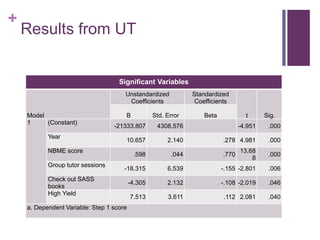
This document analyzes different methods for preparing for the USMLE Step 1 exam. The author conducted surveys of medical students at UT Health Science Center (UTHSC) about their study methods and Step 1 scores. Regression analysis found that using High Yield review materials had a positive impact on scores, while group tutoring sessions and checking out books from the student academic support services had negative impacts. Surveys of students on an online forum found some differences in common study resources compared to UTHSC students. The author concludes that specific study resources may have little effect and recommends schools provide alternative prep support and consider curricular reforms. Future research with multiple schools and better controls is needed.