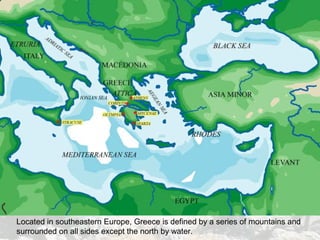
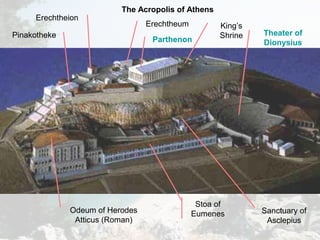
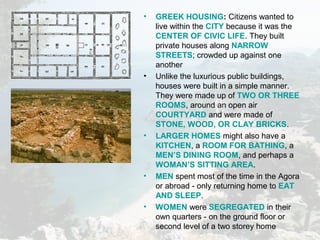
Ancient Greece had a geography defined by mountains and water that influenced its development. The numerous mountain ranges and indented coastline encouraged the formation of independent city-states. Greek civilization began around 2000 BC and experienced a Dark Age after wars like the Trojan War. Power later alternated between Athens and Sparta as dominant city-states before Greece was conquered by Macedonia and then Rome. Daily life for Greeks centered around agriculture, with staple crops of olives, grapes, and barley, and a diet supplemented with fish and legumes. Religion was polytheistic and centered on animal sacrifices to the major gods like Zeus.