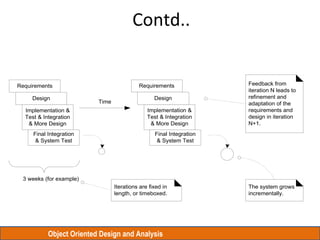
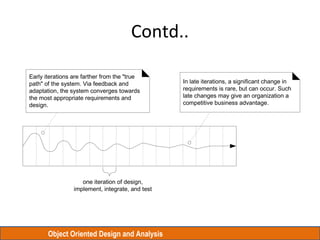
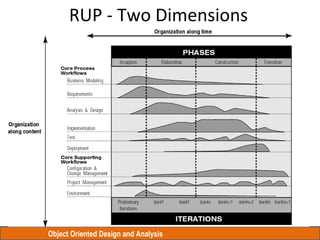
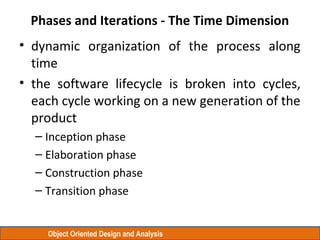
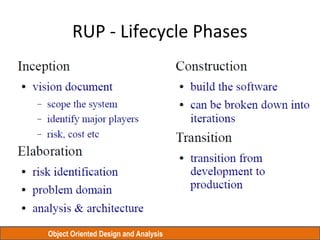
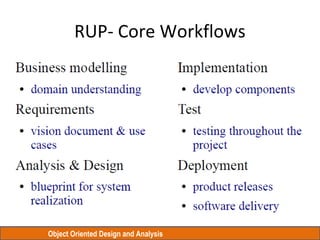
The document discusses Object Oriented Design and Analysis using the Rational Unified Process (RUP). RUP is an iterative software development process framework for building object-oriented systems. It is comprised of four phases - Inception, Elaboration, Construction, and Transition. Within each phase are iterative cycles of requirements analysis, design, implementation, testing and feedback. The goal is to produce high-quality software that meets user needs within schedule and budget.