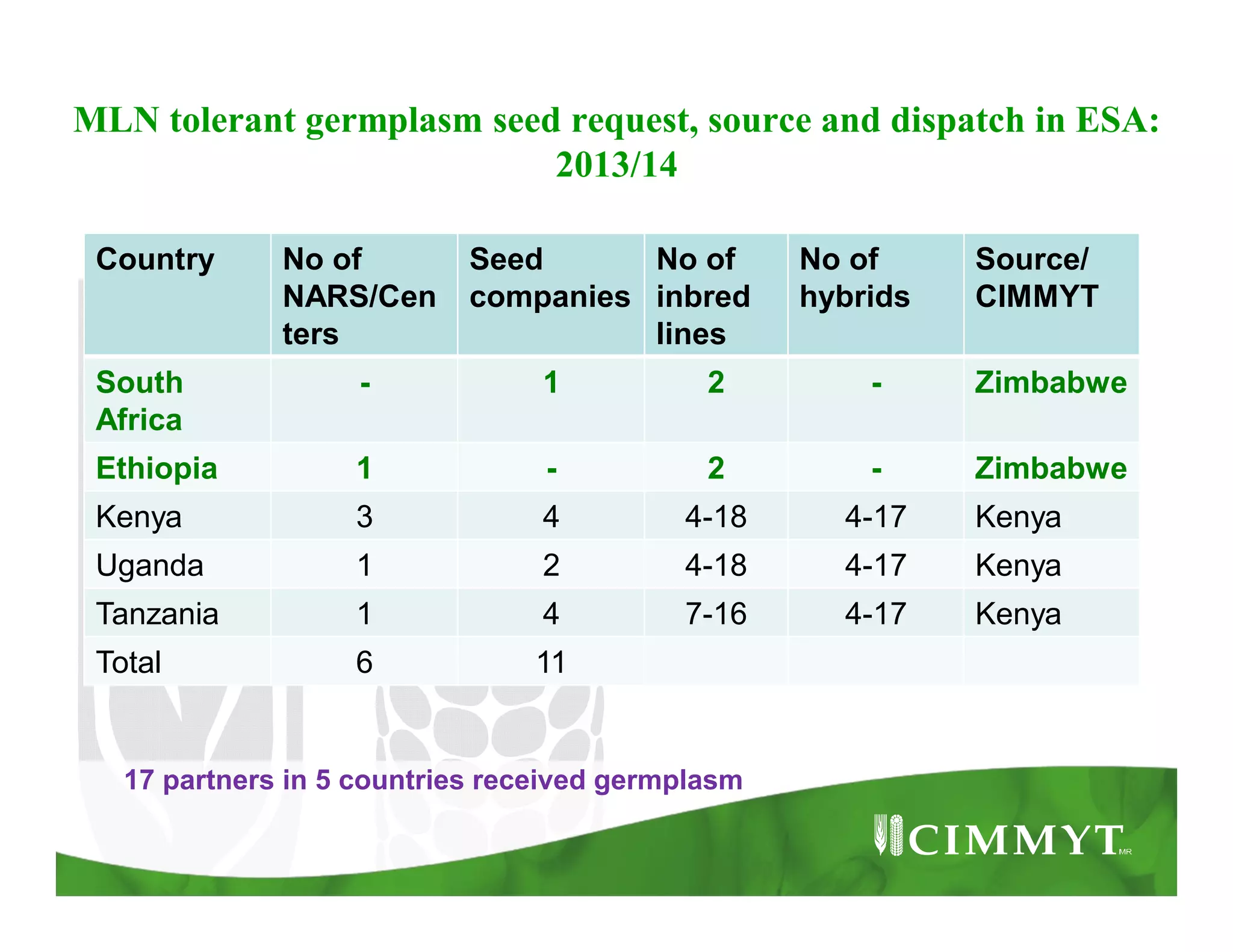
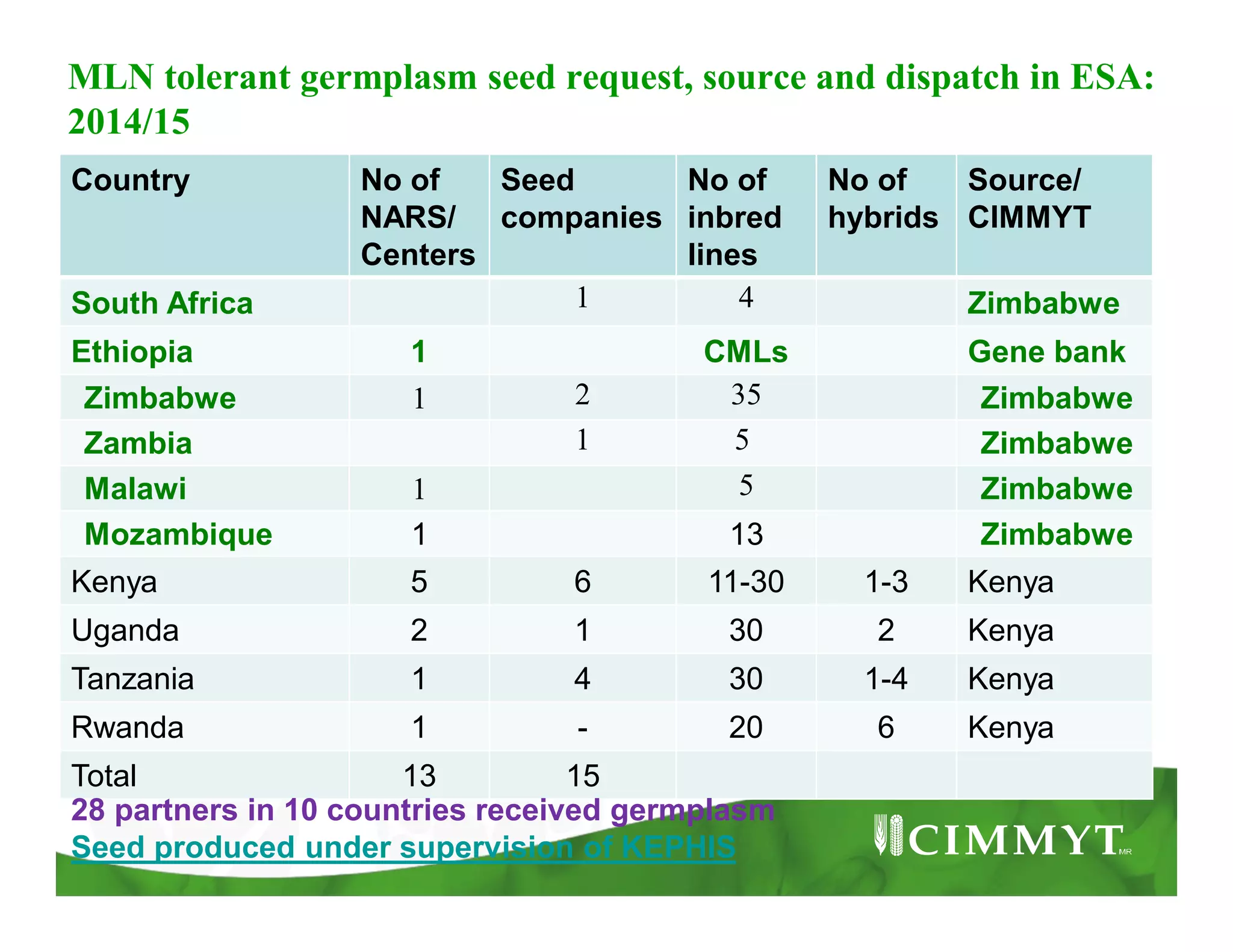
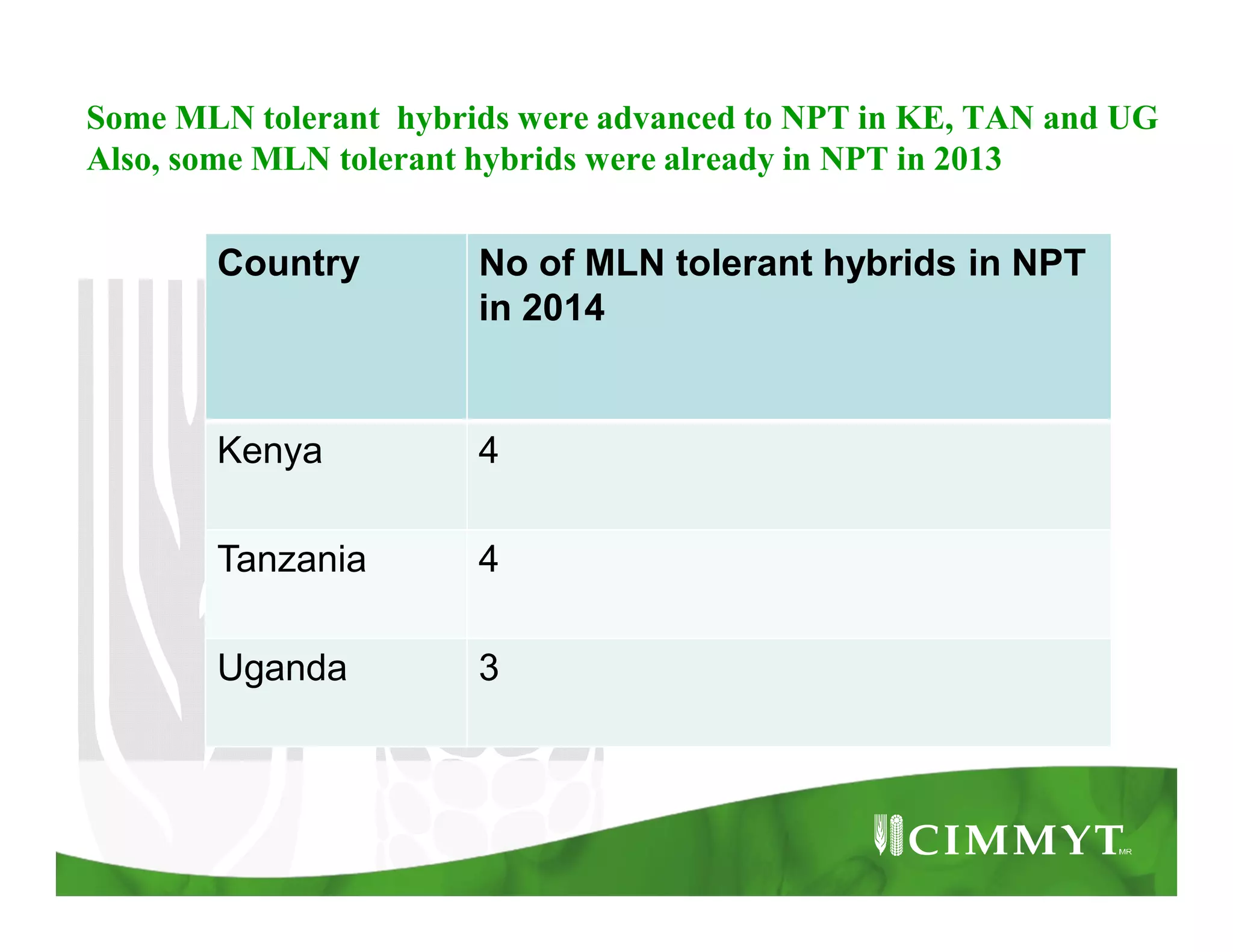
