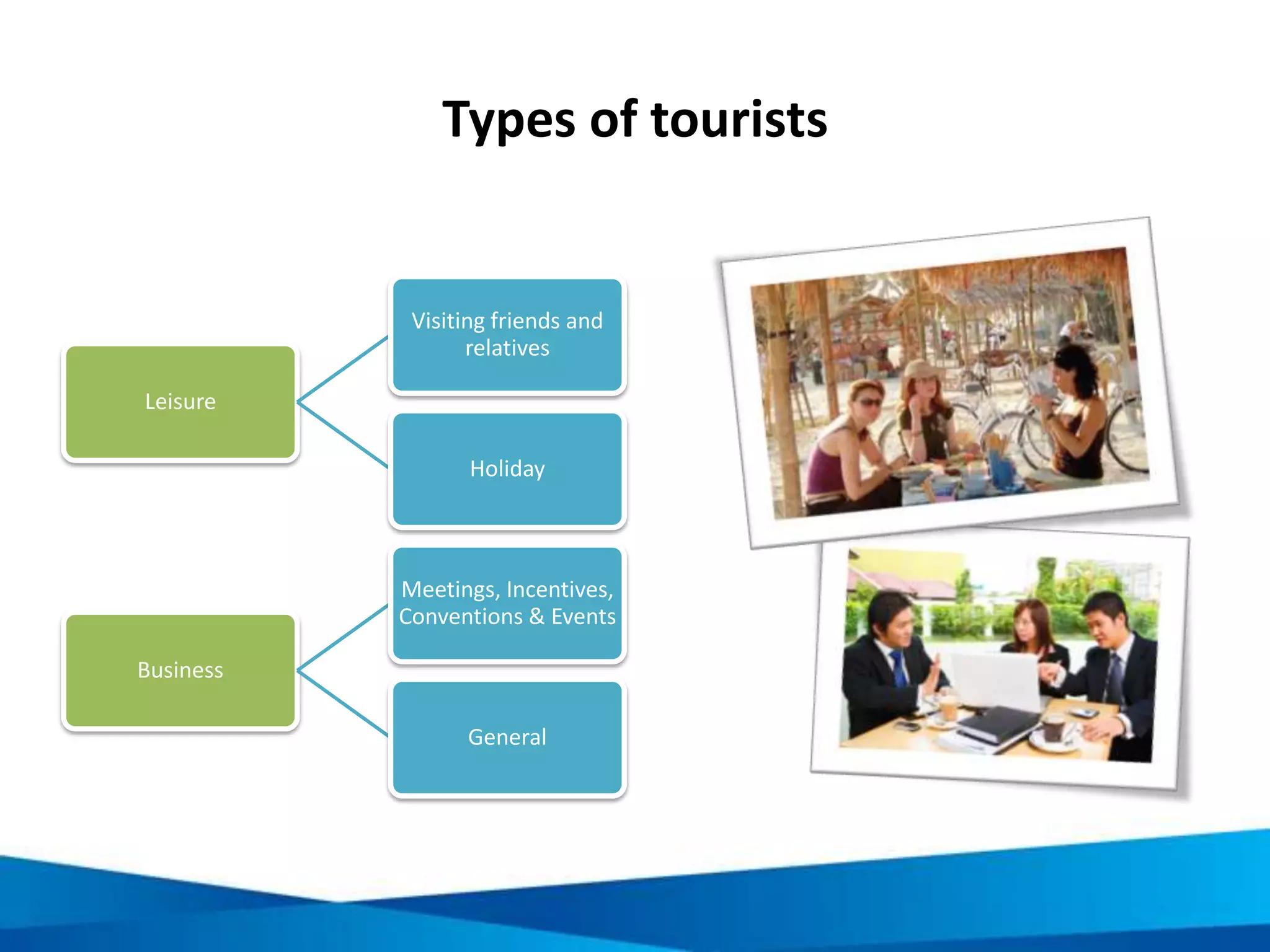
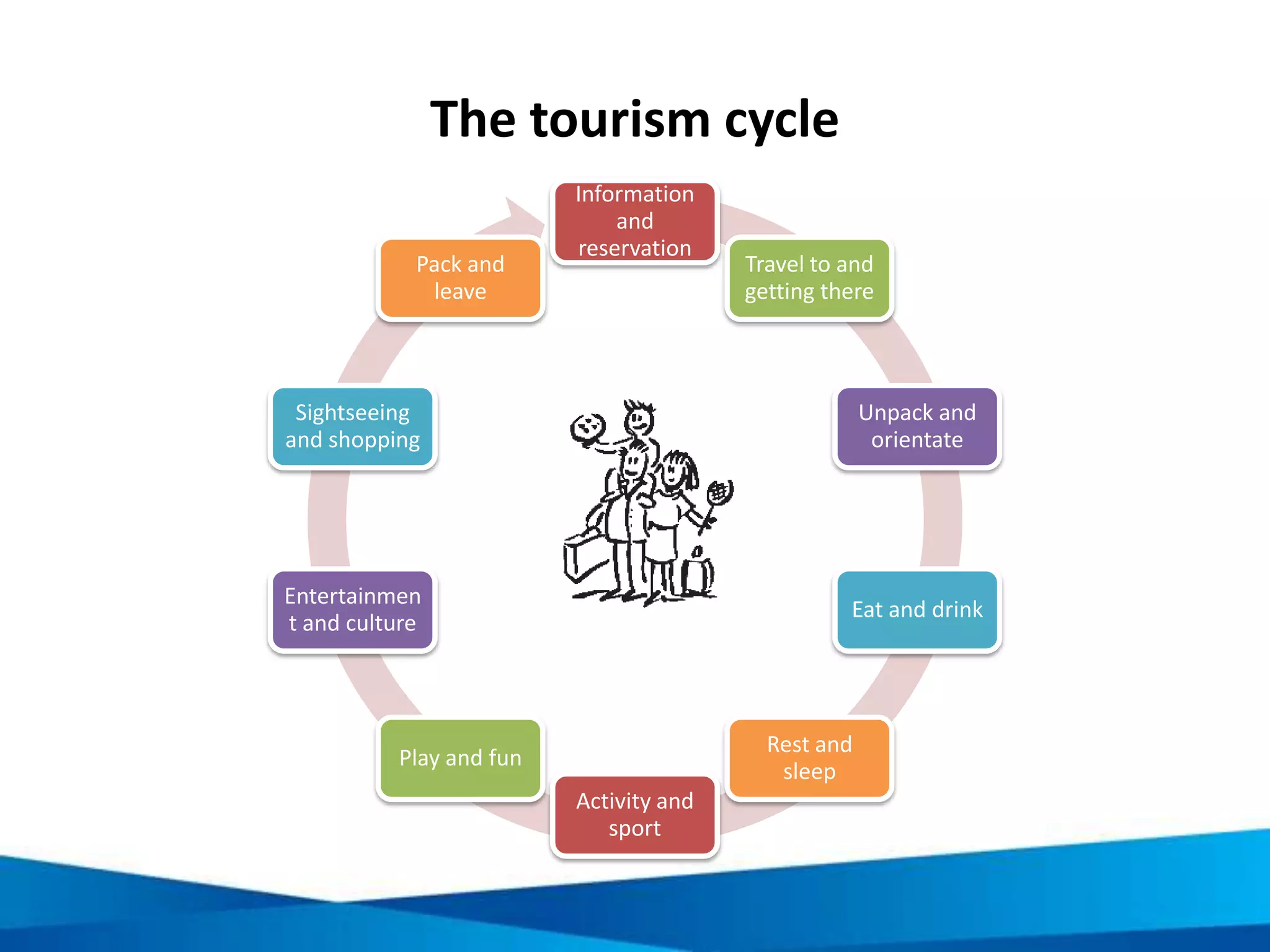
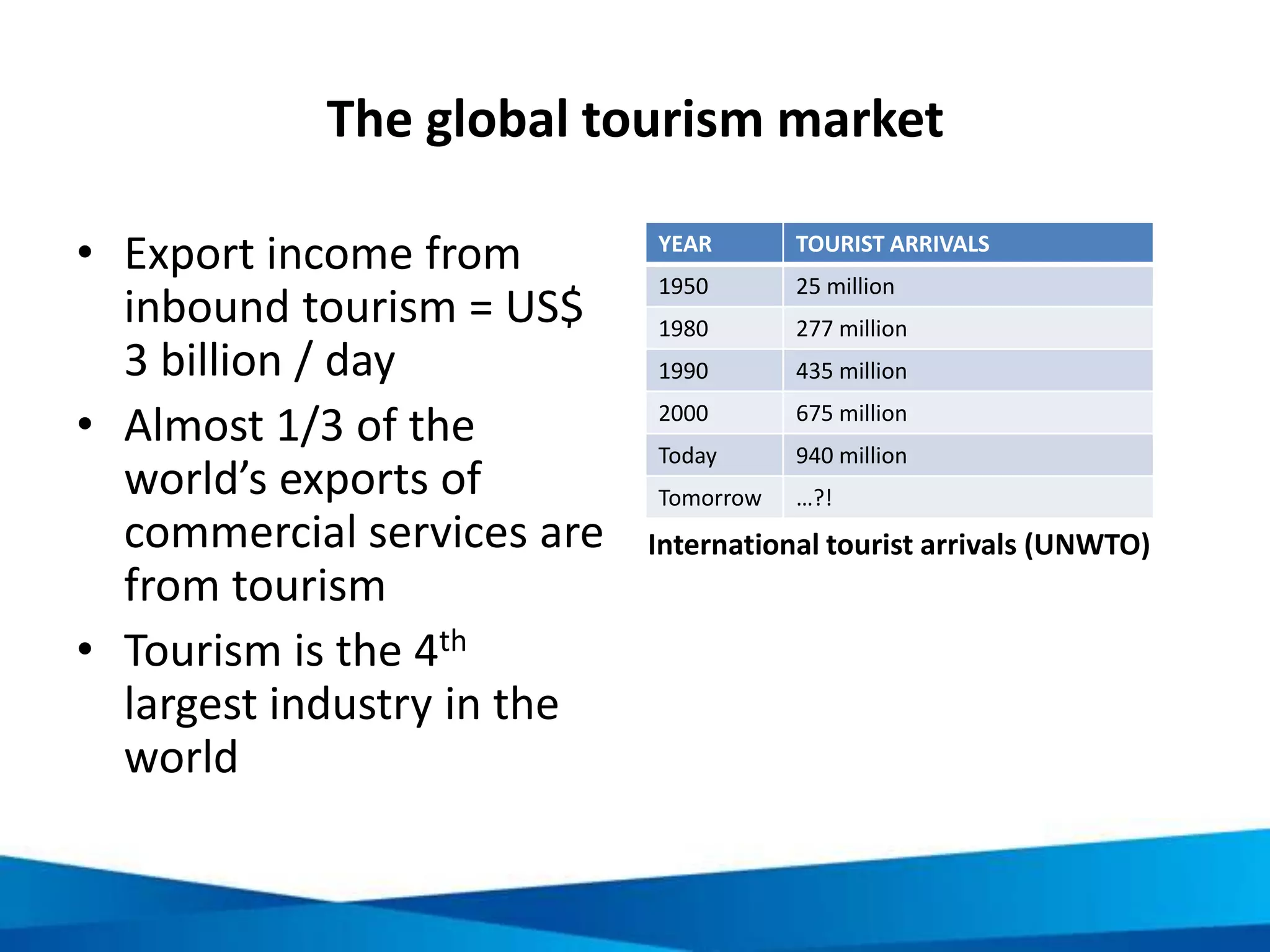
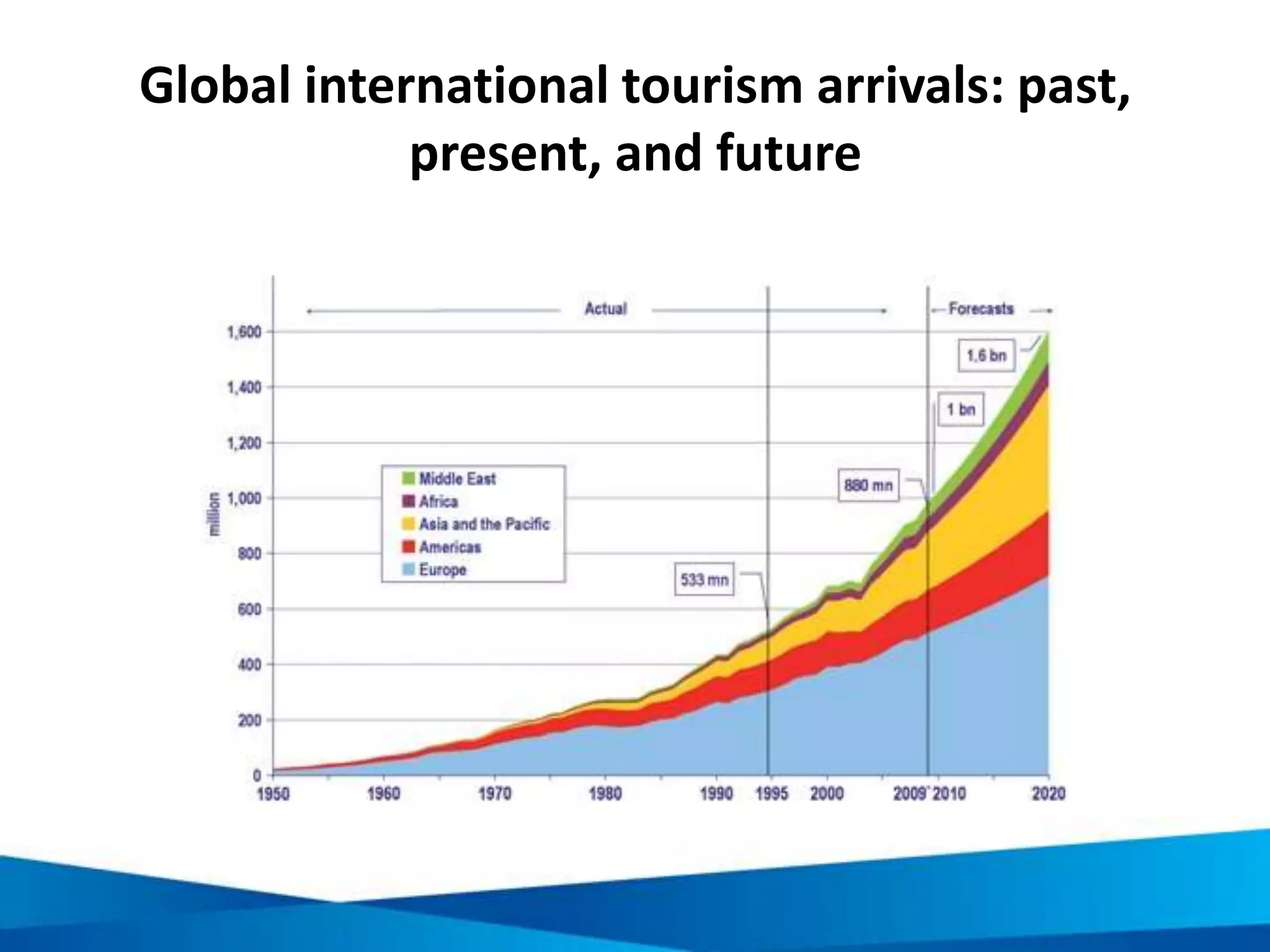
