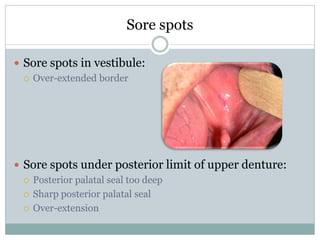
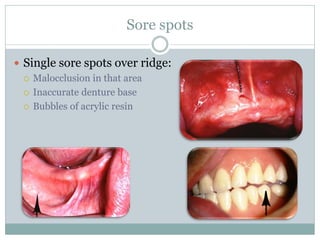
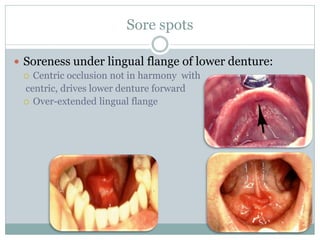
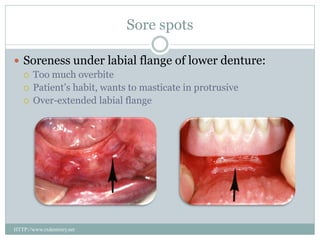
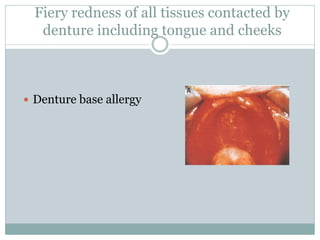
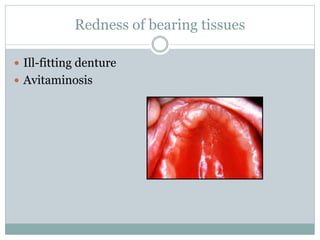
Most patients experience some problems adjusting to new dentures. Common complaints include sore spots from poor fit, burning sensations from pressure on nerves, and instability when not chewing. Bite issues can also cause difficulties with eating, talking, and jaw pain. Regular checkups are important to identify and address issues through relines or new dentures. Proper fit is key to comfort and function.