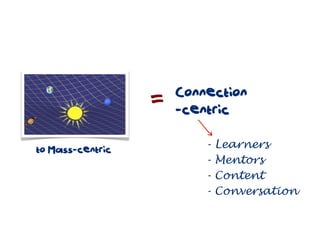
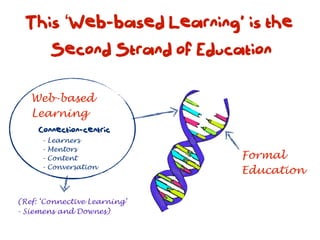
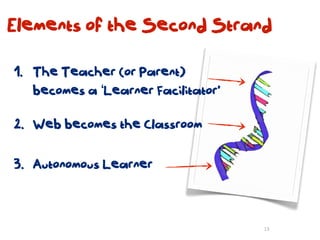
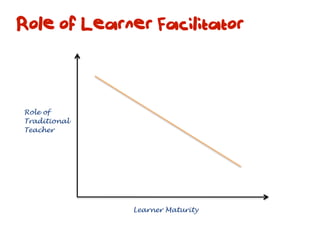
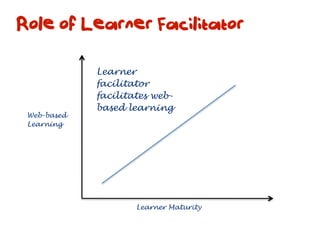
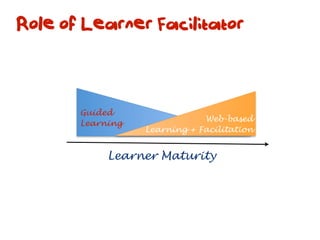
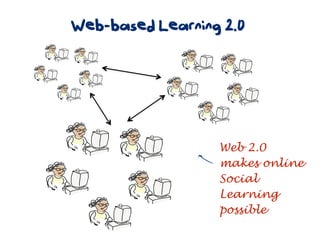
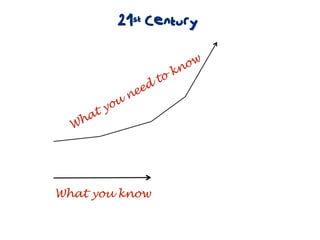
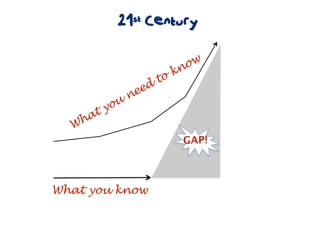
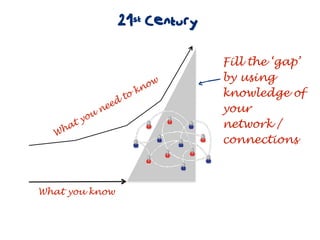
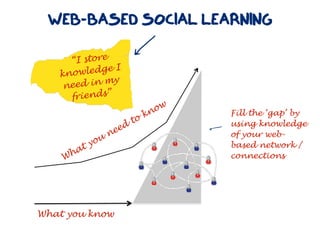
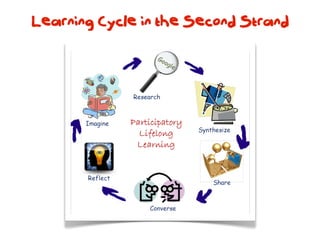
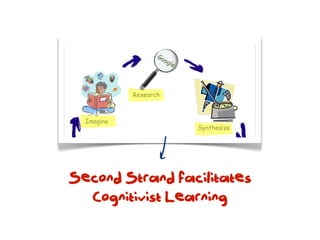
The document discusses a framework for web-based learning that draws from various learning theories and positions the teacher as a learner facilitator, the web as the classroom, and the learner as autonomous. It also outlines the roles of the learner facilitator in understanding learners, curating content, bringing coherence, and co-exploring with learners based on cognitive, social, and constructivist learning theories. The framework aims to integrate formal education with informal, connection-centric web-based learning.