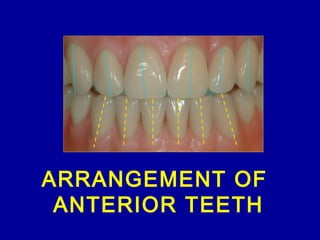
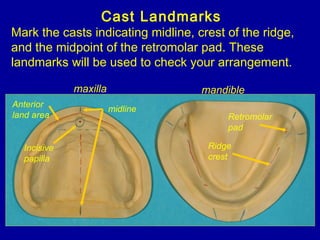
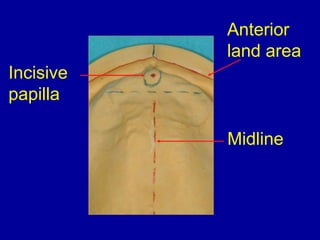
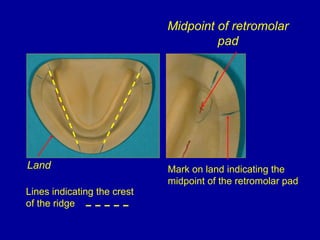
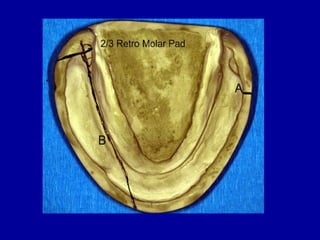
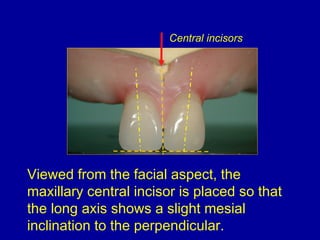
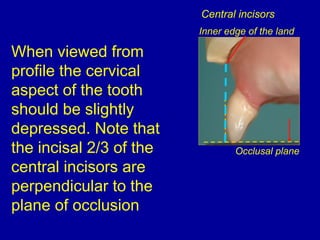
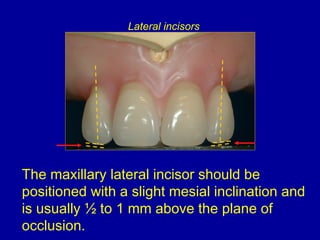
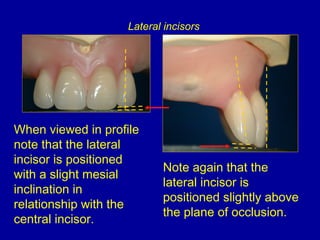
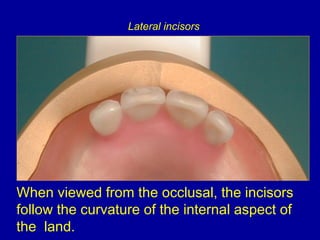
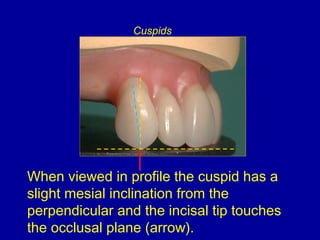
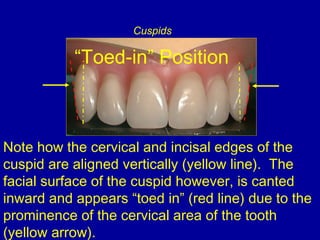
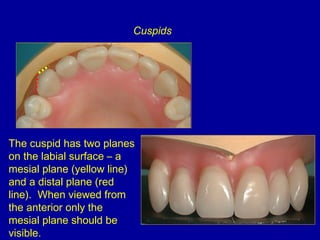
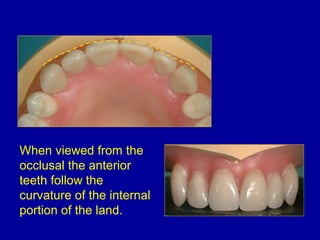
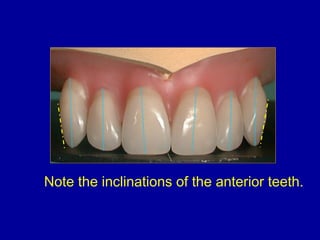
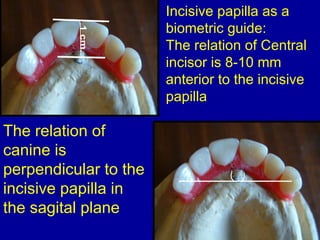
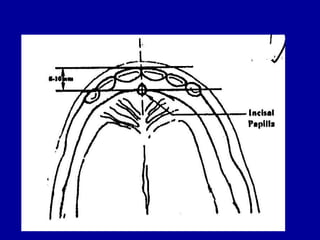
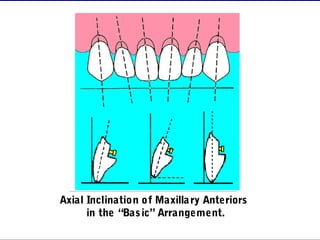
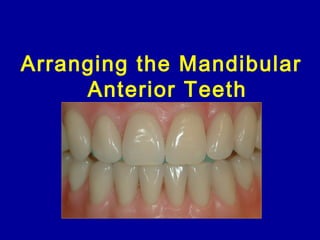
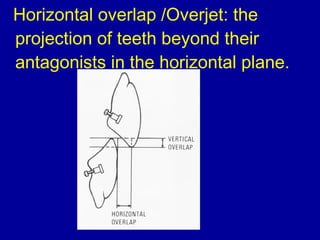
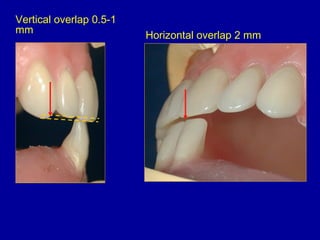
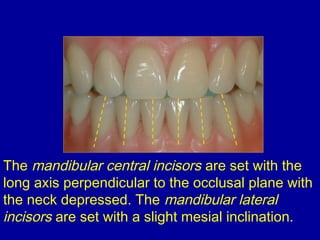
