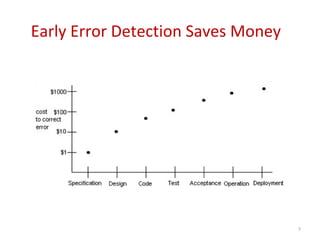
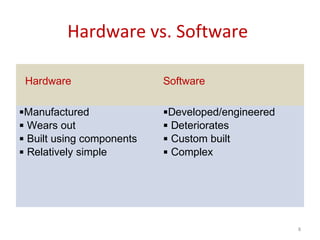
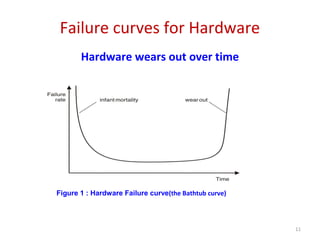
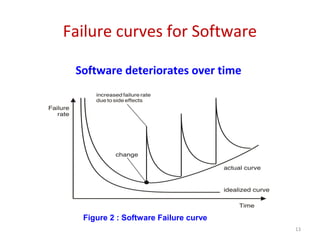
Software engineering is concerned with all aspects of software production. It aims to develop software using systematic and disciplined approaches to reduce errors and costs. Some key challenges in software development are its high cost, difficulty delivering on time, and producing low quality software. Software engineering methods strive to address these challenges and produce software with attributes like maintainability, dependability, efficiency, usability and acceptability.