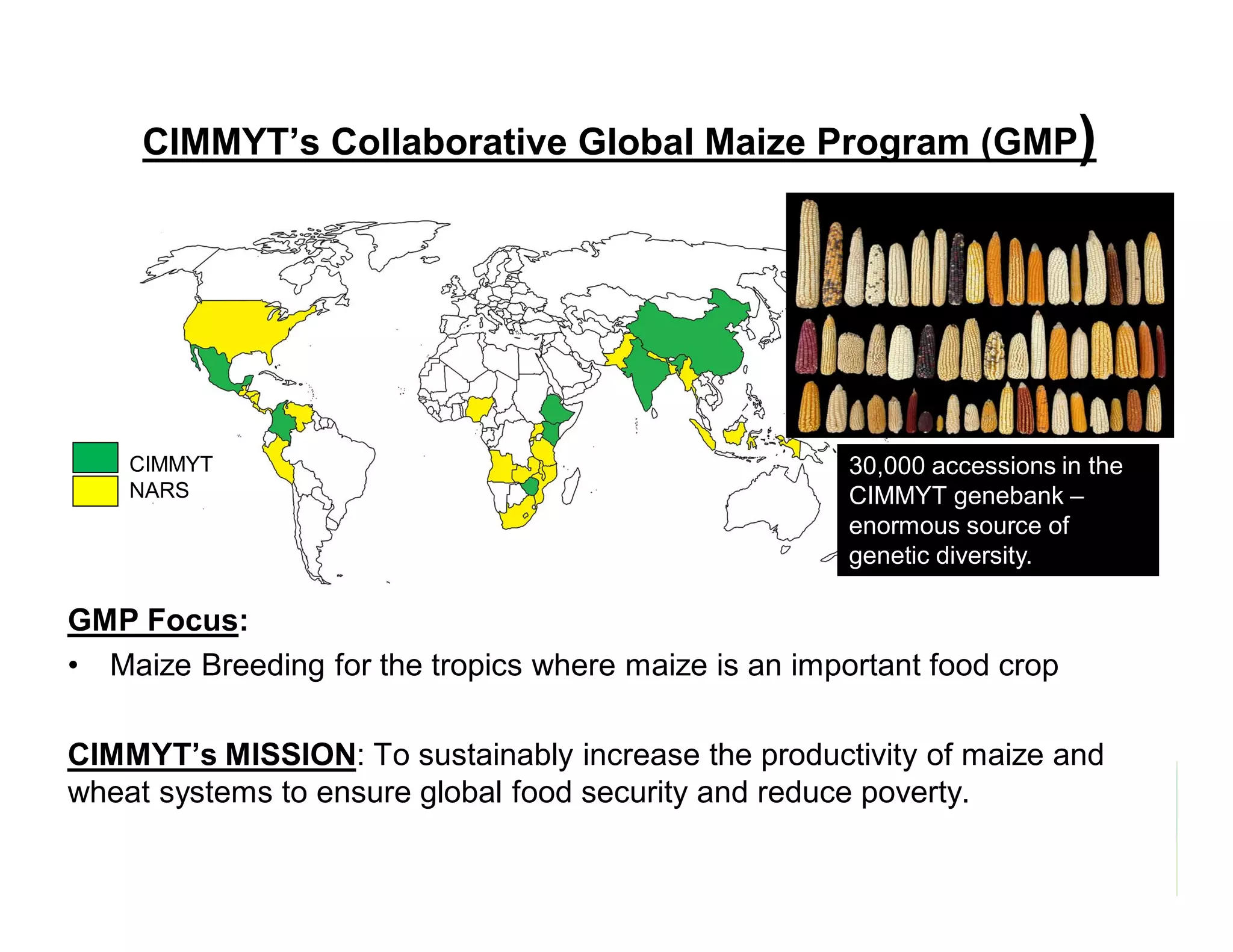
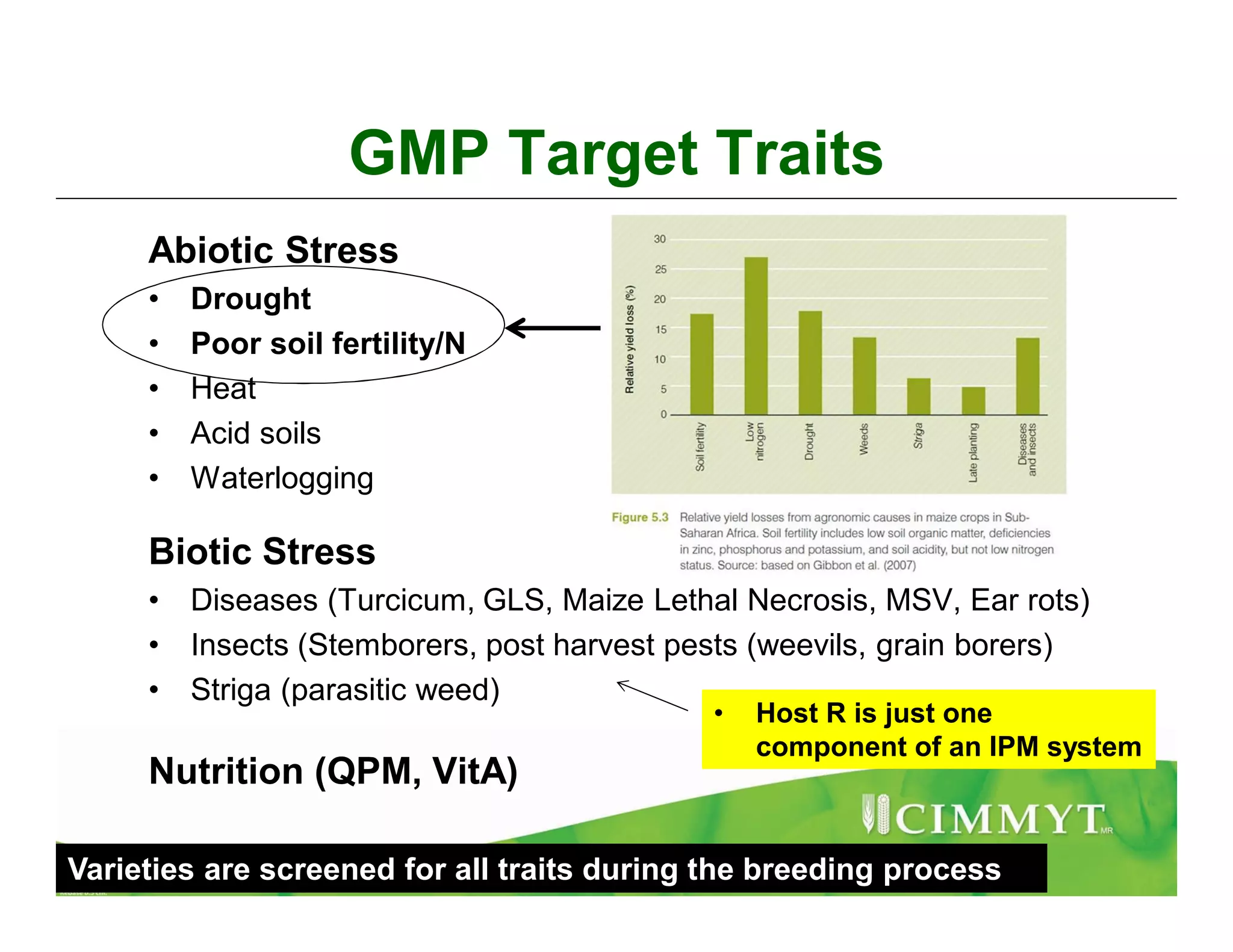
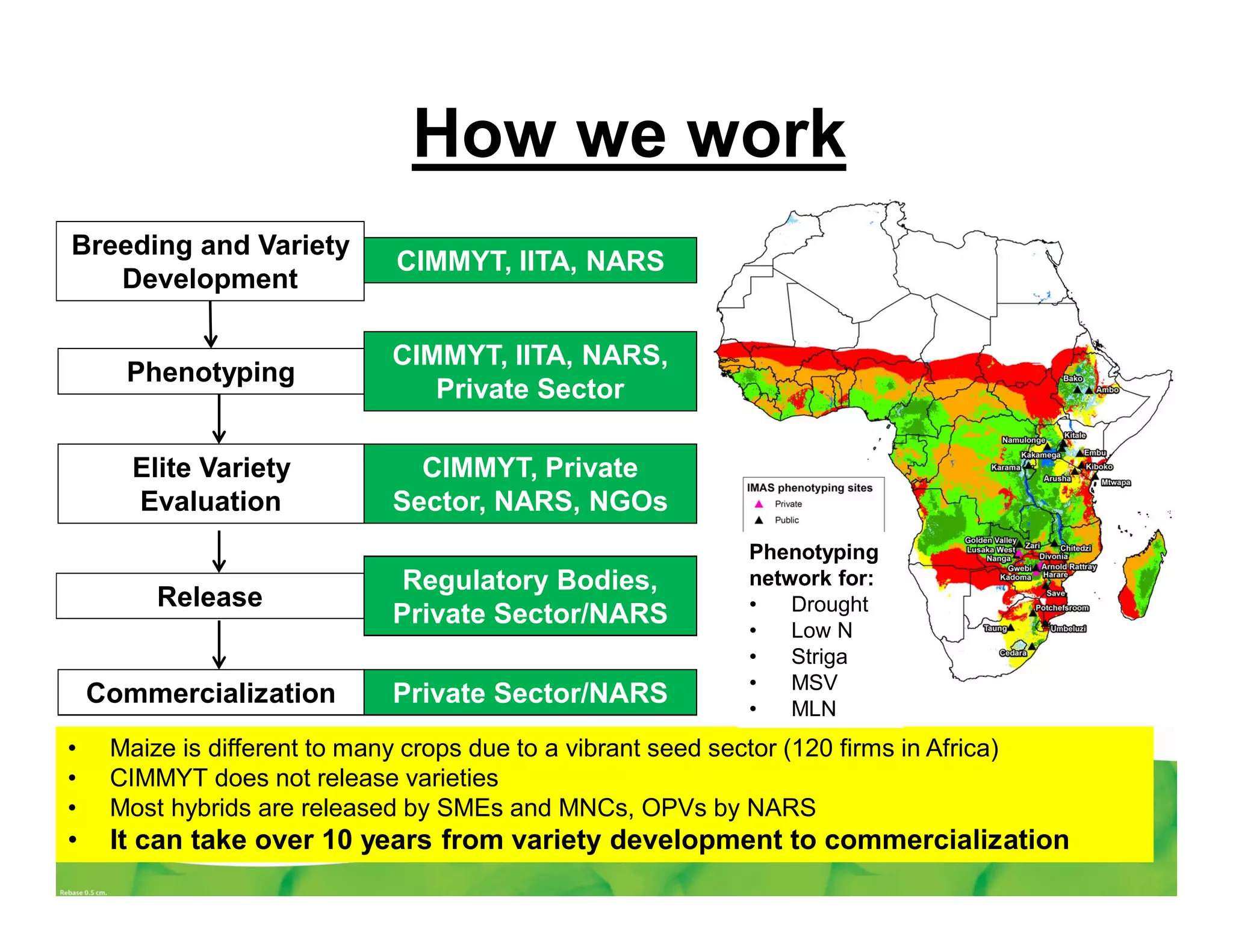
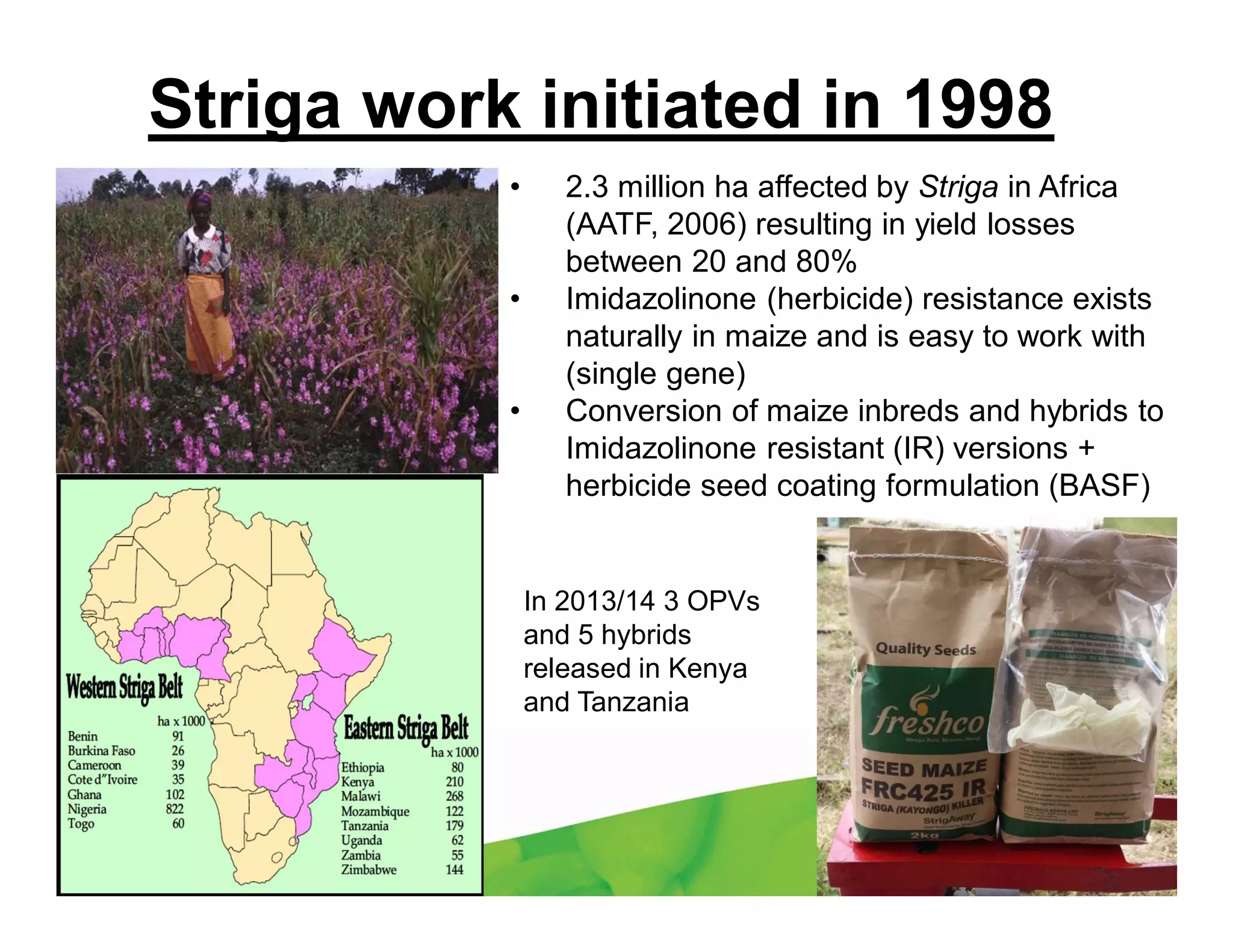
