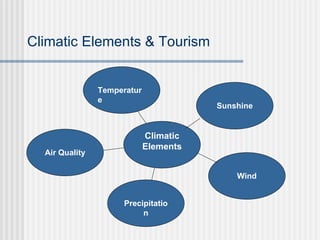
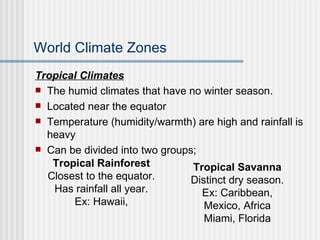
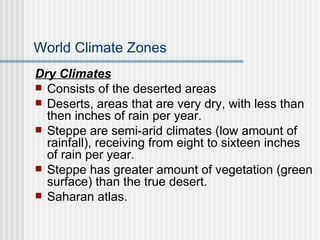
The document discusses how climate affects tourism and recreational activities. It describes the main climatic elements of temperature, sunshine, precipitation, wind and air quality and how each influences tourism. It then outlines the major world climate zones including tropical, dry, mesothermal humid, microthermal humid, and polar climates and provides examples of locations that fall within each zone. Climate is a key factor in determining the types of tourism and activities suitable for different places around the world.