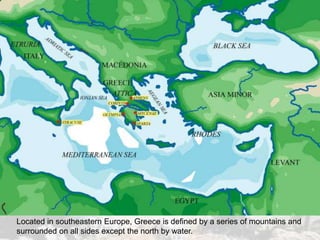
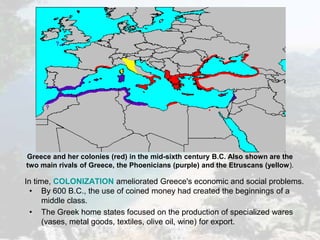
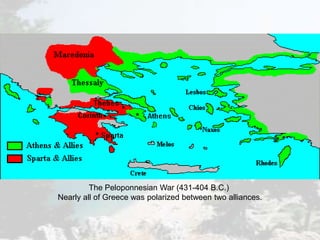
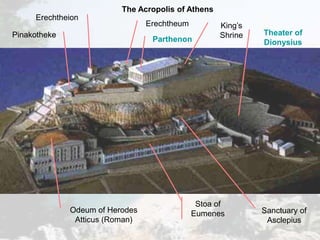
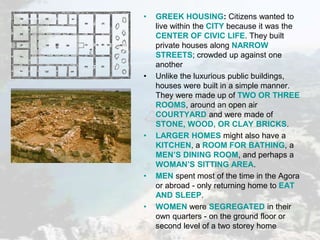
Ancient Greece was defined by its rugged geography of mountains and seas. This geography fostered the development of independent city-states and a seafaring culture. Greek civilization began around 2000 BC and went through periods of war, decline known as the Dark Age, and emergence of new city-states like Athens and Sparta. Athens developed the first democratic system of government, though it excluded women, slaves, and foreigners. Sparta took a militaristic and totalitarian approach. Both city-states were eventually conquered by Macedonia and Rome, though Greek culture and philosophy spread through the Roman Empire and influenced the Renaissance.