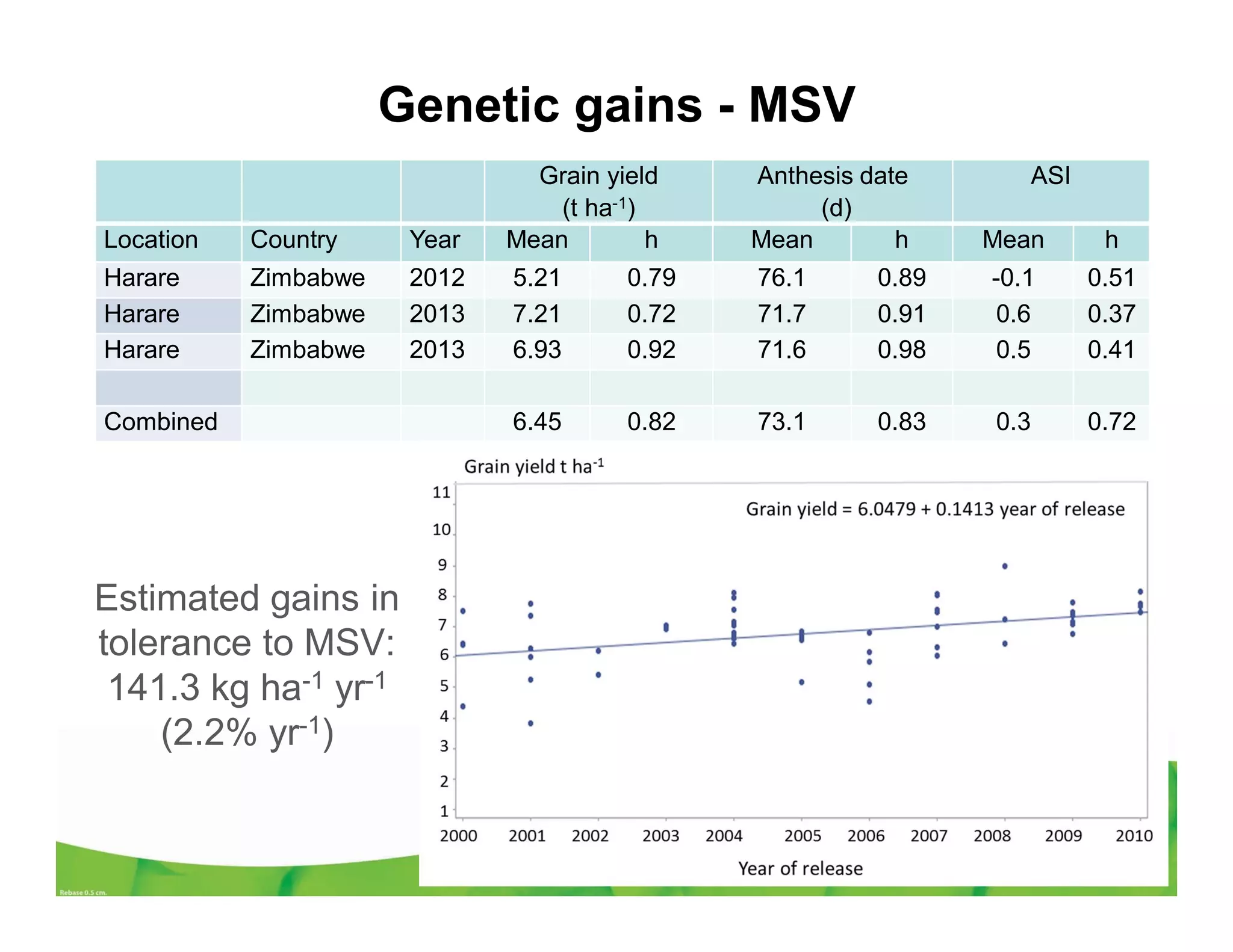
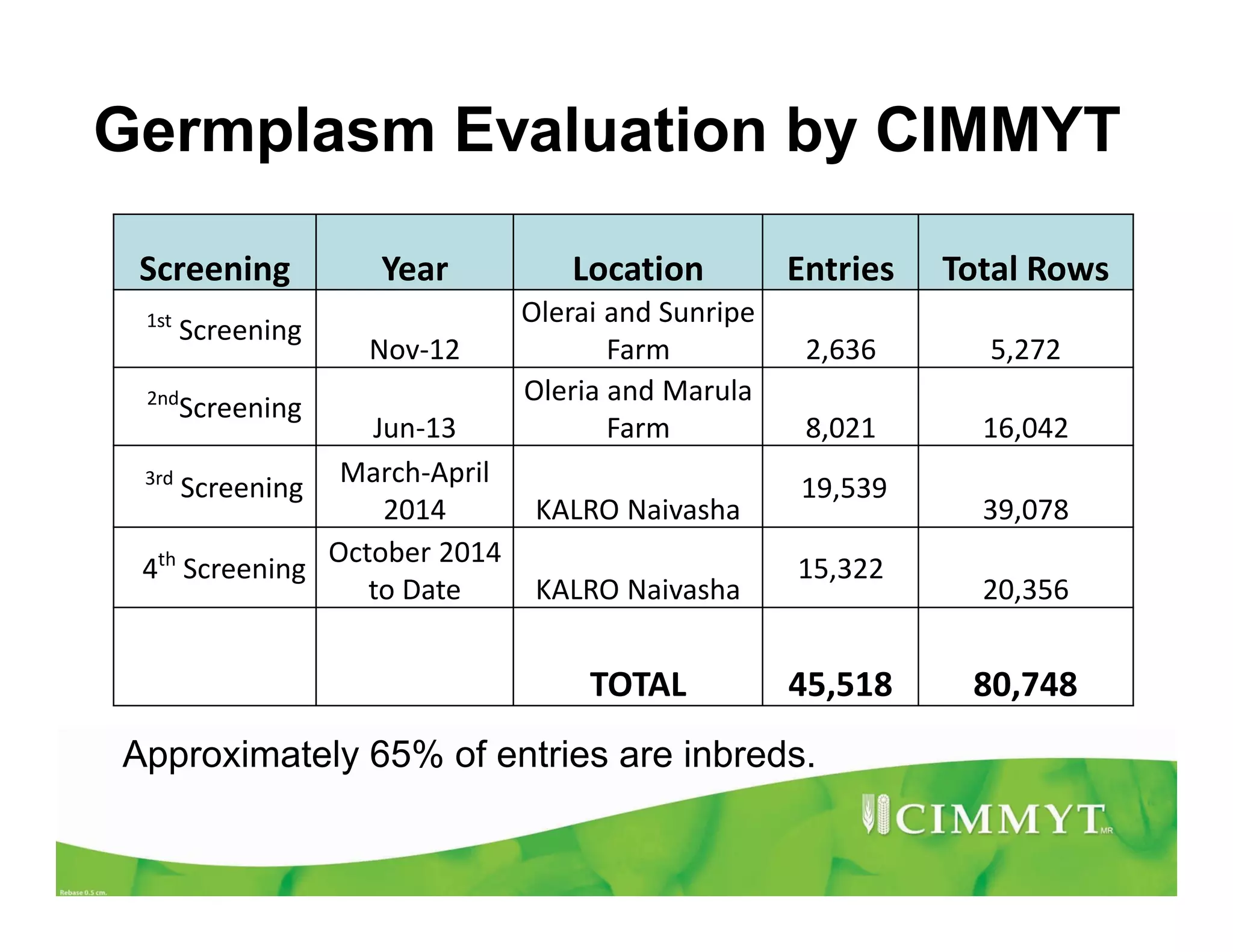
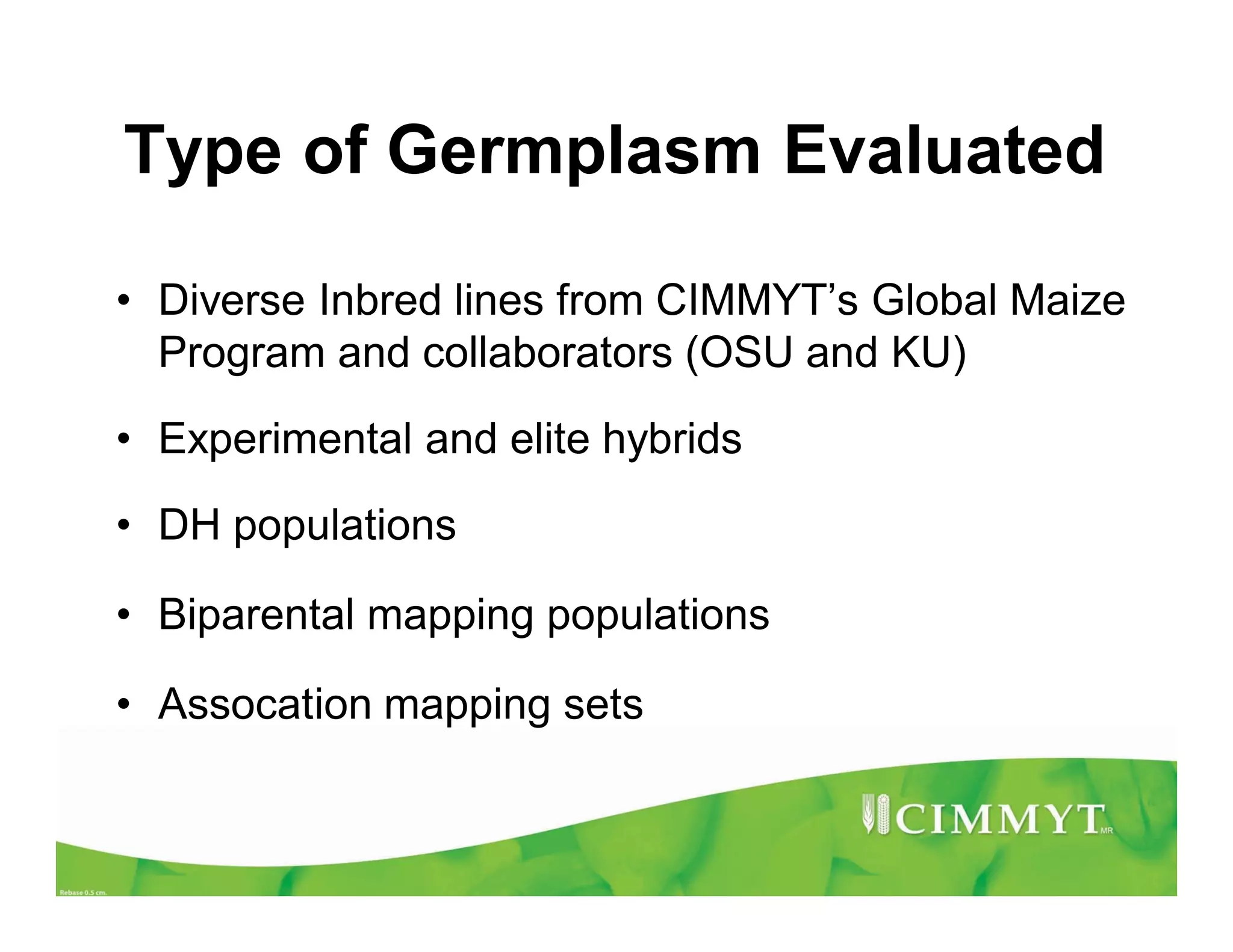
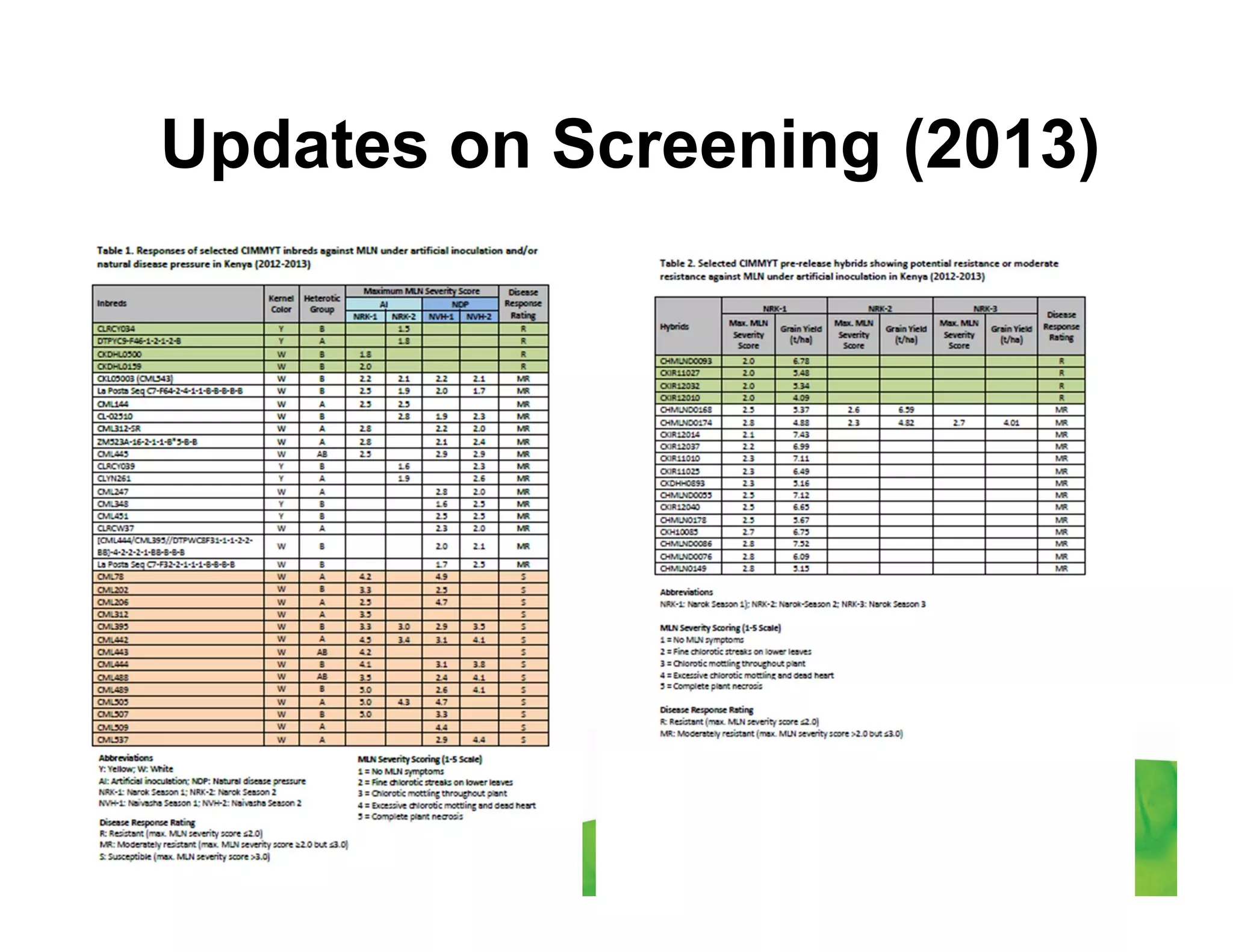
