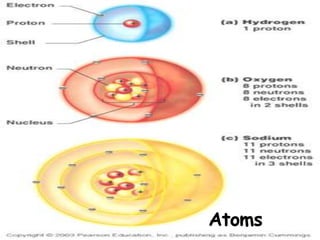
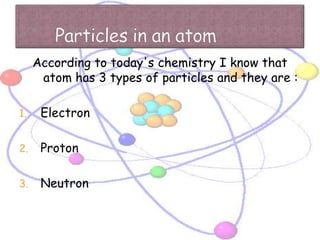
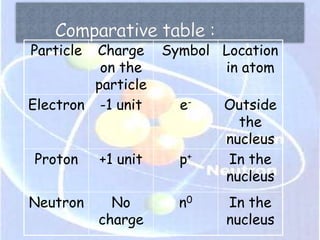
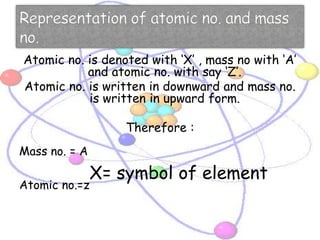
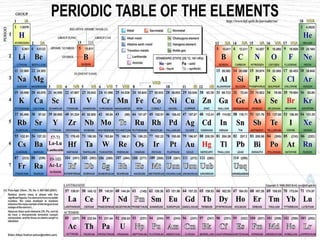
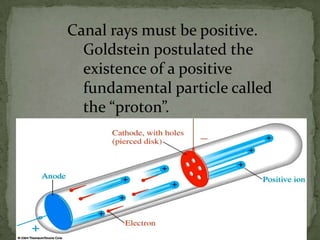
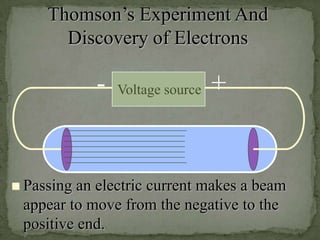
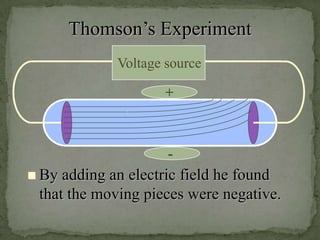
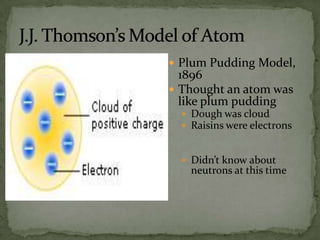
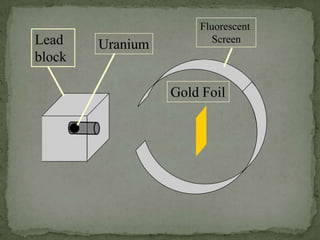
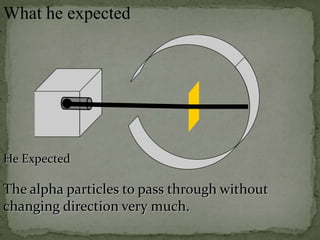
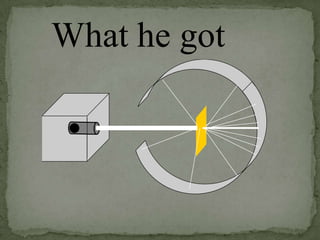
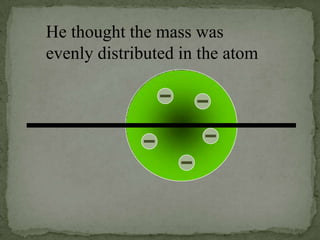
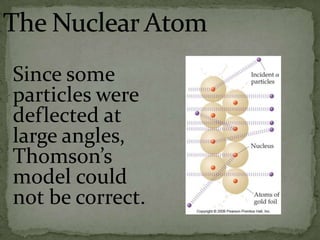
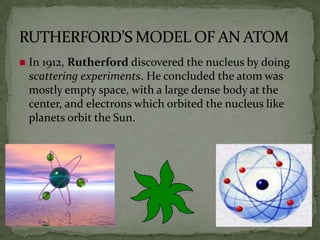
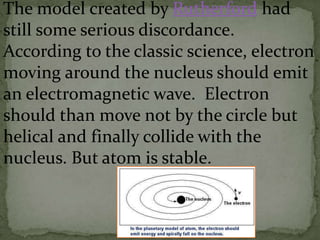
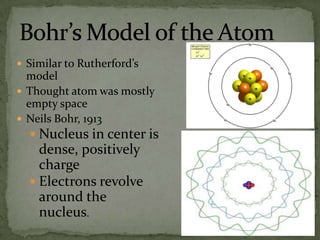
Atoms are made up of tiny particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the center of the atom in the nucleus, while electrons orbit around the nucleus. Over time, scientists developed models of the atom, starting with plum pudding model where electrons were embedded in a positive sphere, then Rutherford's model with a small dense nucleus at the center, and Bohr's model where electrons orbit in fixed shells around the nucleus. The number of protons determines the element, while the number of neutrons varies between isotopes of that element.