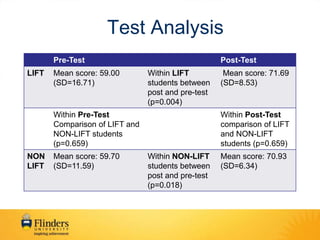
This document evaluates the Longitudinal Integrated Flinders Training (LIFT) program, which places students in longitudinal half-year placements at Flinders Medical Centre. The evaluation found that students in the LIFT program showed a significant increase in their scores on a clinical reasoning test from pre-to-post, and the LIFT students significantly increased their class ranking by the end of the program. Clinicians provided feedback that the longitudinal nature of the program allowed them to better monitor student progress and assess clinical abilities, though noted weaknesses included a lack of inpatient exposure and not enough clinician preceptors across all disciplines.