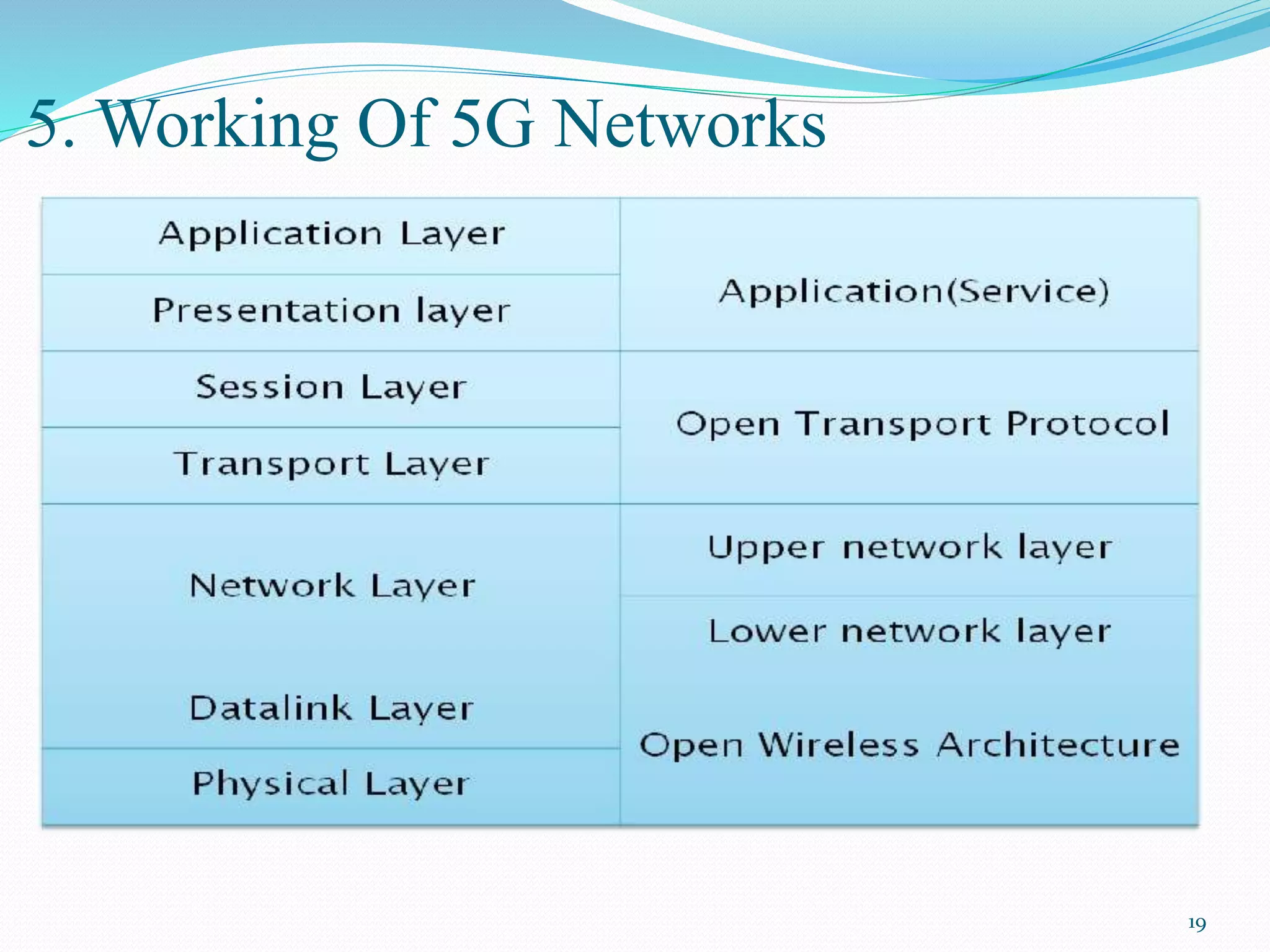
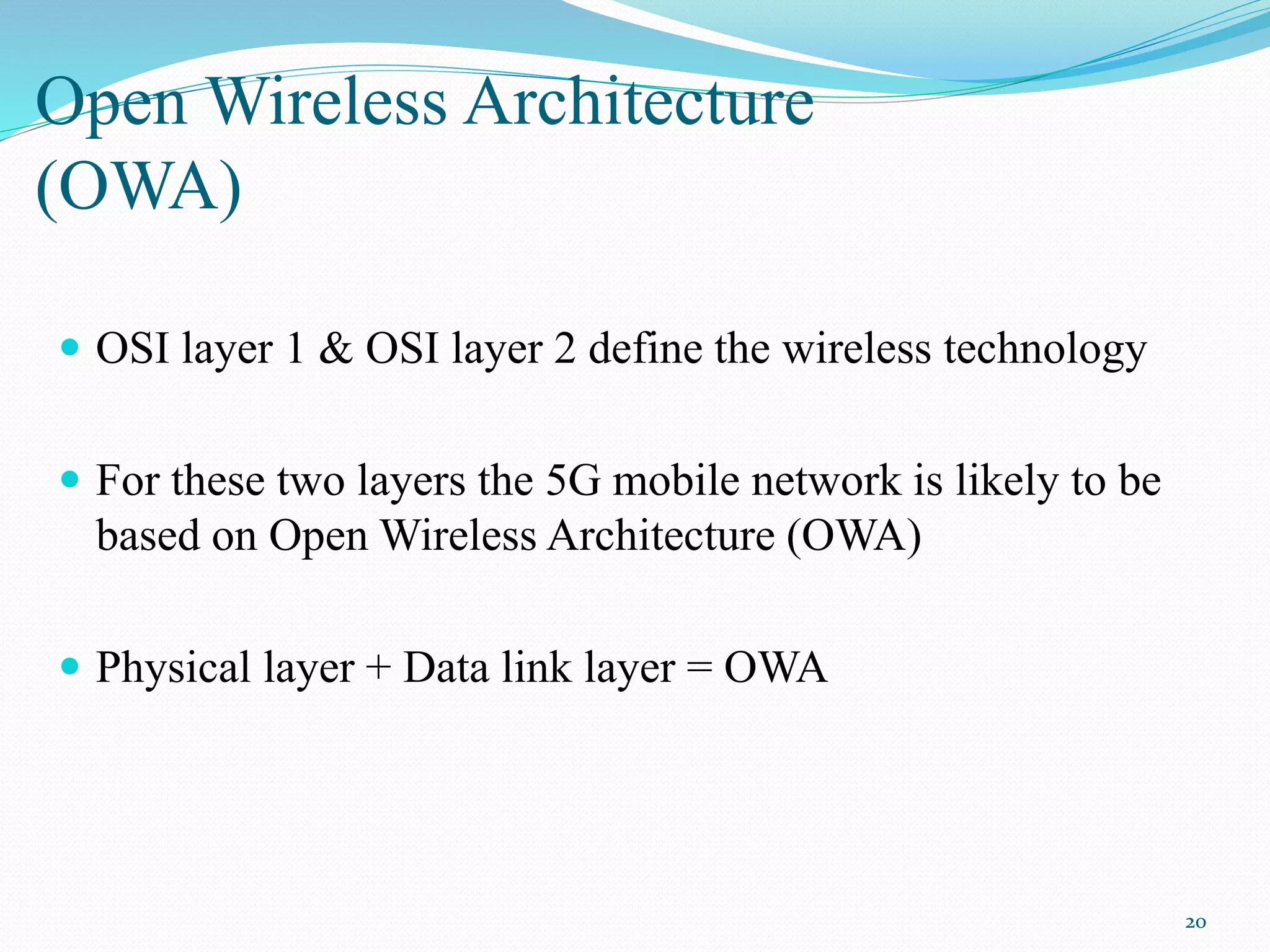
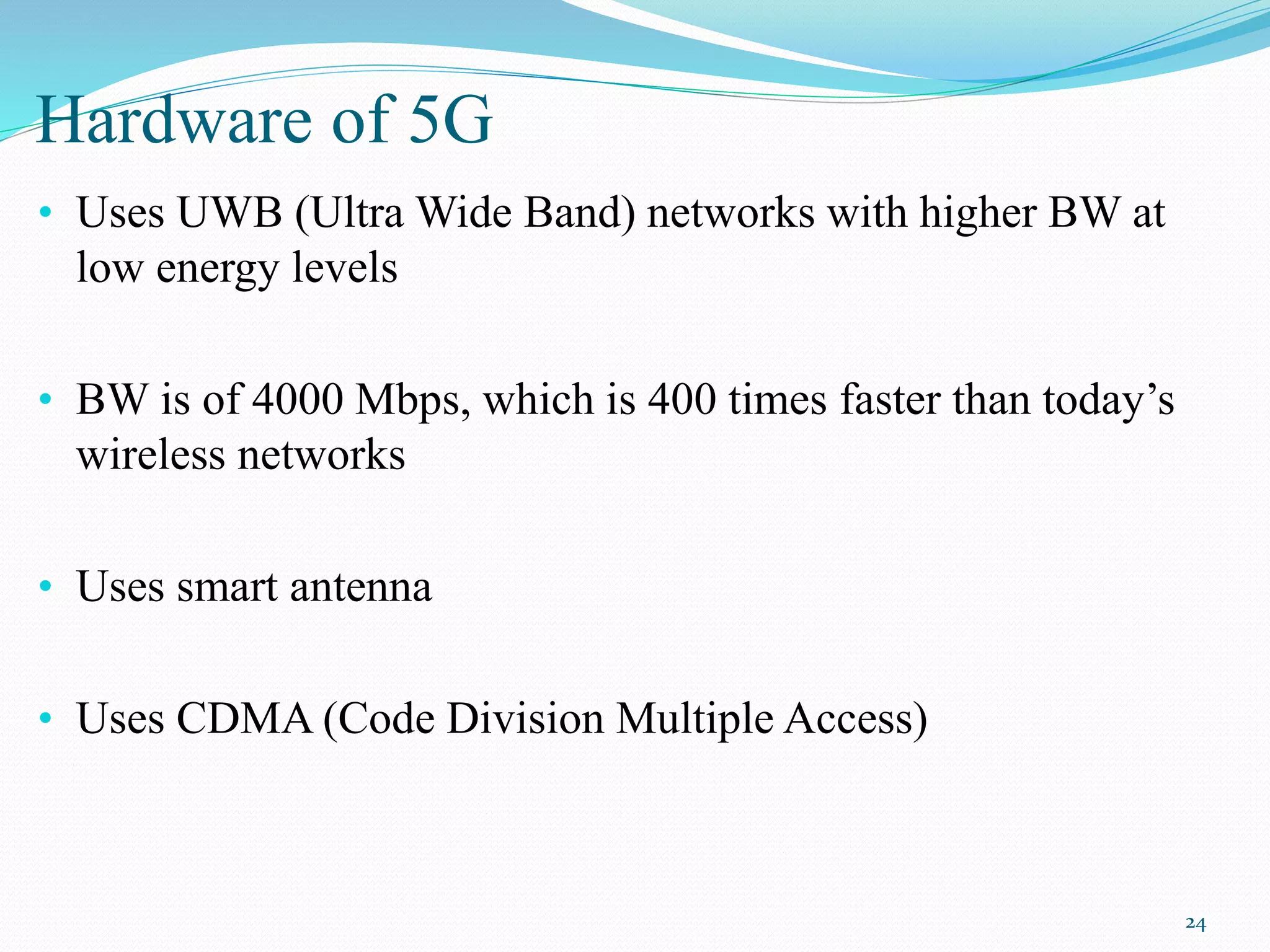
5G is the next generation of wireless technology that will provide significantly faster data speeds, reduced latency, and the ability to connect many more devices simultaneously. The document discusses the evolution of wireless technologies from 1G to 5G, providing details on the key features and capabilities of each generation. It then describes the proposed 5G architecture and working, highlighting aspects like its IP-based design, use of cognitive radio technology, and open wireless and transport protocols. The remaining sections cover the expected features, advantages, challenges and applications of 5G networks.