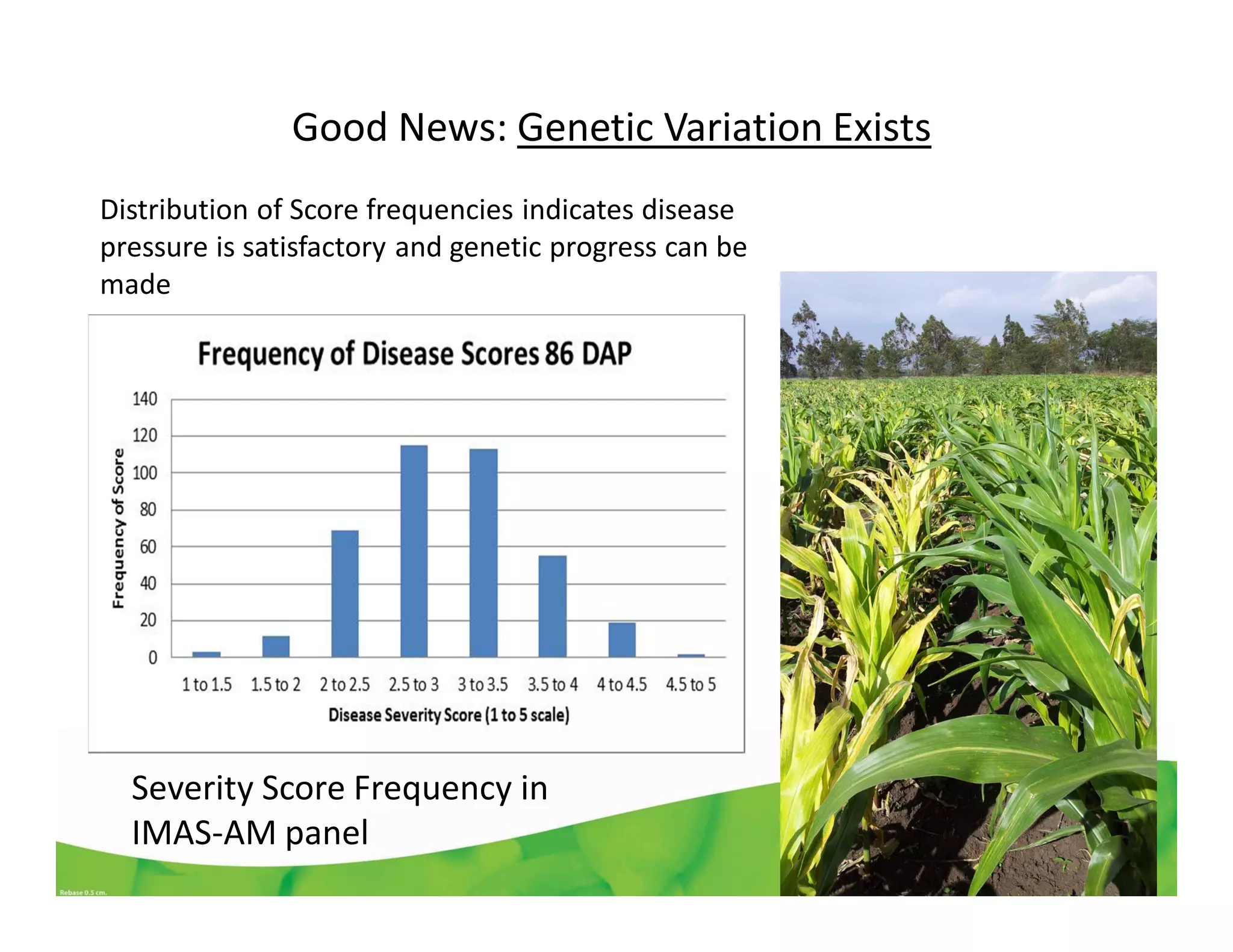
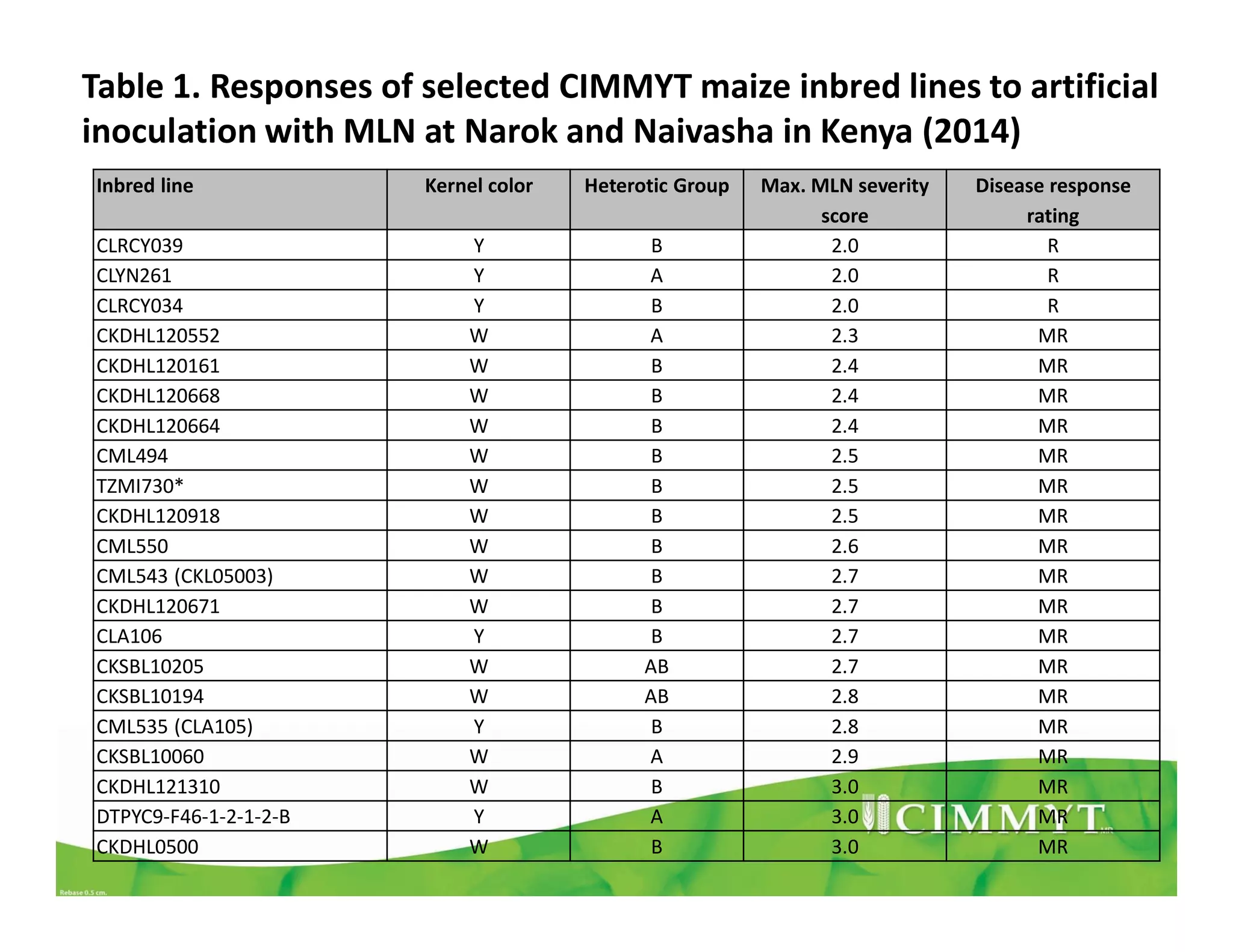
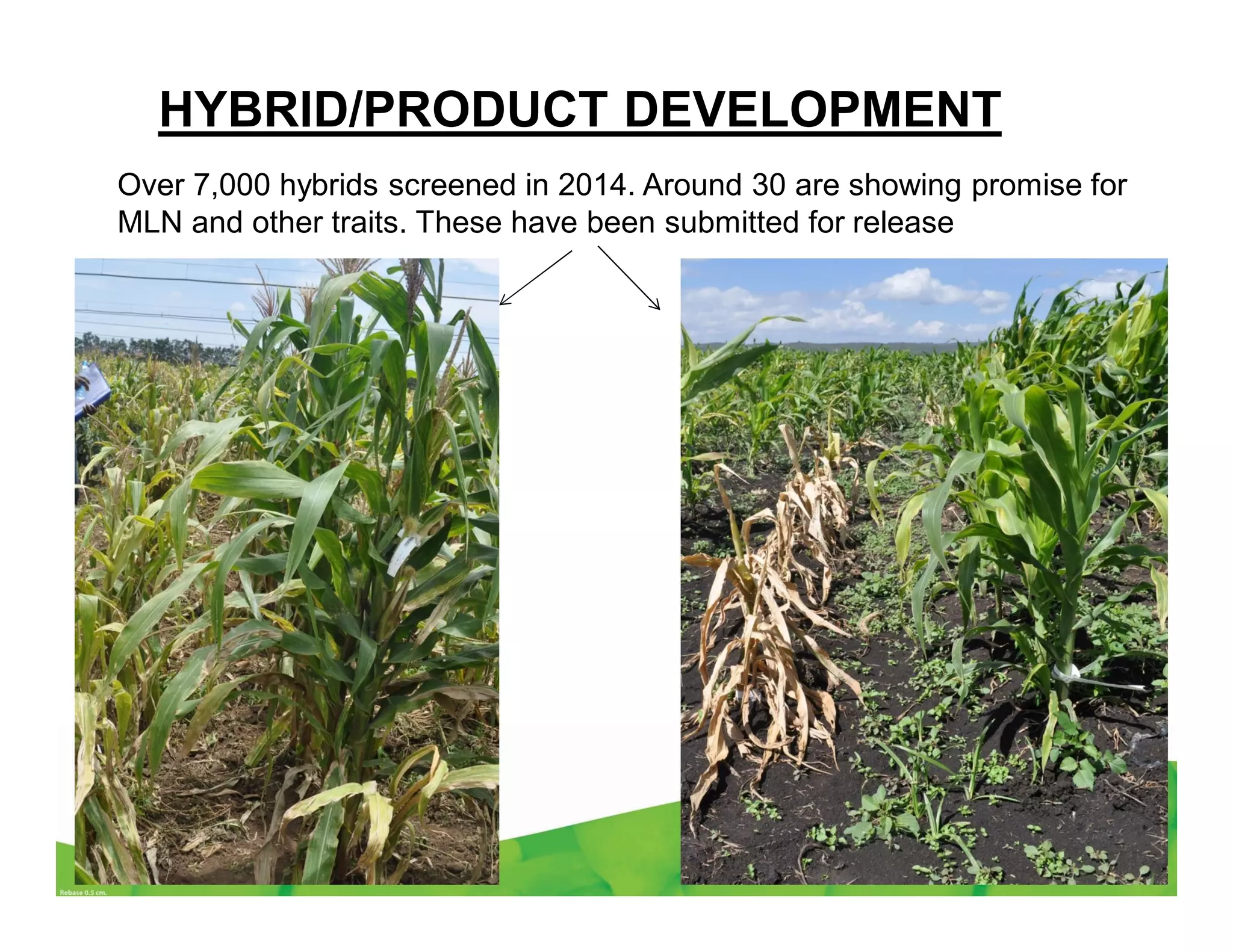
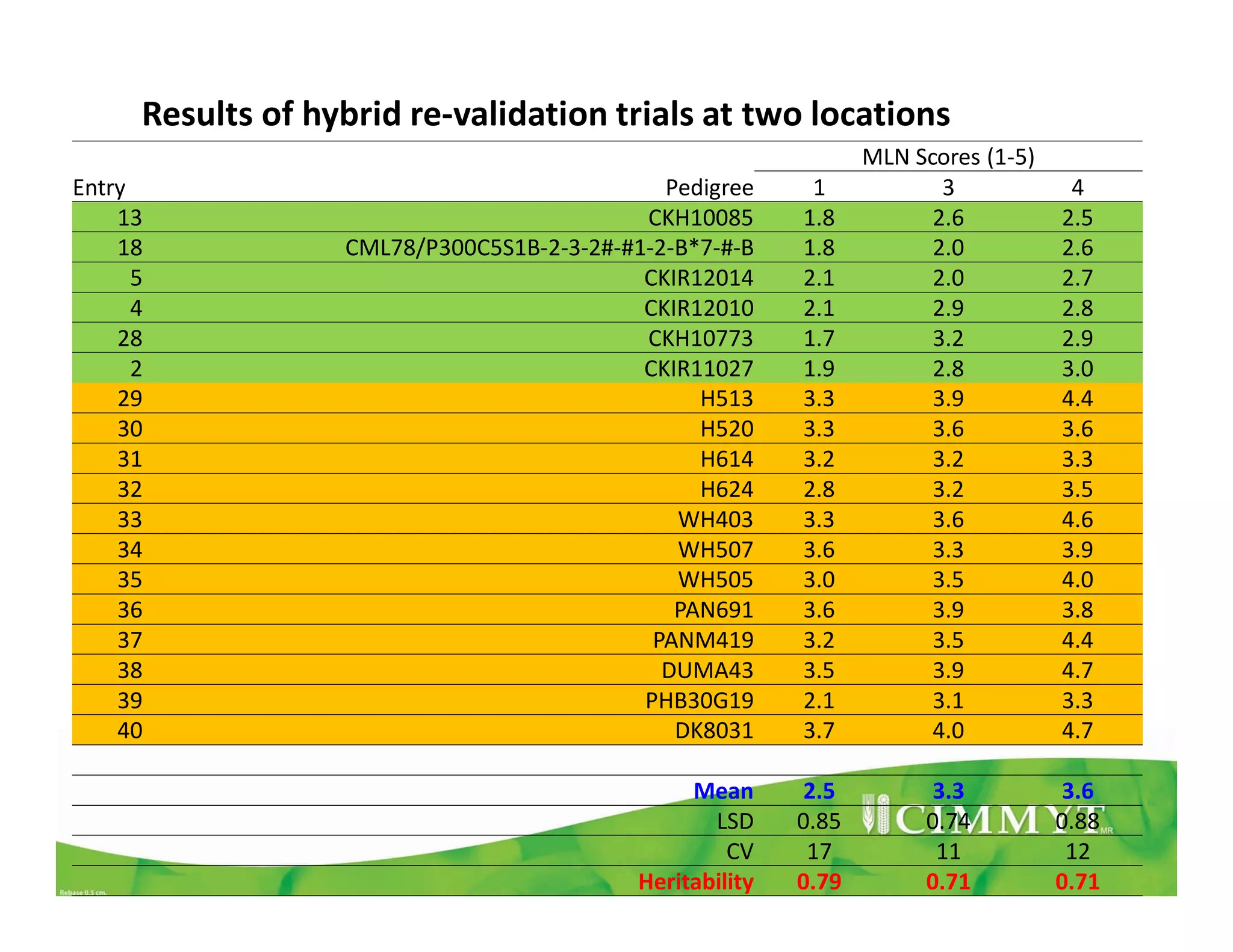