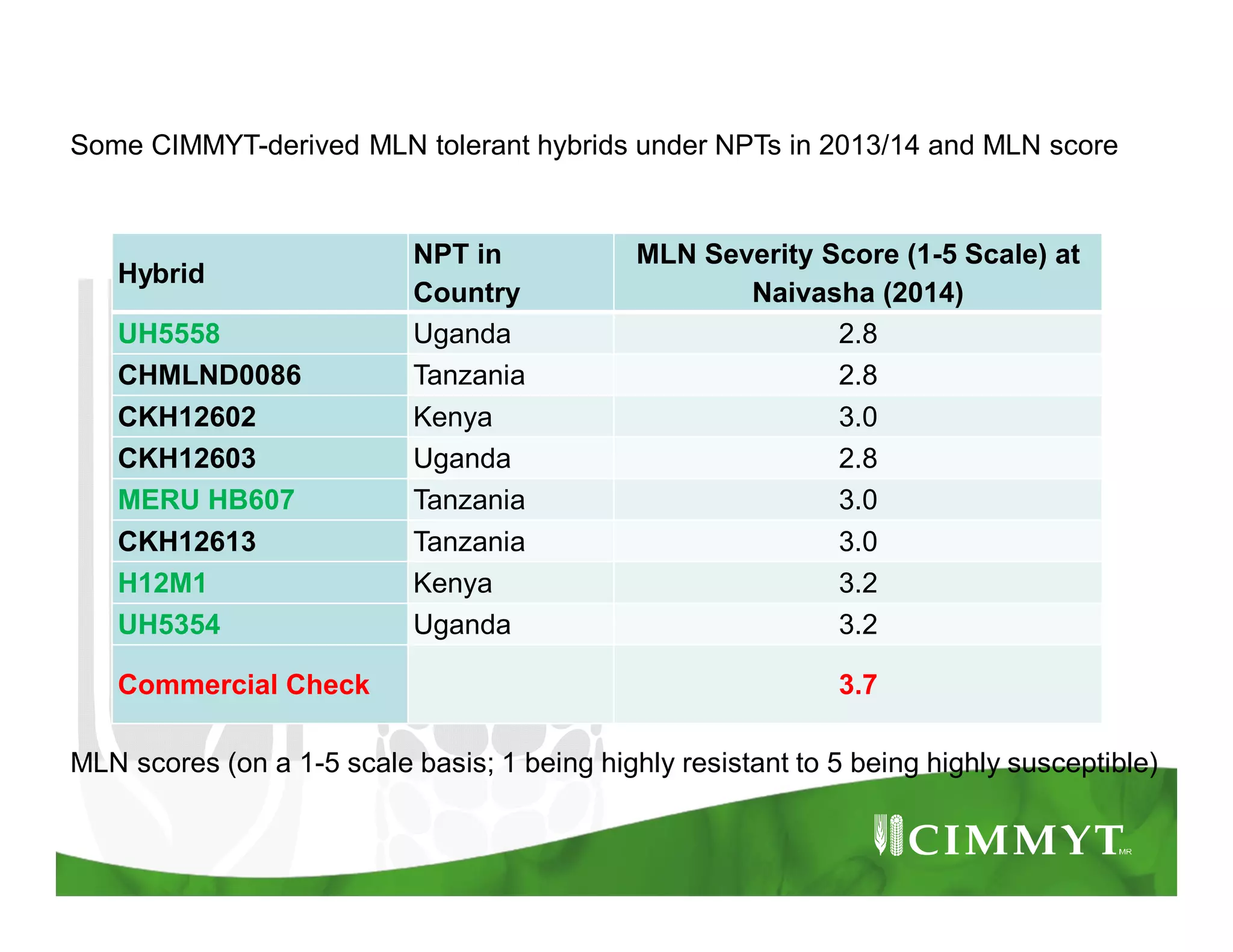
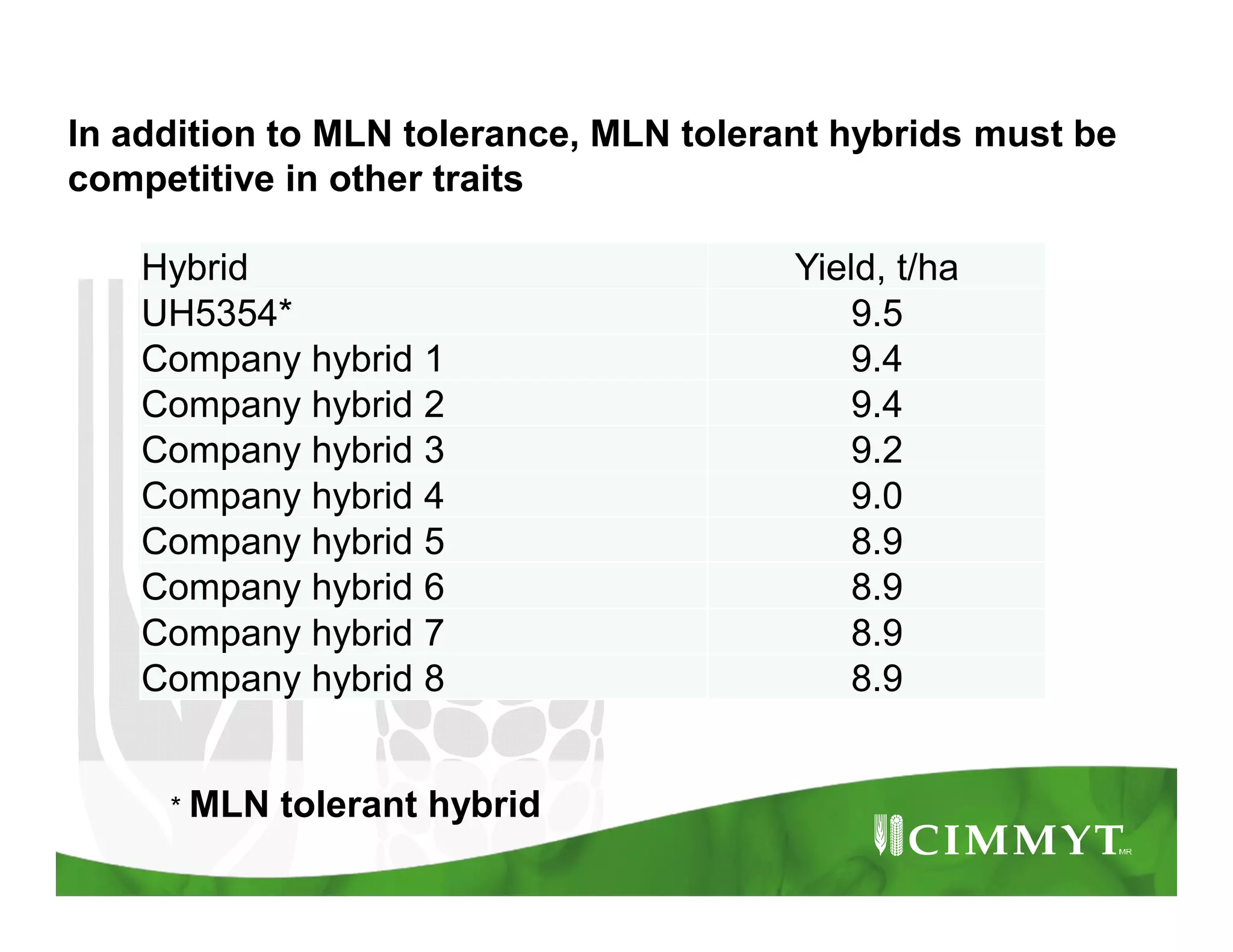
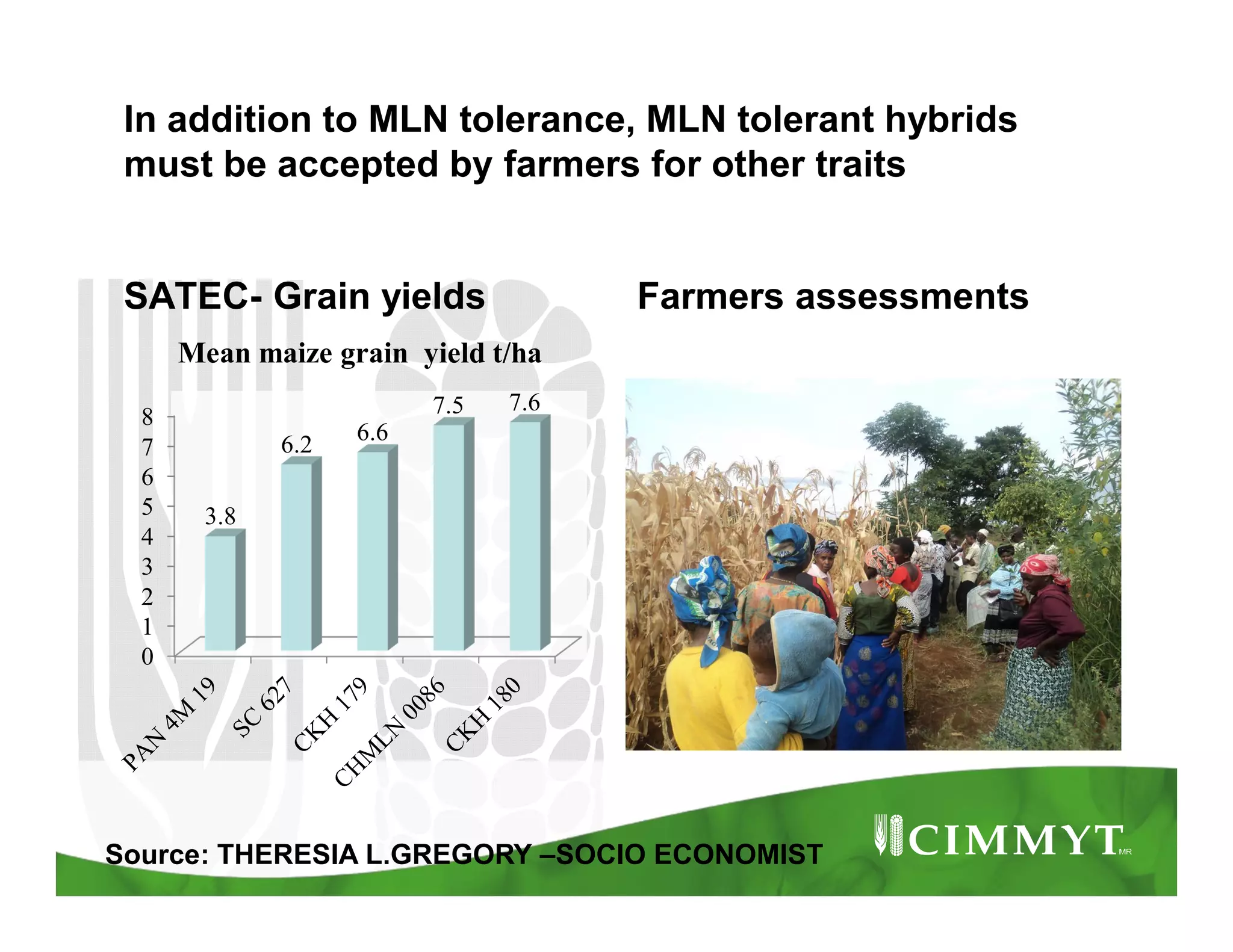
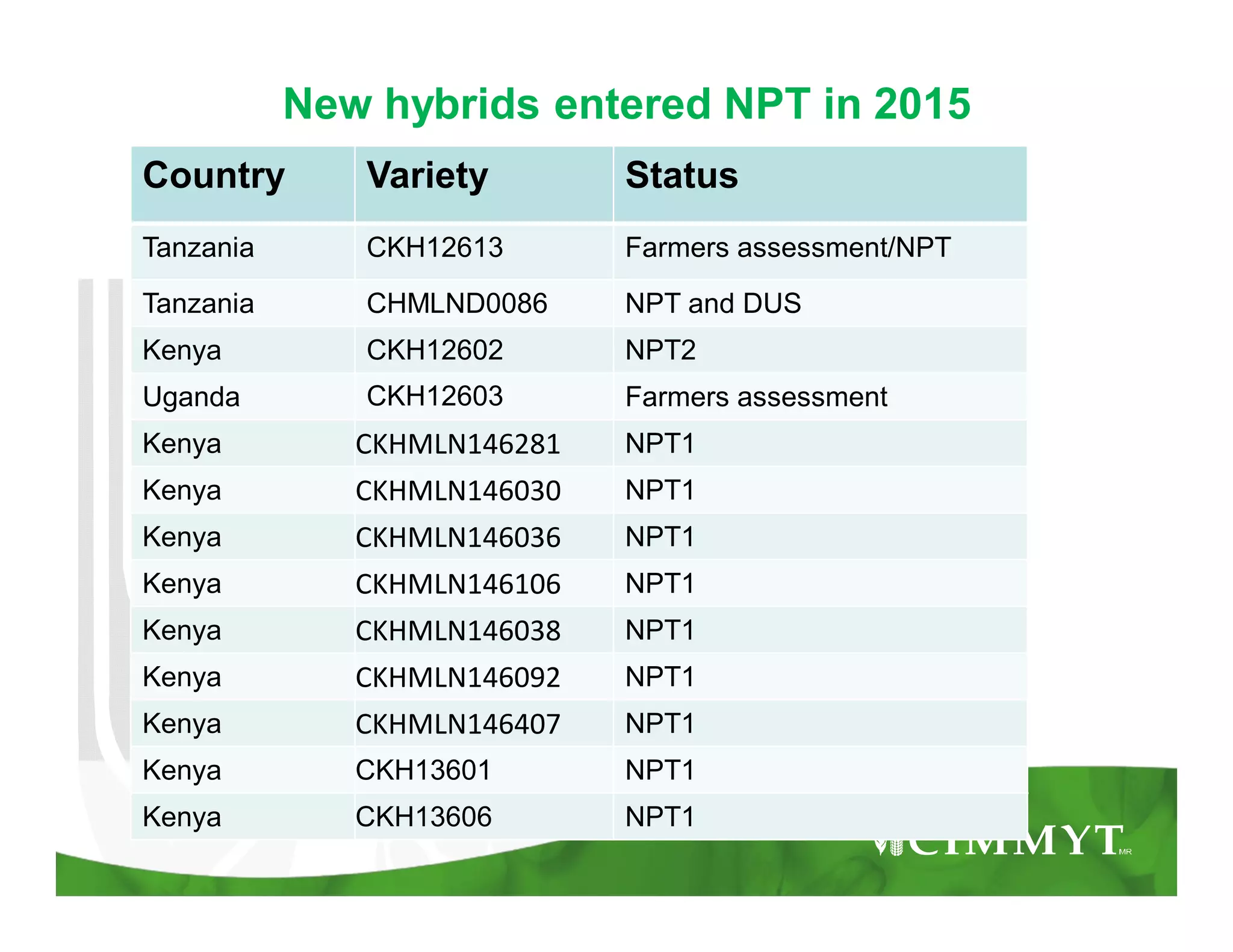
