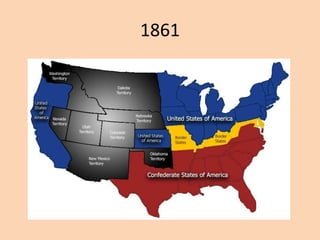
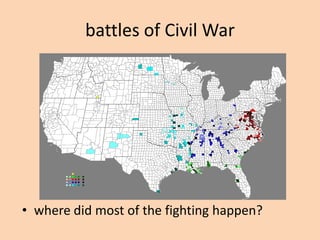
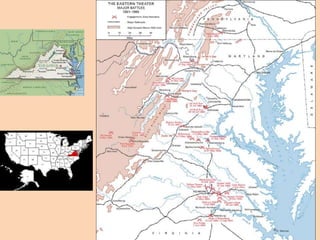
This document provides an overview of key events and developments during the US Civil War and Reconstruction era from 1861 to 1870. It discusses major battles of the Civil War, the Emancipation Proclamation, treatment of fugitive slaves who fled to Union lines, Sherman's March to the Sea in 1864, and the surrender at Appomattox in 1865. It also summarizes President Lincoln's and Congress's differing plans for Reconstruction, the passage of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments, and the establishment of the Freedmen's Bureau to aid freed slaves.