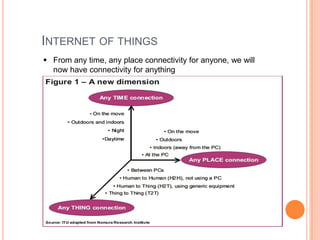
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT). It defines IoT as a wireless network that connects everyday objects. Key points:
- IoT allows any device with an on/off switch to be connected to the internet and to be controlled remotely, including things like home appliances and traffic lights.
- Important enabling technologies include RFID, WiFi, sensors, and ZigBee communication protocol.
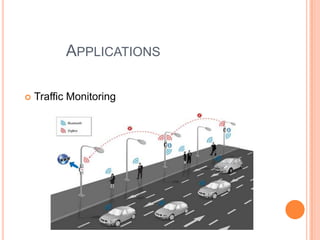
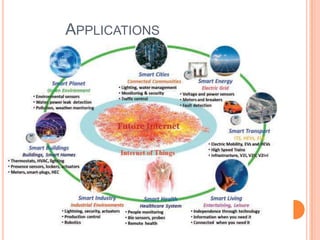
- Current applications include traffic monitoring, smart homes, smart parking, environmental monitoring, supply chain management and more.
- The future of IoT will focus on standardization, security/privacy, identification and improved user interfaces as the number of connected devices is expected to exceed 30 billion by 2020.