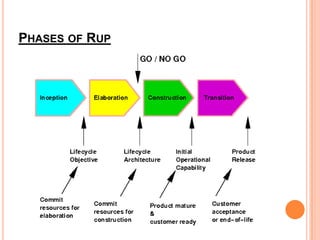
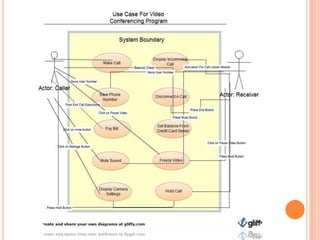
The document proposes adding video calling capabilities to iPads by following the Rational Unified Process (RUP) model of software development. RUP includes four phases - Inception, Elaboration, Construction, and Transition. In the Inception phase, requirements and scope are understood. Elaboration involves use case analysis and modeling. Construction focuses on implementation. Transition delivers the working system and transfers control to a maintenance team. The document outlines each RUP phase and notes pros like improved risk management and cons like complexity. It concludes the presented software development phases are commonly used in industry.