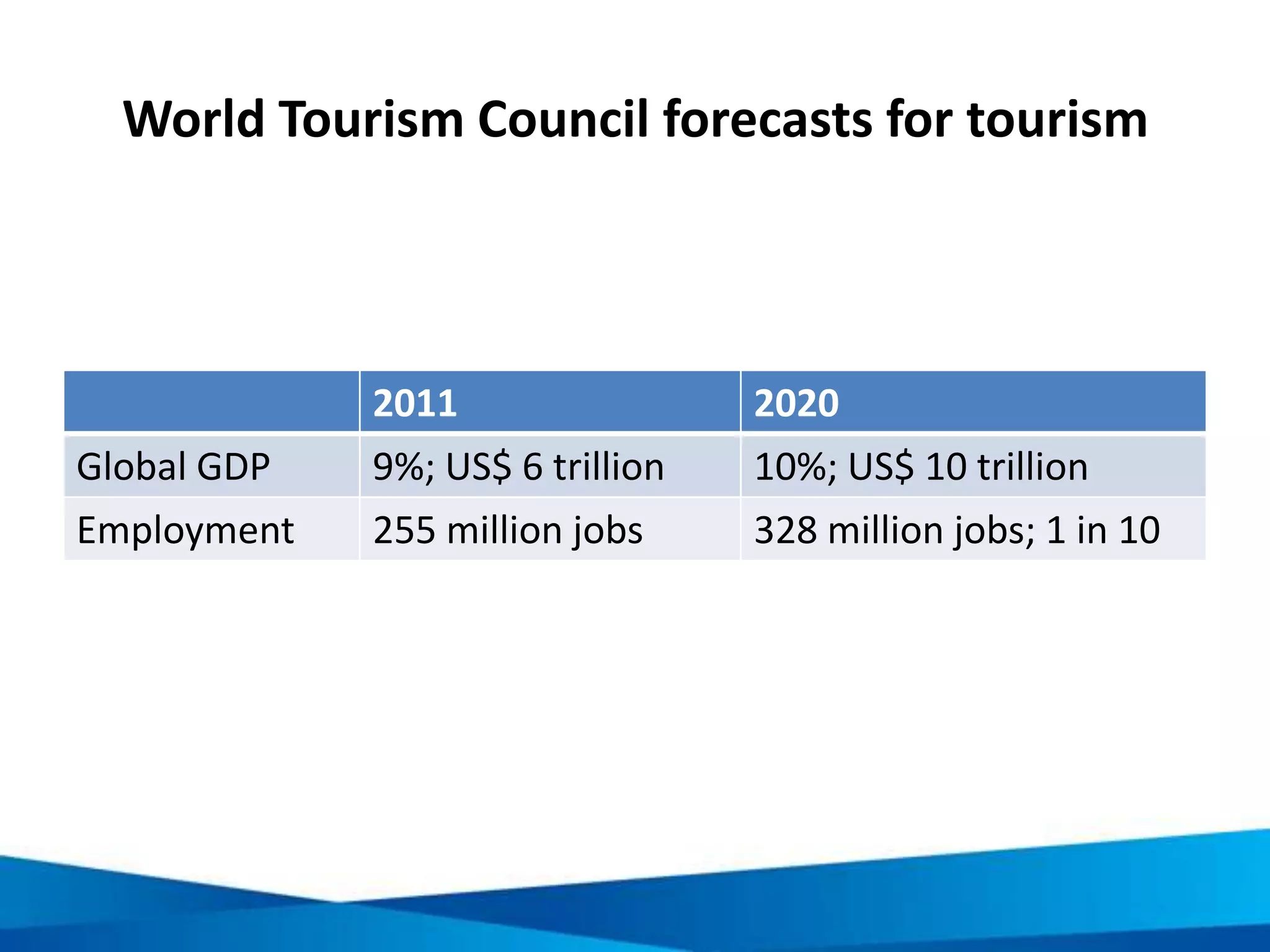
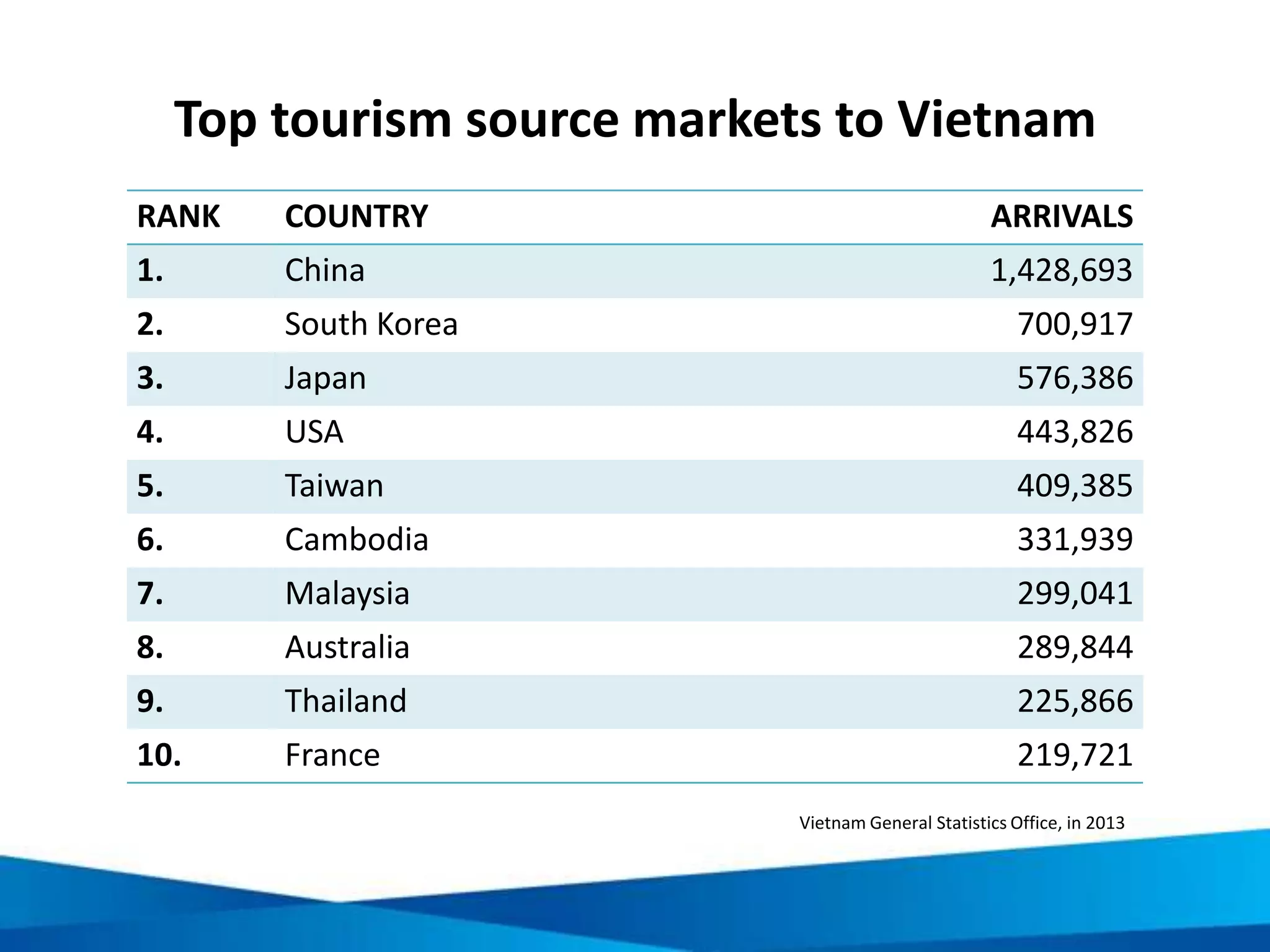
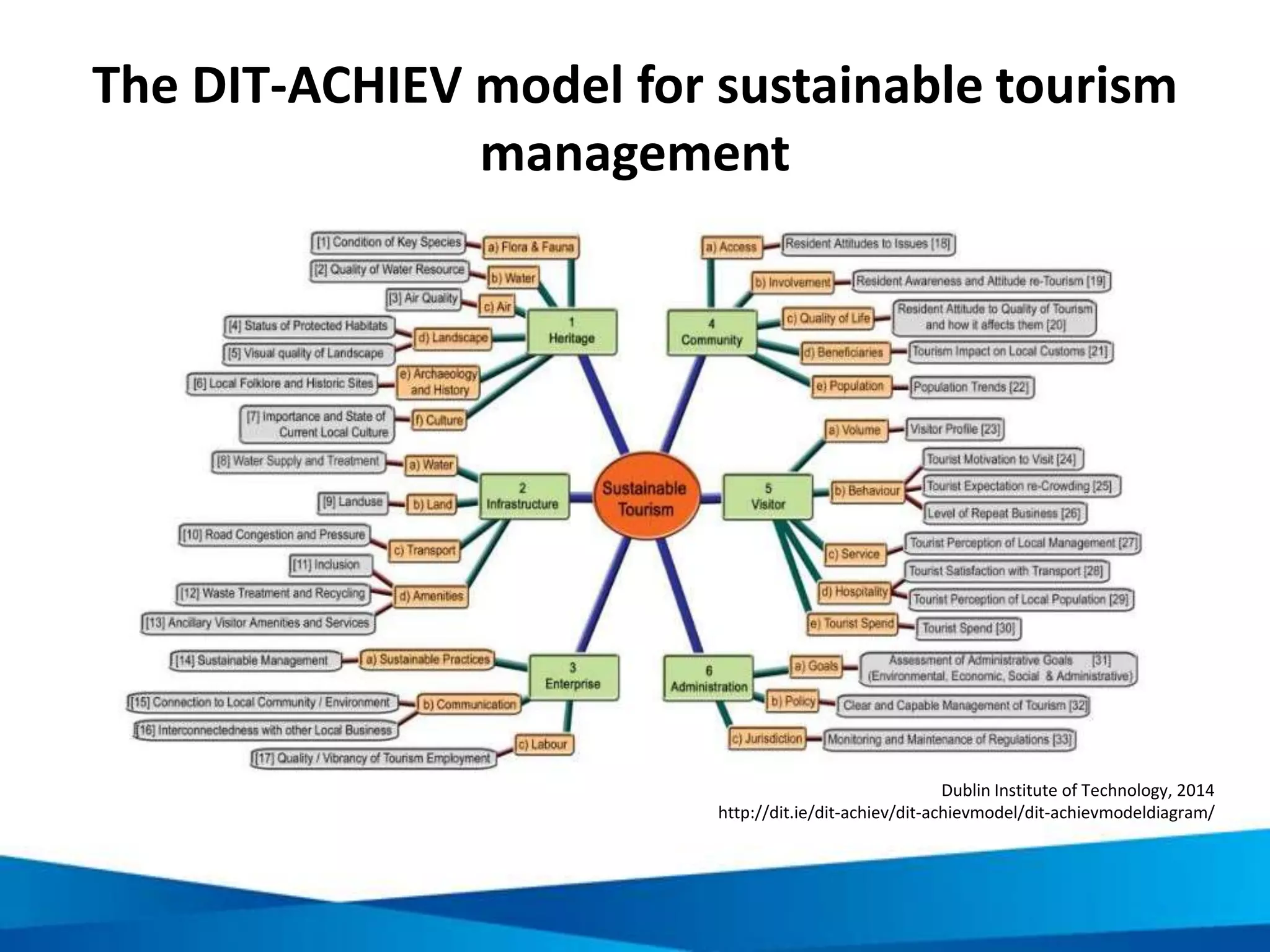
This document provides an overview of responsible tourism principles. It begins by defining tourism and describing the global tourism market. It then discusses the positive and negative social, economic, and environmental impacts of tourism. The principles of responsible tourism and sustainable development are explained, including the triple bottom line of considering economic, environmental and social factors. The benefits of responsible tourism for businesses, tourists, and local communities are outlined. Finally, the document discusses the Cape Town Declaration which established guiding principles for responsible tourism, including minimizing impacts and maximizing benefits for local communities while involving them in decisions.