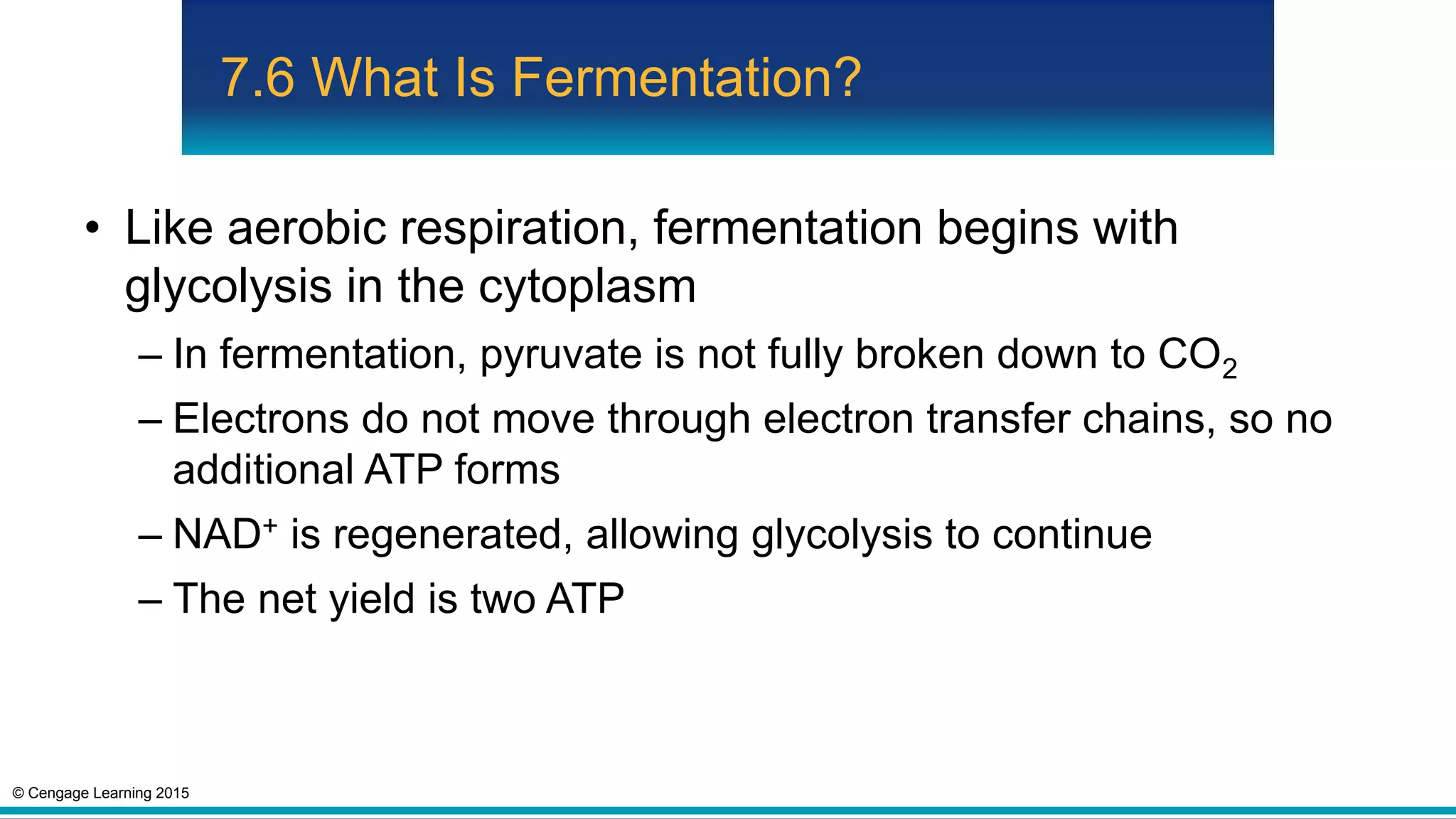
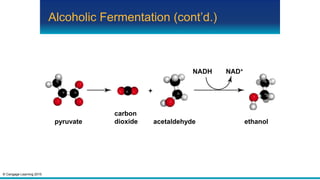
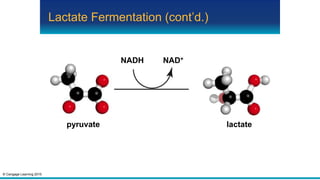
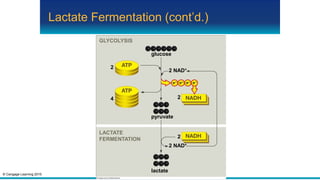
Fermentation is an anaerobic pathway that produces a small amount of ATP without using oxygen. There are two main fermentation pathways: alcoholic fermentation produces ATP, CO2, and ethanol from sugar, while lactate fermentation produces ATP and lactate. Both pathways regenerate NAD+ to allow glycolysis to continue yielding energy. Fermentation occurs in yeast during alcohol production and in animal muscle cells during short, intense activity when oxygen is limited.