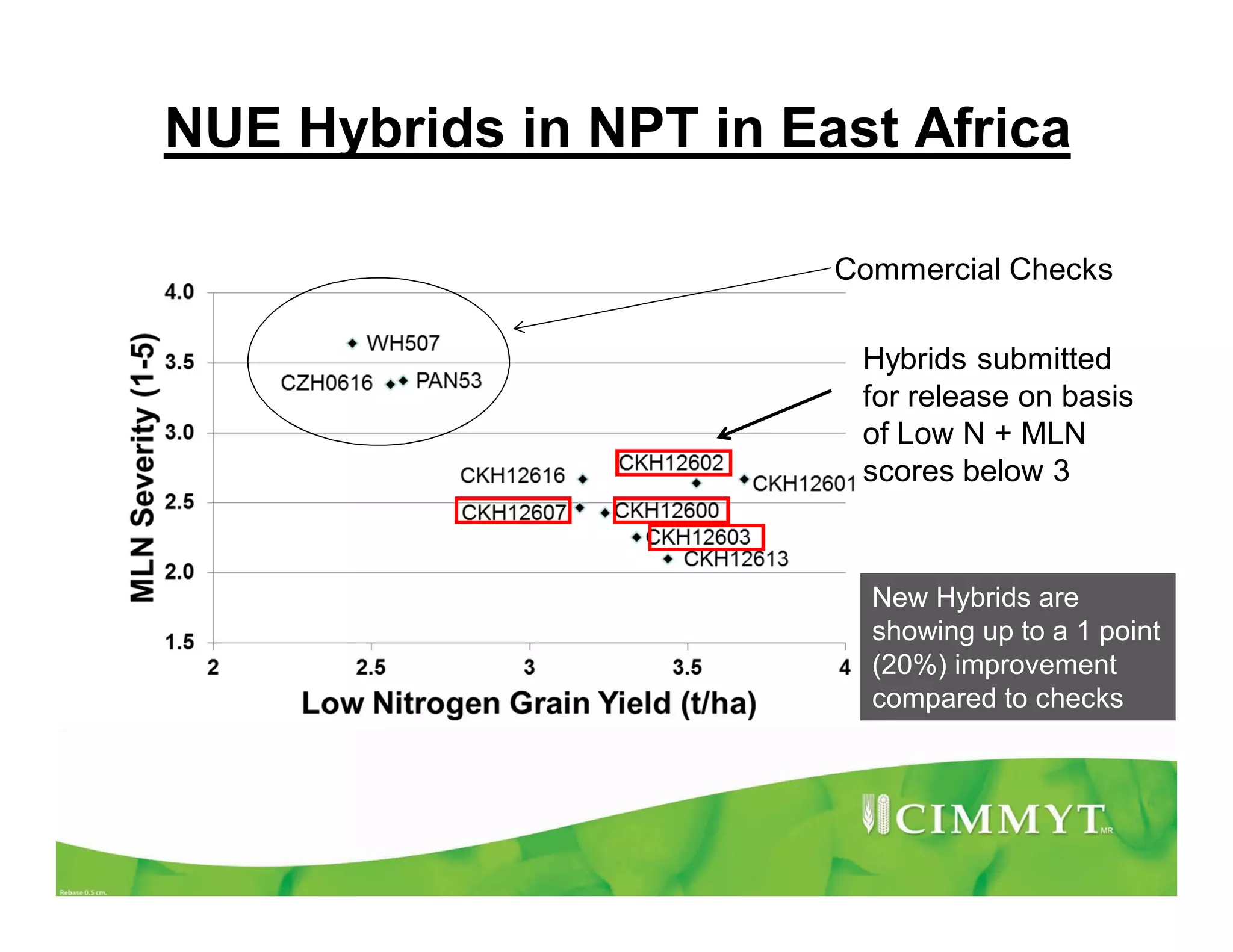
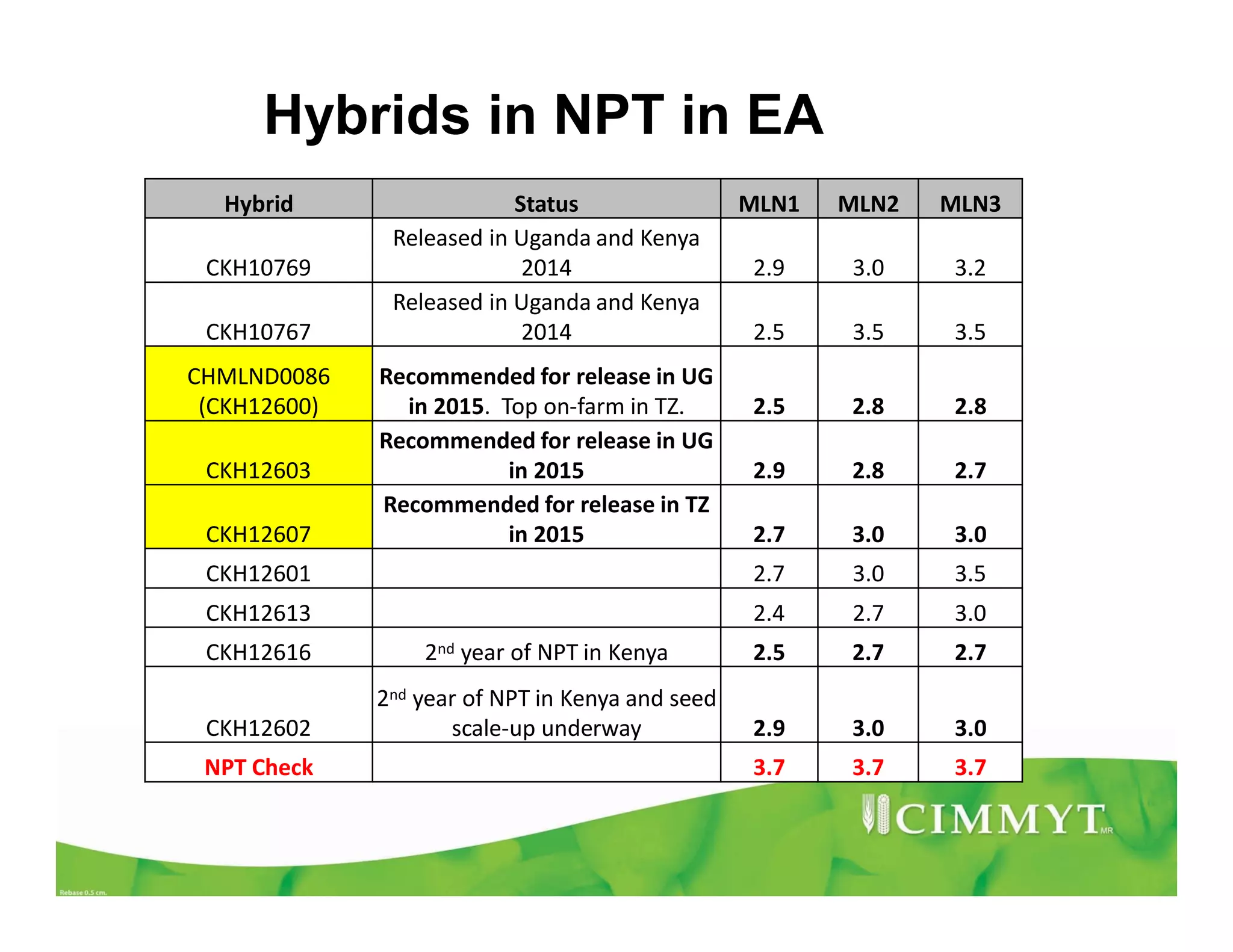
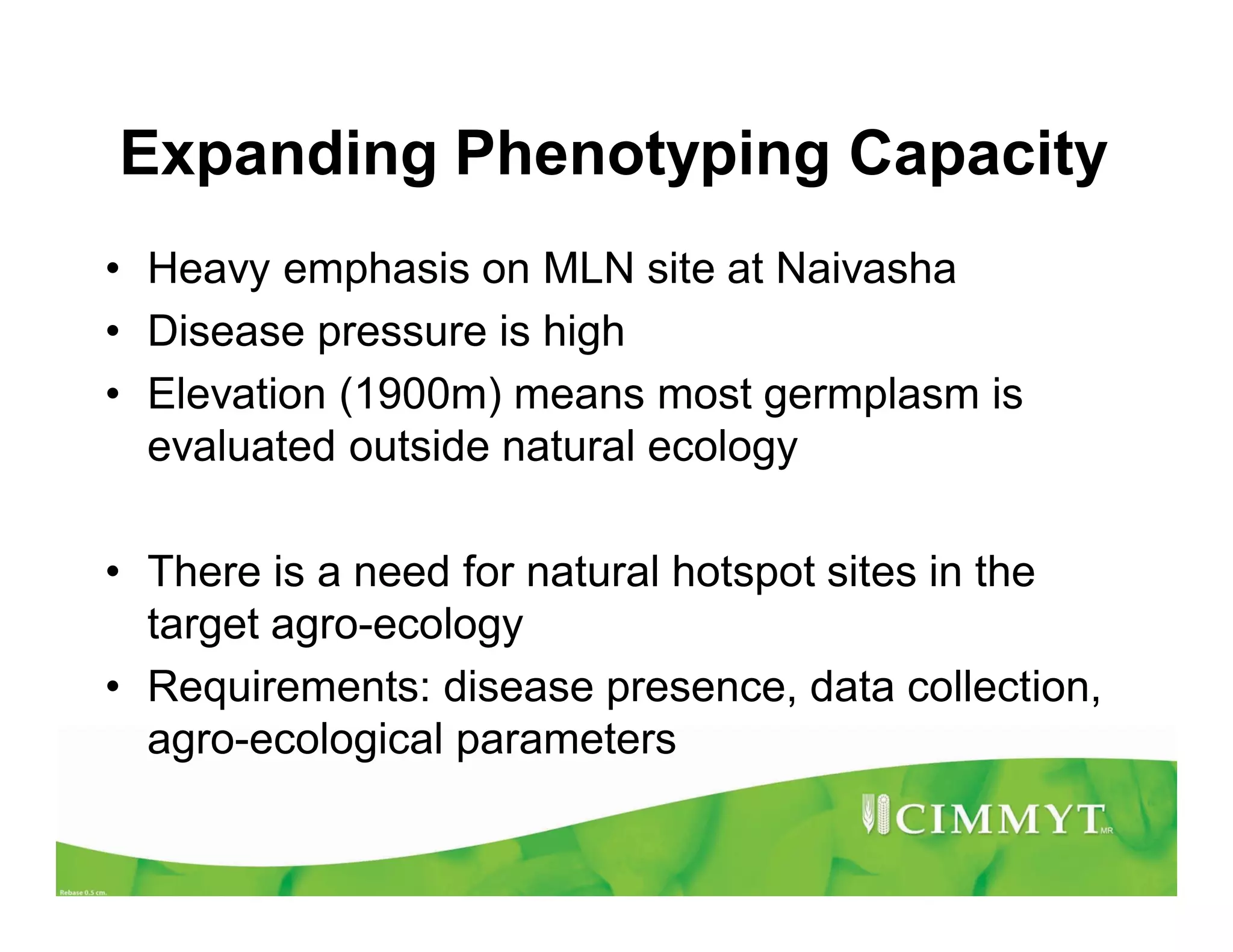
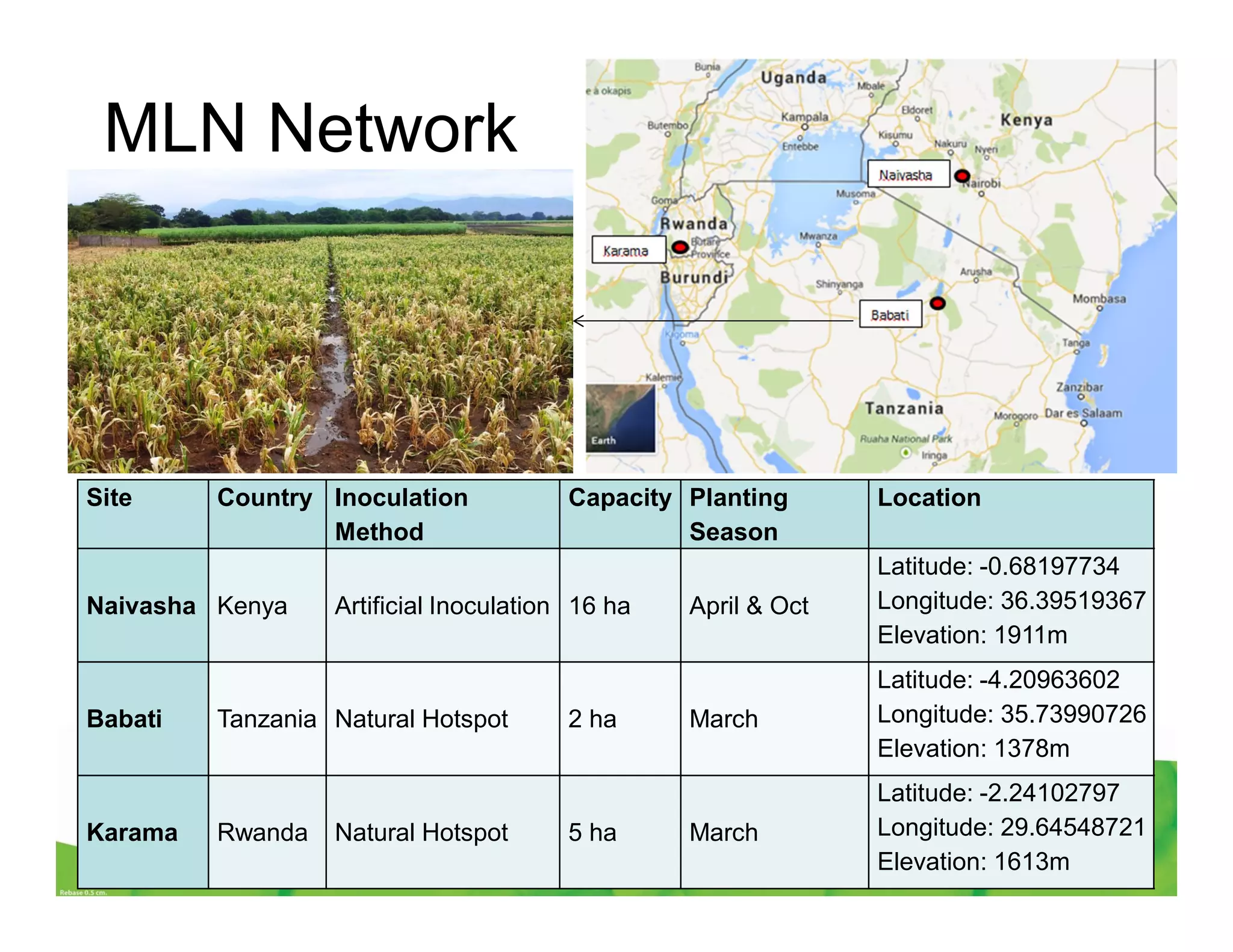
CIMMYT's maize breeding program focuses on developing varieties tolerant to biotic and abiotic stresses for tropical regions where maize is an important food crop. The program has screened over 45,000 varieties for tolerance to Maize Lethal Necrosis (MLN), finding that around 10% show some tolerance. Promising tolerant inbred lines and hybrids have been identified and some recommended for release. CIMMYT is expanding its MLN screening capacity through additional sites in East Africa that experience natural MLN infection. The goal is to accelerate the development and release of MLN-tolerant varieties to address the devastating impacts of the disease.