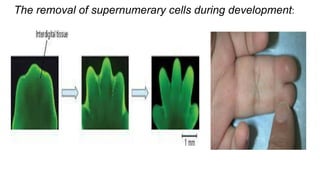
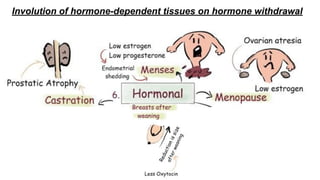
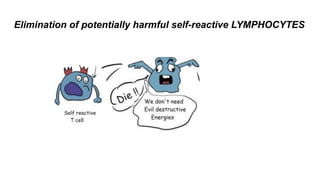
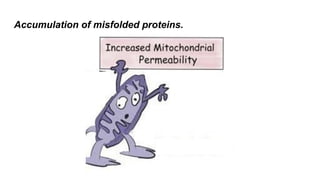
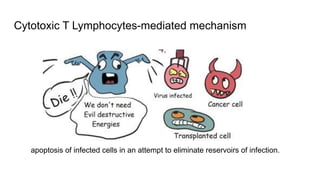
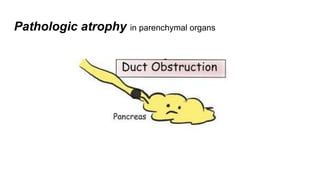
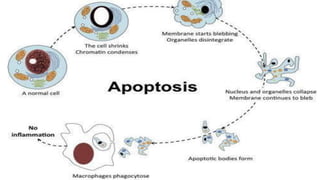
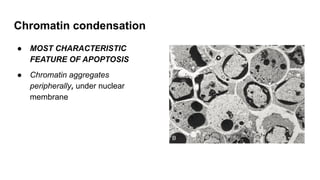
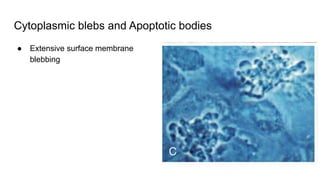
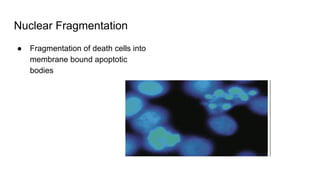
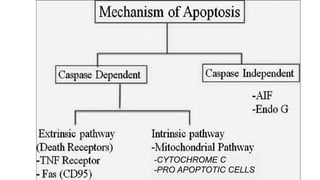
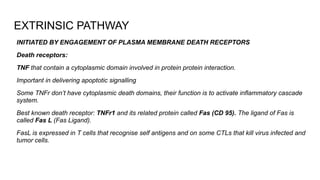
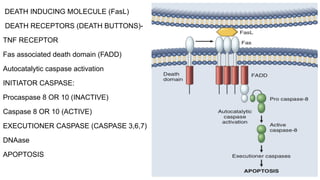
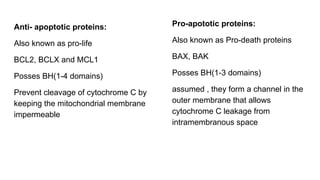
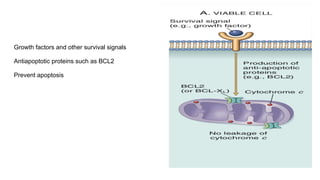
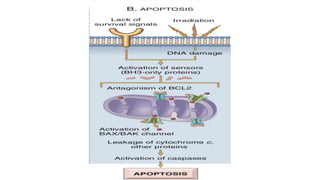
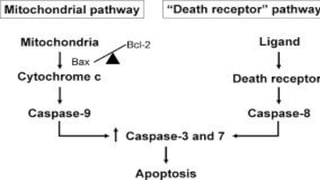
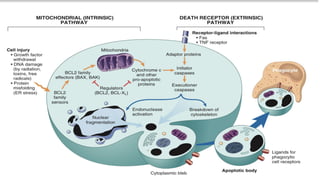
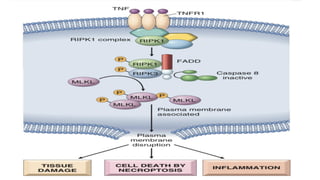
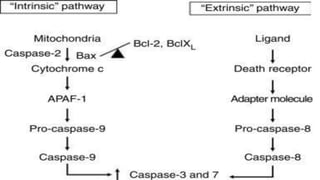
Apoptosis is a tightly regulated form of programmed cell death that involves the activation of caspases. There are intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis. The intrinsic pathway involves signals within the cell such as DNA damage, causing mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and cytochrome c release. This forms the apoptosome and activates caspase-9 and caspase-3. The extrinsic pathway involves death receptors and activates caspase-8. Caspases cleave cellular proteins leading to cell death. Phagocytes then engulf and degrade the apoptotic bodies. Other forms of regulated cell death include necroptosis, pyroptosis and ferroptosis.