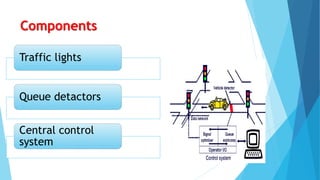
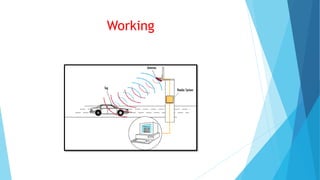
This document discusses 8 components of intelligent transportation systems (ITS). It describes smart traffic signal control systems, freeway management systems, electronic toll collection systems, incident management systems, and emergency vehicle preemption systems. The key components discussed are traffic lights, sensors, central control centers, ramp meters, cameras, dynamic message signs, RFID tags, and acoustic and line-of-sight signaling devices for emergency vehicles. The goal of these systems is to efficiently manage traffic flow, provide traveler information, and prioritize emergency response.