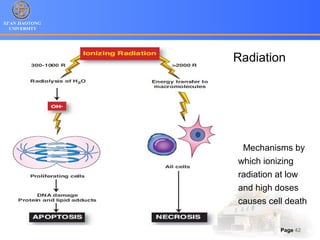
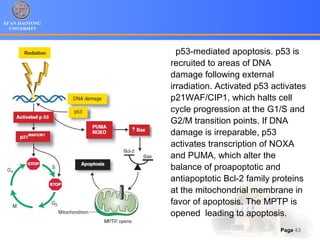
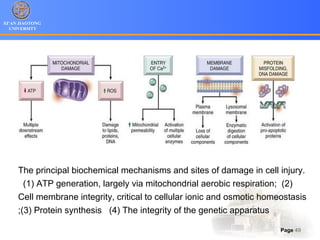
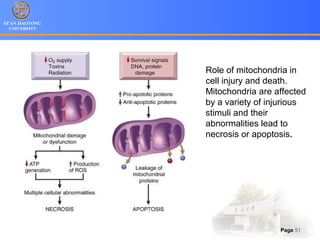
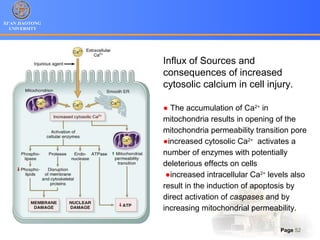
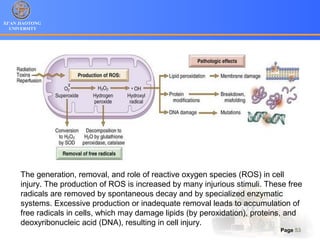
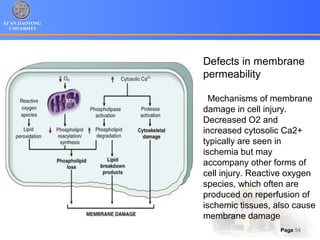
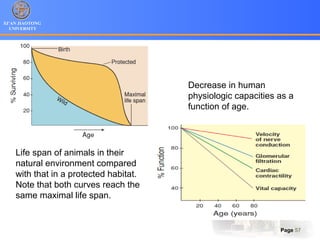
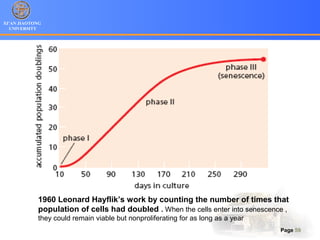
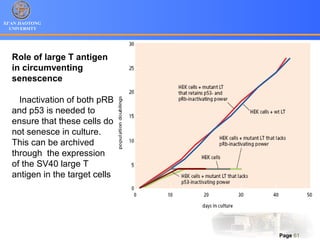
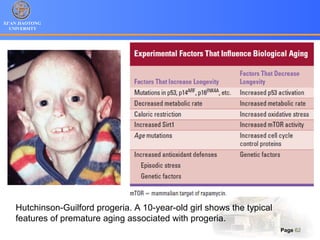
1. Programmed cell death (PCD) refers to regulated cell death processes that eliminate cells when they are no longer useful or potentially harmful.
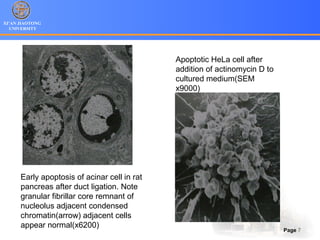
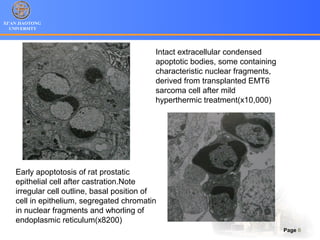
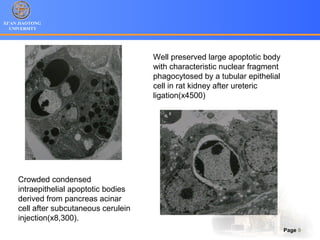
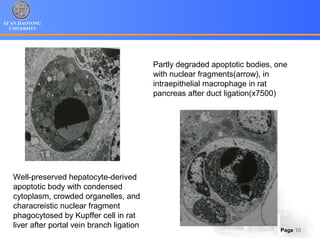
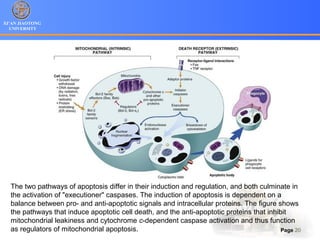
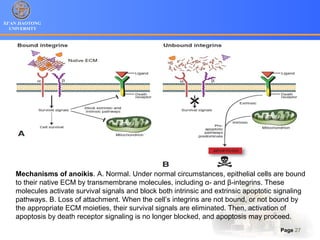
2. Apoptosis is a form of PCD characterized by nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, cell shrinkage and blebbing, and formation of apoptotic bodies that are quickly phagocytosed, avoiding inflammation. It relies on caspase activation through the mitochondrial or death receptor pathways.
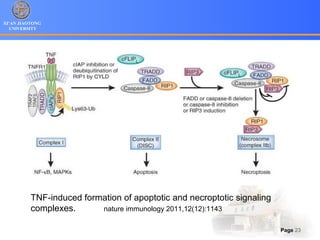
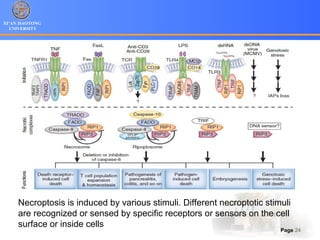
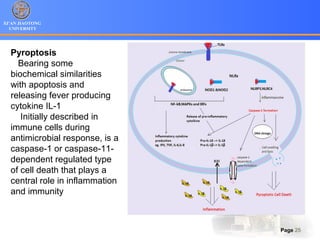
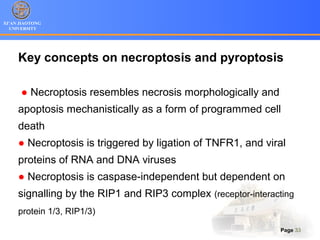
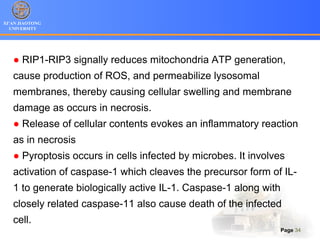
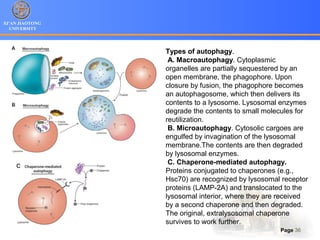
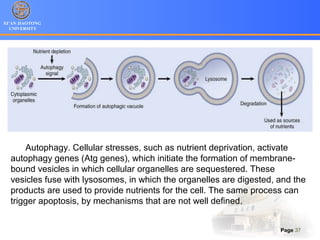
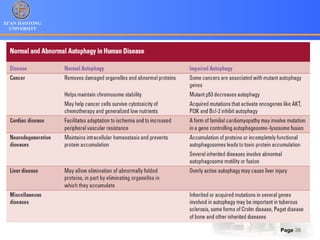
3. Alternative cell death pathways include necroptosis, pyroptosis and autophagy. Necroptosis resembles necrosis morphologically but is caspase-independent and regulated. Pyroptosis involves caspase-1 and occurs during microbial infection, triggering inflammation. Autophagy