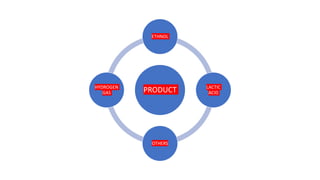
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through enzyme action, typically extracting energy from carbohydrates without oxygen. It is used to preserve foods through lactic acid production and make alcoholic beverages. Key products include ethanol, lactic acid, hydrogen gas, and others. It is an ancient metabolic pathway common to bacteria and eukaryotes that takes place in anaerobic environments.