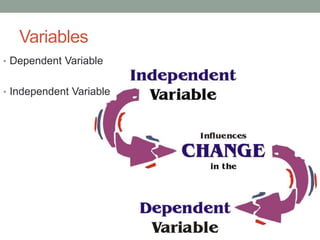
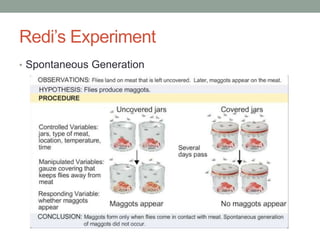
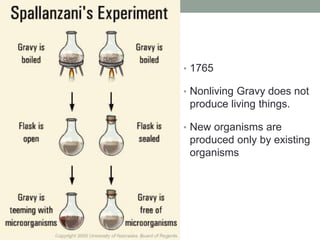
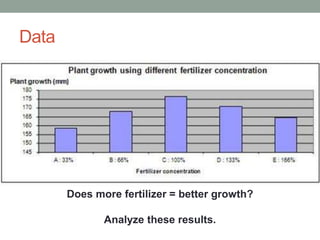
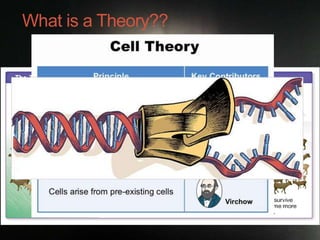
This document summarizes a biology chapter that discusses the scientific method and key experiments investigating spontaneous generation. It introduces important scientific terms like independent variable, dependent variable, theory, and controlled experiment. It summarizes three landmark experiments - Redi's in 1668, Needham's in 1748, and Spallanzini's in 1765 - that disproved the theory of spontaneous generation and established that life only comes from other life. The document encourages applying the scientific method to design experiments and considers how theories can be developed without experimentation through models.