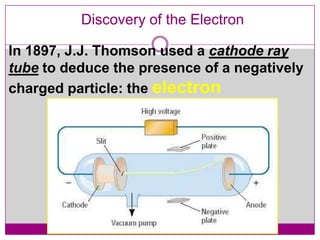
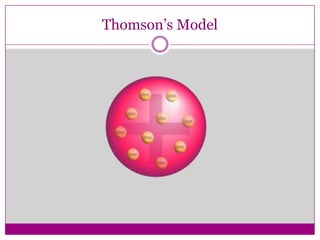
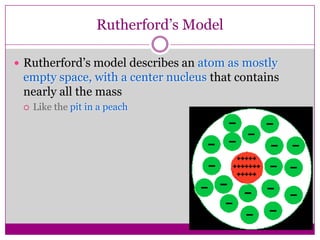
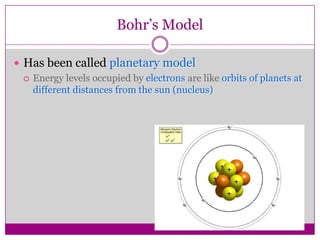
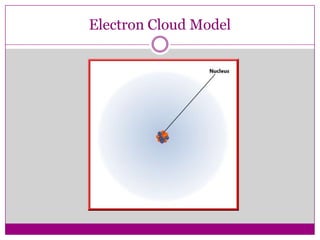
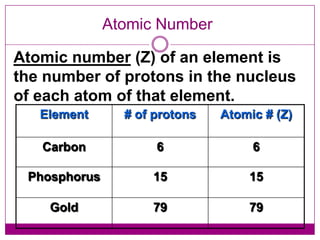
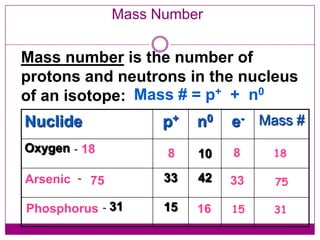
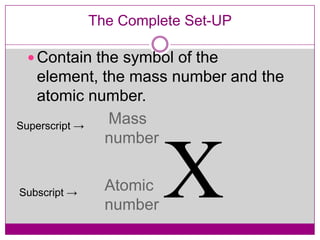
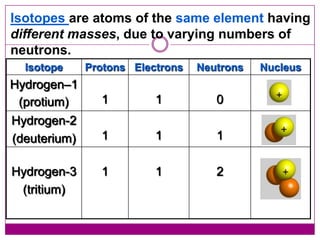
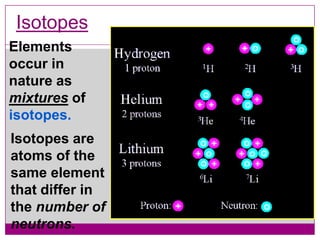
This document provides an overview of the history and development of atomic theory from Dalton's model to the modern electron cloud model. It discusses key scientists and experiments that led to important discoveries, such as Thomson discovering electrons, Rutherford determining the structure of the nucleus, and Bohr proposing electron energy levels. The document also defines important atomic concepts like atomic number, mass number, isotopes, and how elements are distinguished by their number of protons.