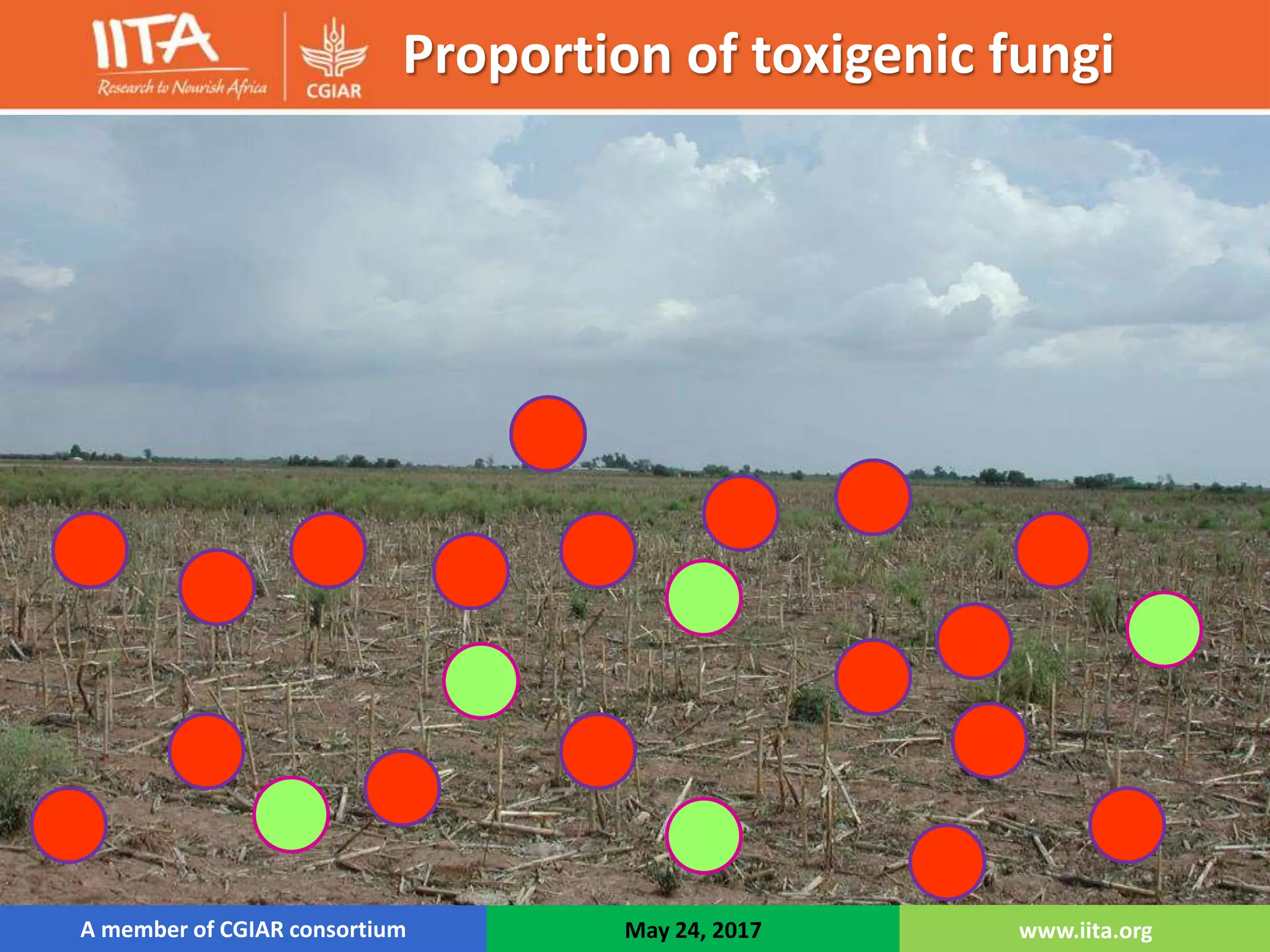
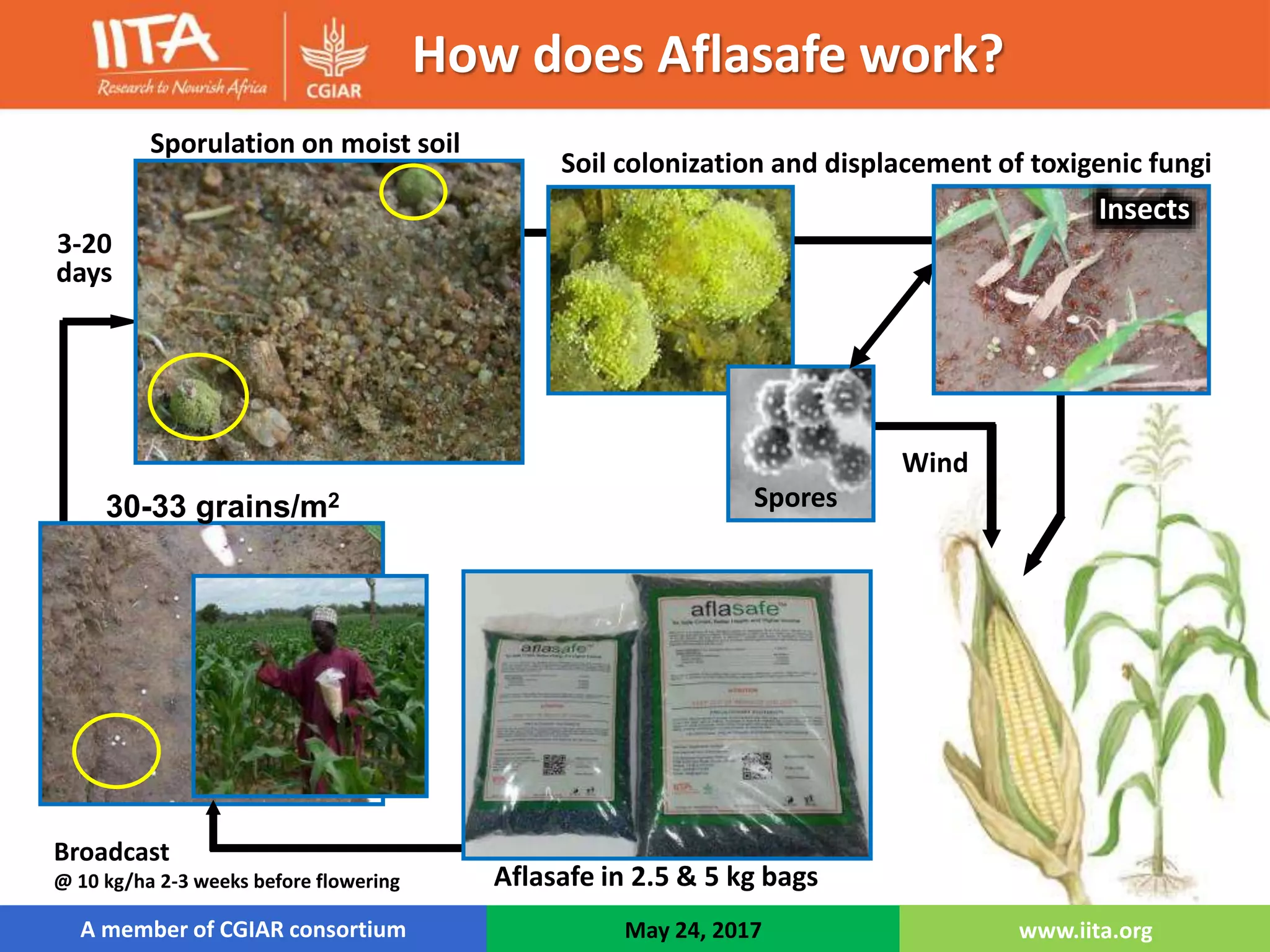
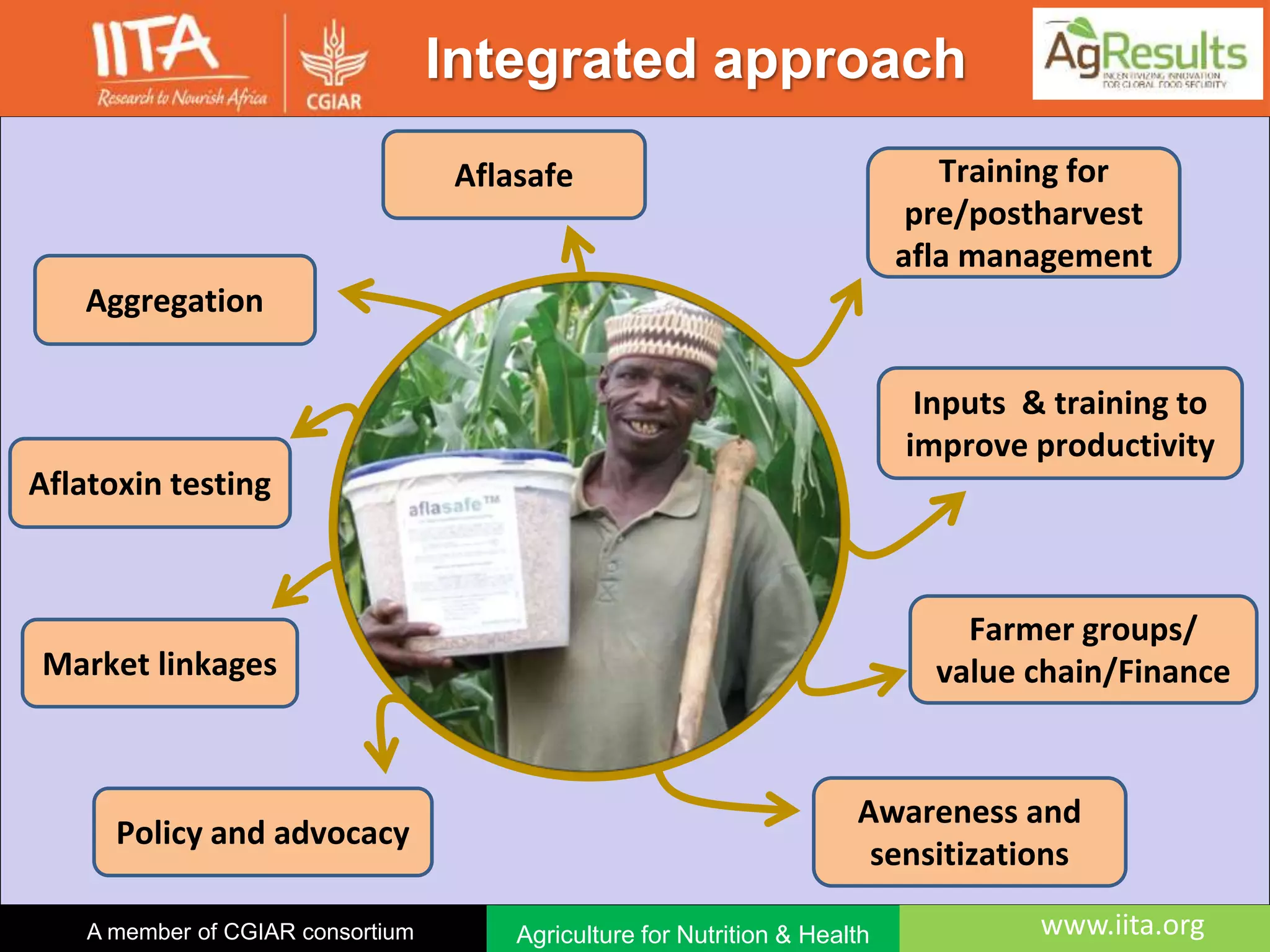
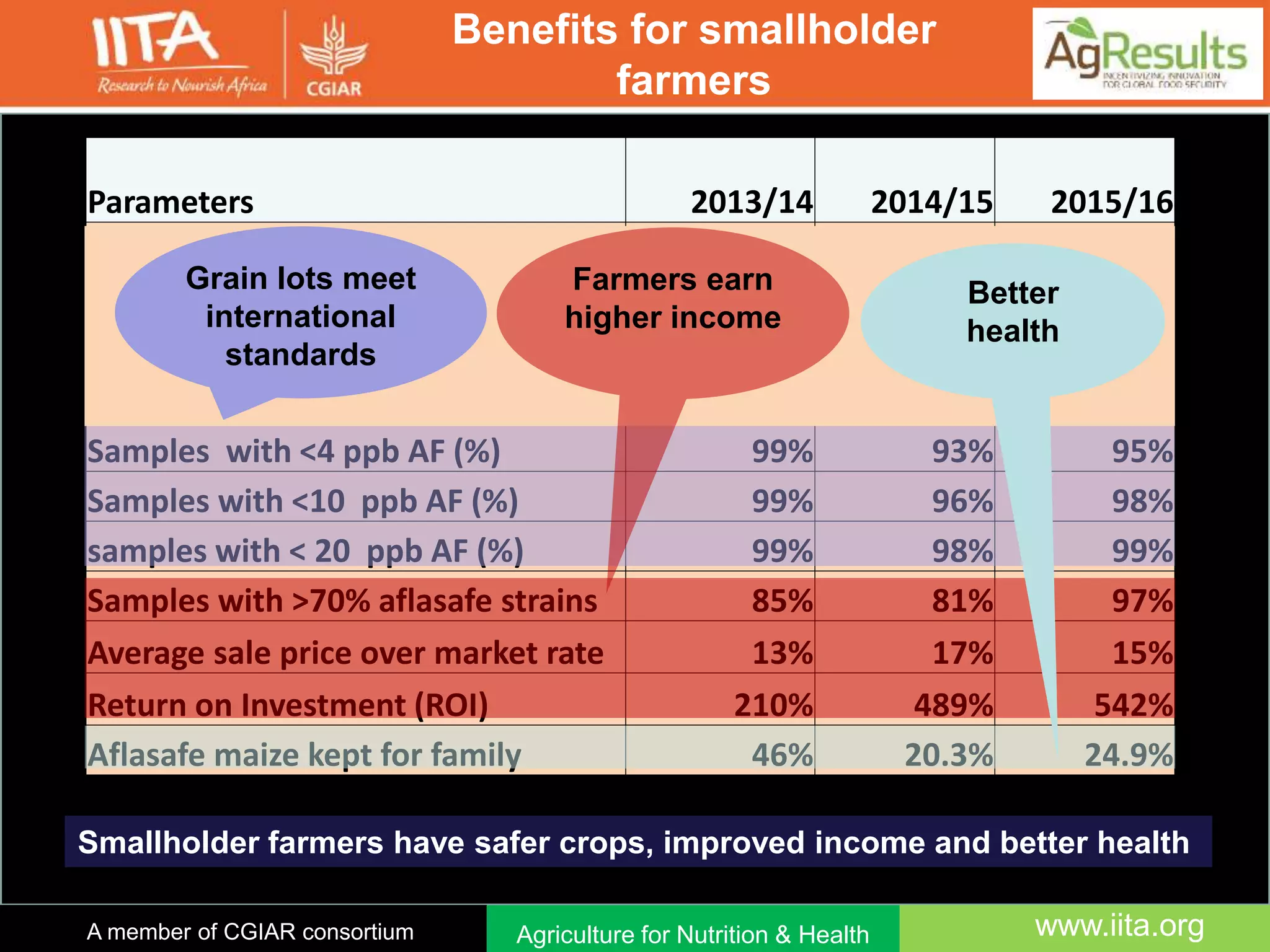
Aflasafe is a biocontrol product developed to reduce aflatoxin contamination in crops like maize and groundnuts. Field trials in multiple African countries found that applying Aflasafe significantly reduced aflatoxin levels at harvest and after storage compared to untreated controls. Aflasafe works by competitively displacing toxigenic fungi with native atoxigenic strains, preventing aflatoxin production. Scaling up Aflasafe use across Africa could help improve food safety, protect health, and increase farmer incomes.