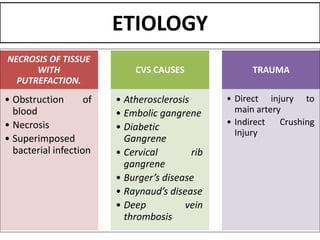
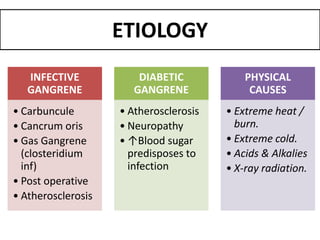
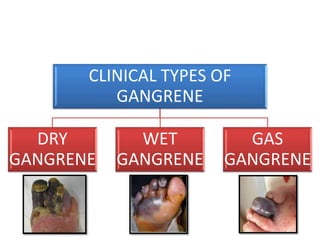
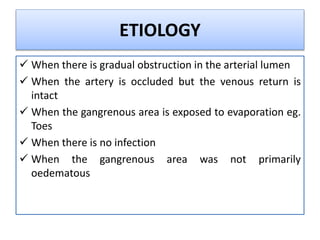
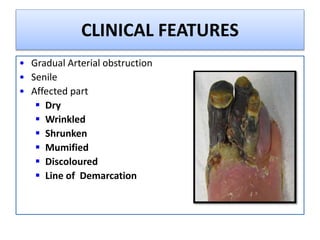
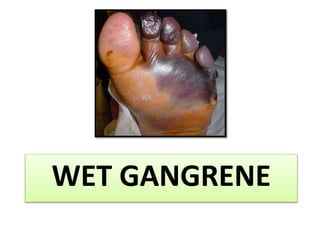
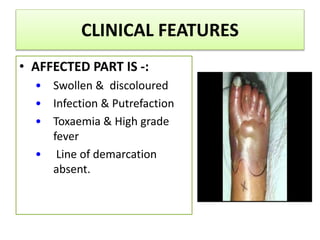
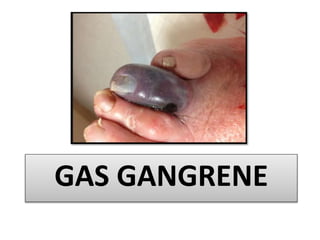
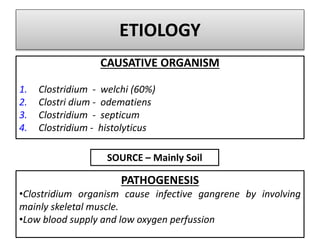
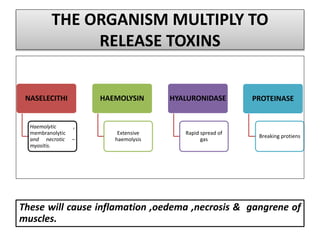
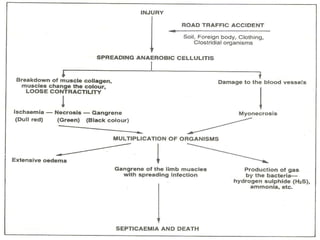
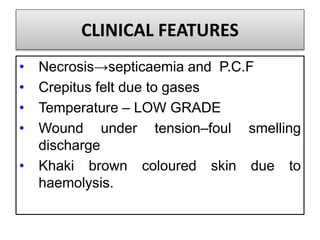
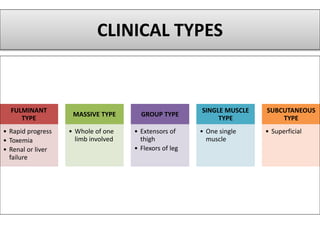
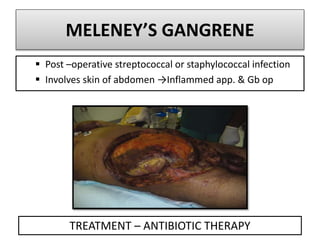
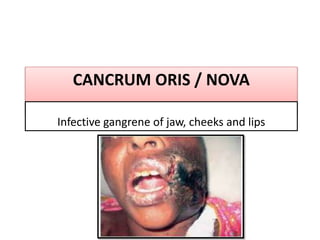
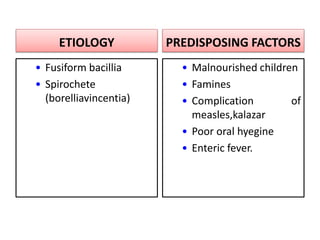
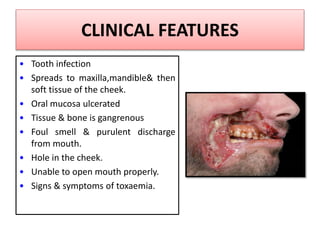
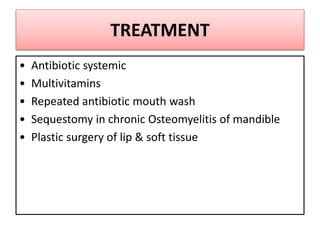
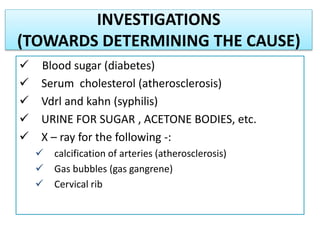
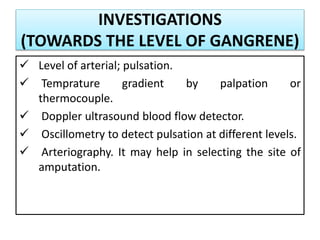
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by lack of blood supply and can be caused by blocked arteries or infection. There are several types of gangrene including dry gangrene caused by gradual arterial blockage, wet gangrene caused by sudden blockage and infection, and gas gangrene caused by Clostridium bacteria infection. Clinical features include discolored, numb skin that is dry in dry gangrene and swollen in wet gangrene, with a foul smell and crepitus in gas gangrene. Treatment depends on the type but may include antibiotics, surgery to remove dead tissue, and amputation in severe cases.