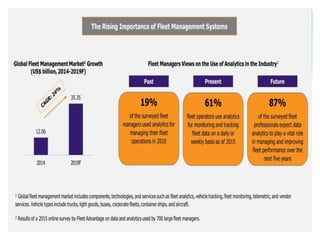
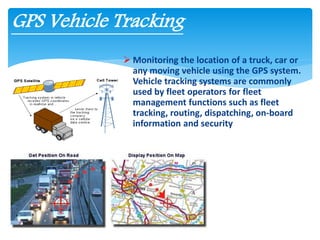
Fleet management involves optimally planning, supervising, and controlling fleet operations using available resources while considering internal and external factors. It focuses on integrating organizational processes with modern information systems. Fleet management systems allow companies to track vehicles using GPS, monitor speed and idle time, plan routes, manage drivers, track assets, and generate various reports. They provide advantages such as improved productivity, reduced costs, enhanced safety, and more transparent transport operations.