This document discusses various atmospheric and meteorological phenomena including:
- How compressed air heats up due to increasing pressure and how air cools when the number of molecules decreases.
- How air warms when rising over mountains and how this process can create deserts on the leeward side.
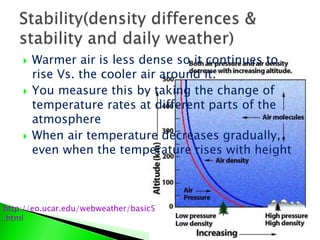
- How warm and cold air interact, with warm air rising above cooler, denser air.
- How unequal heating can lead to air pockets and uplift used by birds to reach high altitudes.
- The three categories of high-level clouds made of ice crystals.
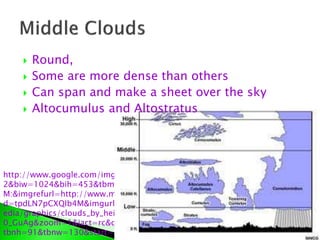
- The signs of rain shown by middle-level clouds and their ability to produce fog.
- How unstable air can lead to cumul