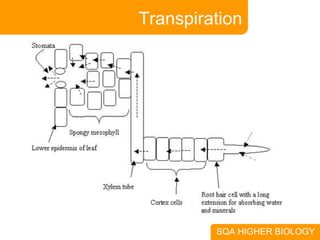
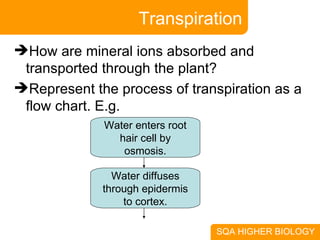
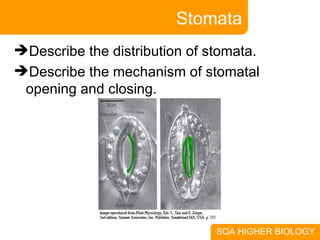
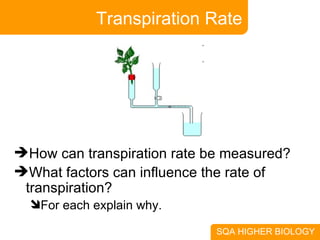
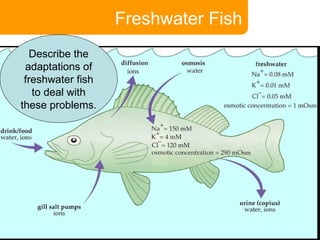
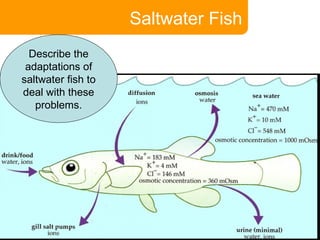
This document covers plant and animal adaptations for maintaining water balance. It discusses how plants transport water and regulate transpiration through structures like stomata. It also examines the challenges of osmoregulation for freshwater and saltwater fish, and the adaptations of salmon, eels, and desert mammals to balance water in their environments. Adaptations include physiological processes, structural features, and behavioral responses that help organisms survive where they live.