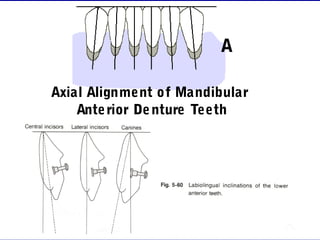
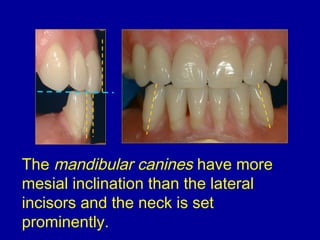
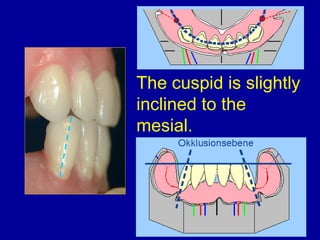
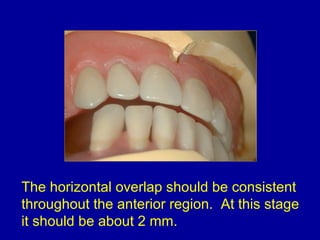
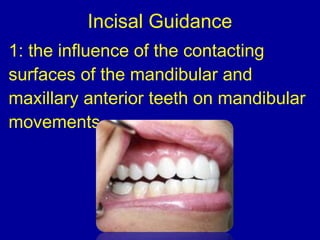
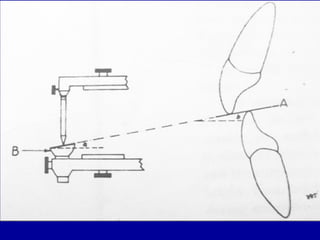
This document provides guidance on arranging anterior teeth. It discusses landmarks for tooth arrangement, positioning maxillary and mandibular anterior teeth, horizontal and vertical overlap, and incisal guidance. The maxillary central incisors should be positioned with a slight mesial inclination and depressed cervical aspect. The lateral incisors are placed slightly above the occlusal plane. The mandibular anterior teeth are set with the central incisors perpendicular and laterals with slight mesial inclination. Horizontal overlap should be consistent at about 2mm, while vertical overlap is 0.5-1mm. Incisal guidance refers to the influence of anterior tooth contacts on jaw movements.