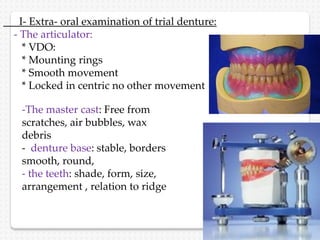
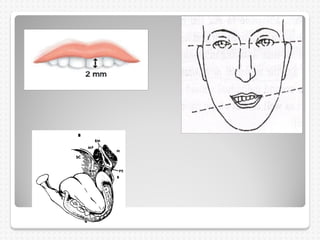
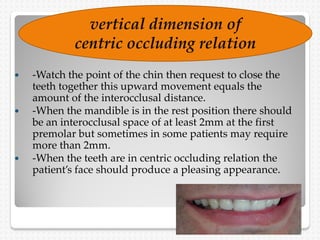
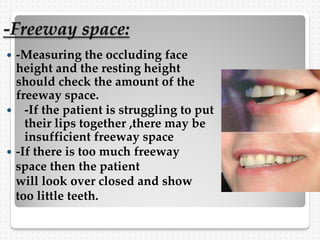
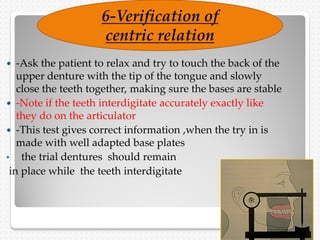
This document summarizes the try-in stage of denture construction. It discusses examining the trial denture extra-orally and intra-orally to check extension, retention, stability, occlusion, vertical dimension, centric relation, even occlusal pressure, esthetics, and phonetics. Any issues identified need to be addressed before proceeding to the next stage of denture fabrication. The try-in allows modifications to be made to the wax denture before processing into the final denture.