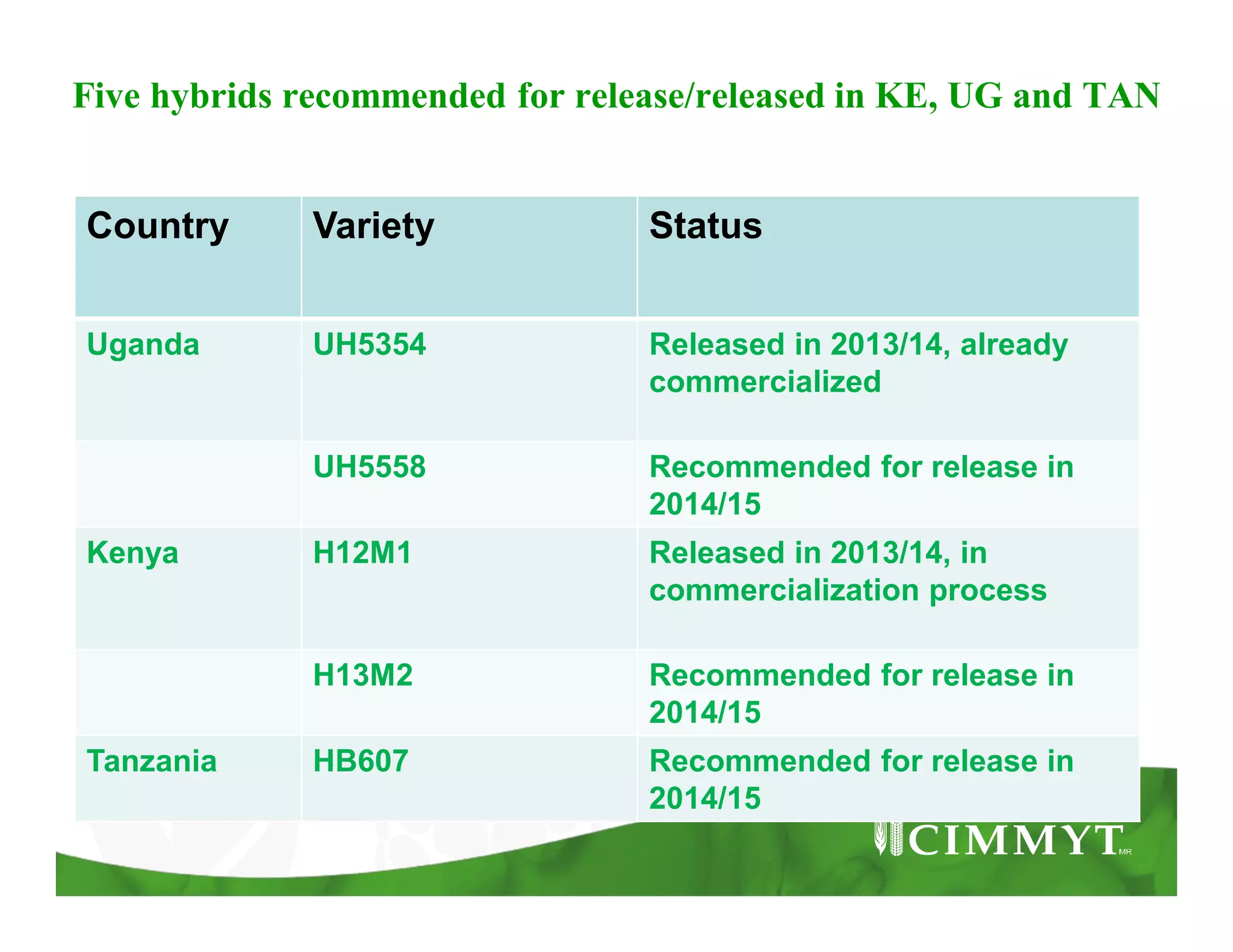
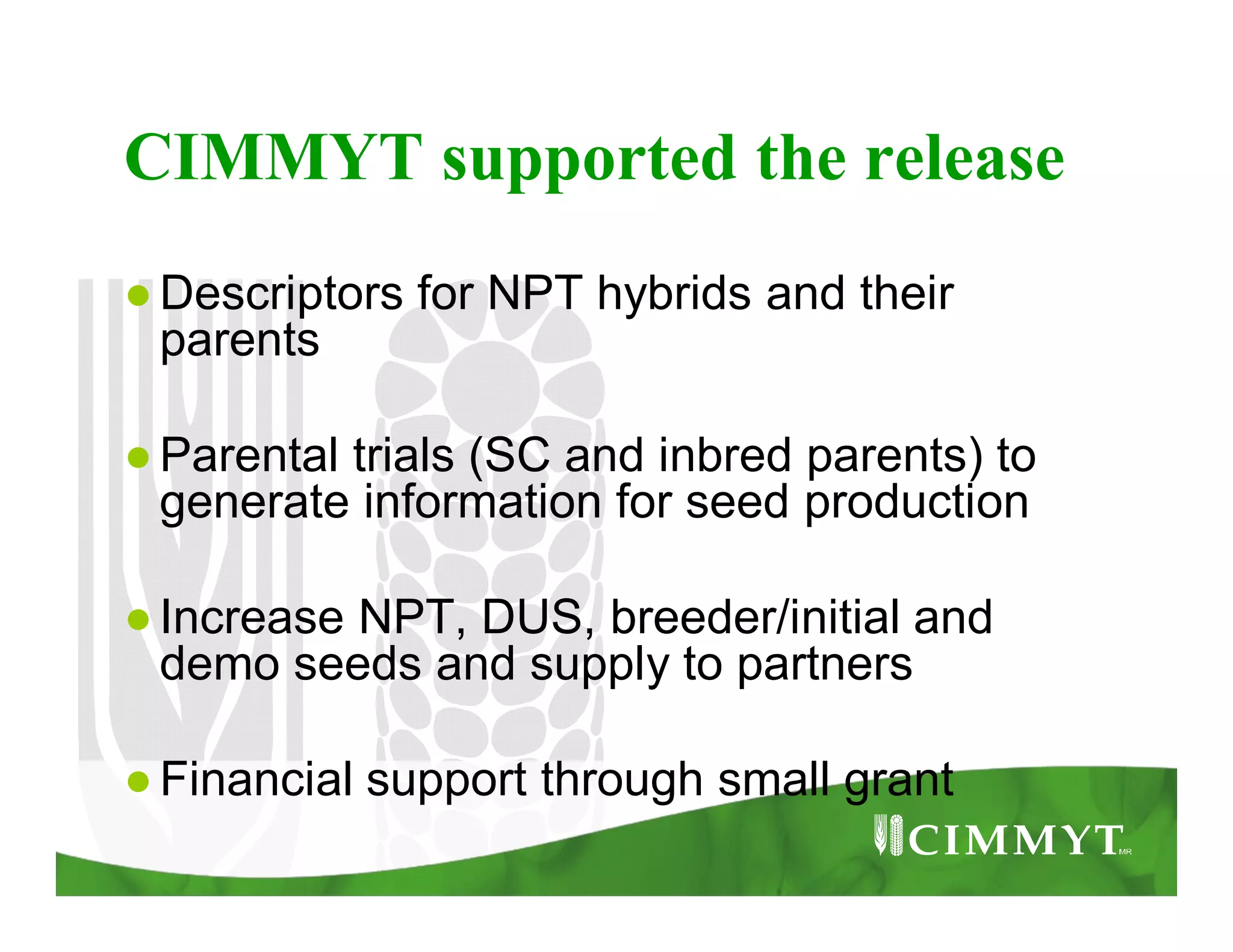
This document provides an update on CIMMYT's maize products that are tolerant to maize lethal necrosis (MLN). It discusses MLN tolerant germplasm that has been distributed to various countries in East and Southern Africa. Some MLN tolerant hybrids have entered national performance trials in Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda and have shown moderate tolerance to MLN. Five hybrids have been recommended for release or already released in Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania. Challenges remain in developing parents that are all resistant to MLN and in finding MLN-free areas for seed production. Overall, progress is being made in developing and distributing MLN tolerant maize varieties and hybrids to countries affected by the disease