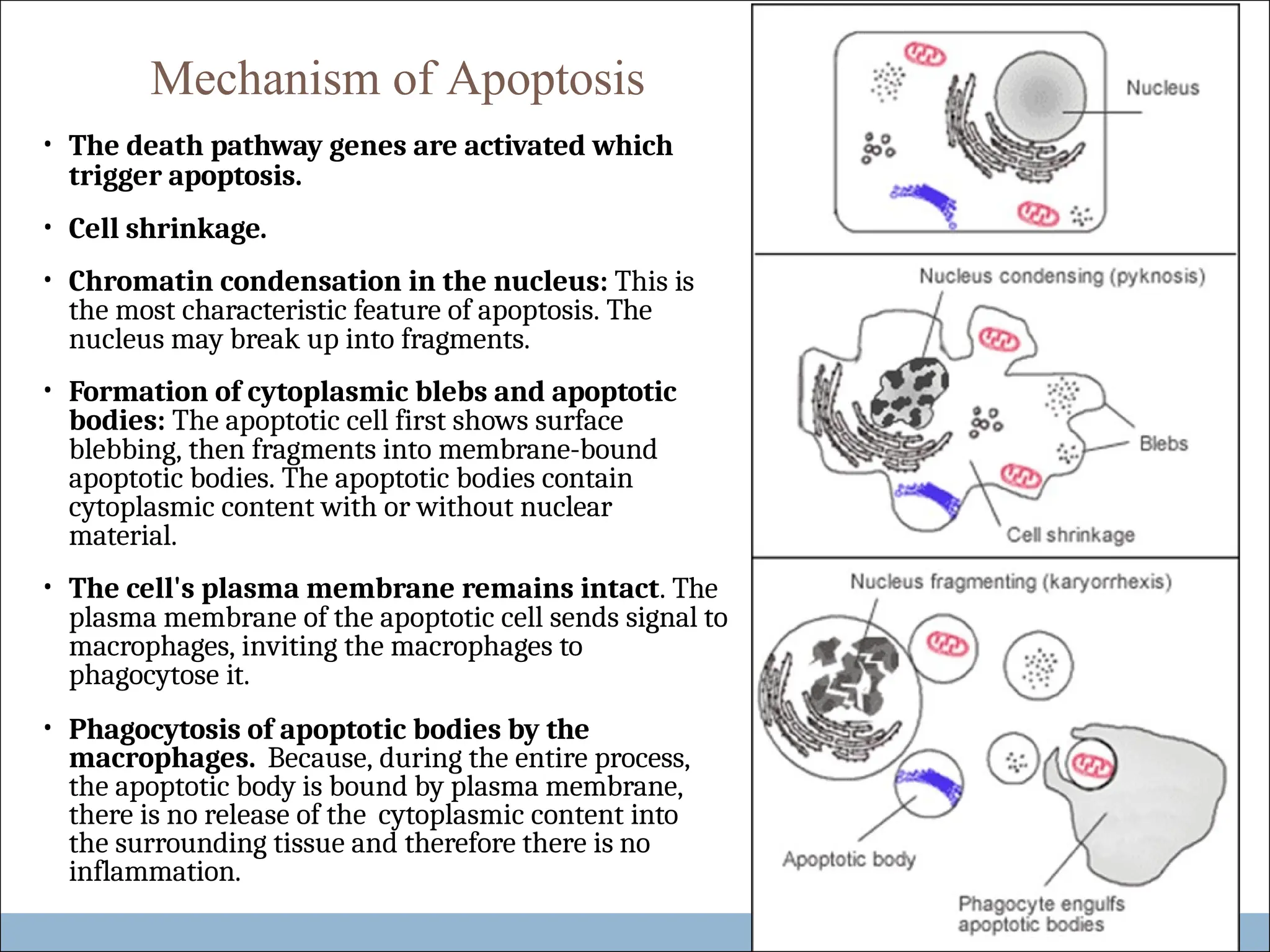
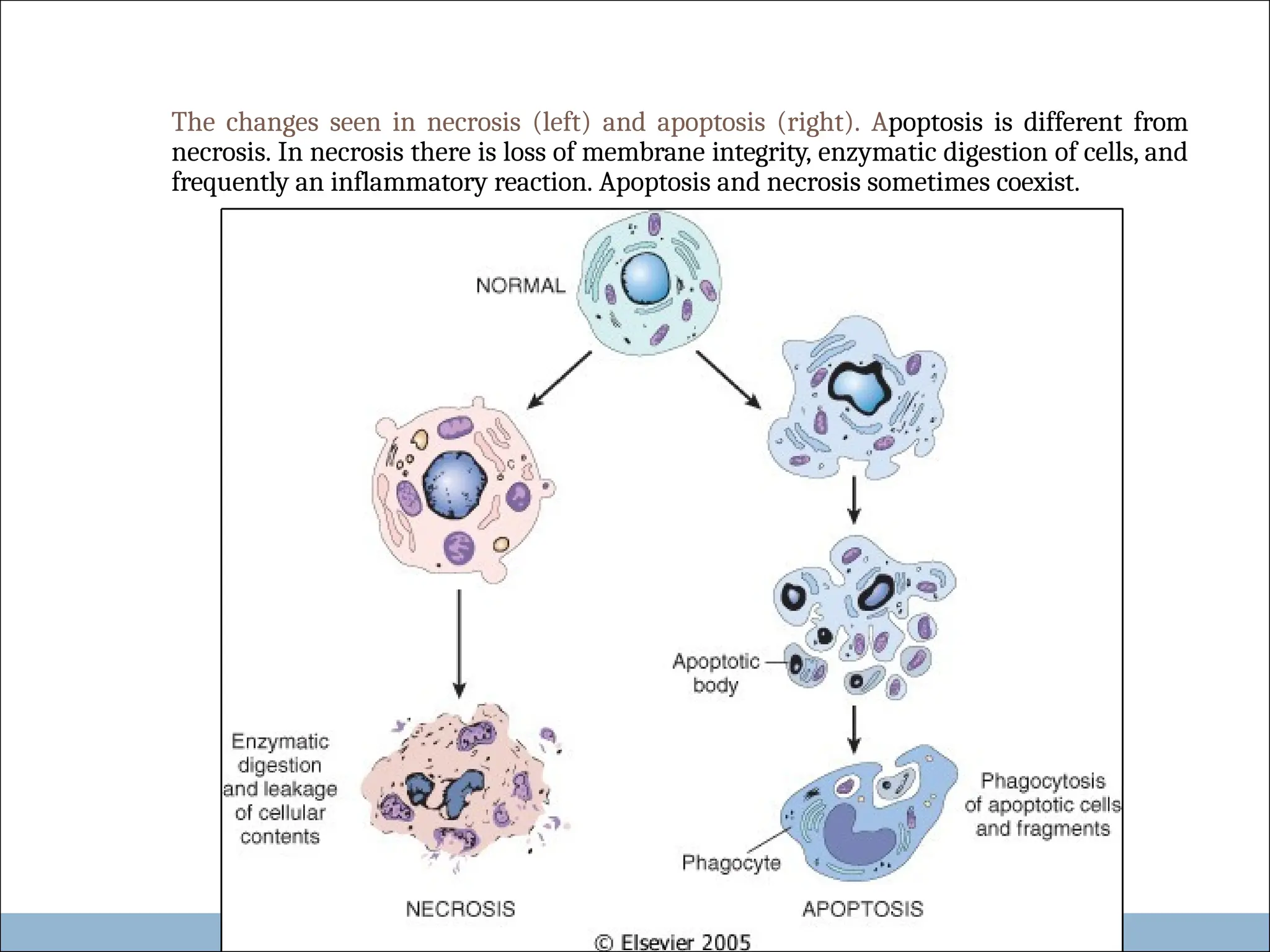
Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death characterized by the activation of death pathway genes, leading to cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, and the formation of apoptotic bodies. It plays crucial roles in both physiological processes, such as embryogenesis and hormone-dependent cell turnover, and pathological conditions like cancer and viral infections. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis occurs without inflammation, as the plasma membrane remains intact throughout the process.